A gamma squeeze occurs when traders buy large amounts of short-dated options, forcing market makers to buy underlying shares aggressively to hedge their positions, driving up stock prices rapidly. A liquidity crunch refers to a market condition where trading volume drops sharply, causing difficulties in executing trades without significant price changes and leading to increased volatility. Explore deeper insights into how gamma squeezes differ from liquidity crunches and their impact on trading strategies.
Why it is important
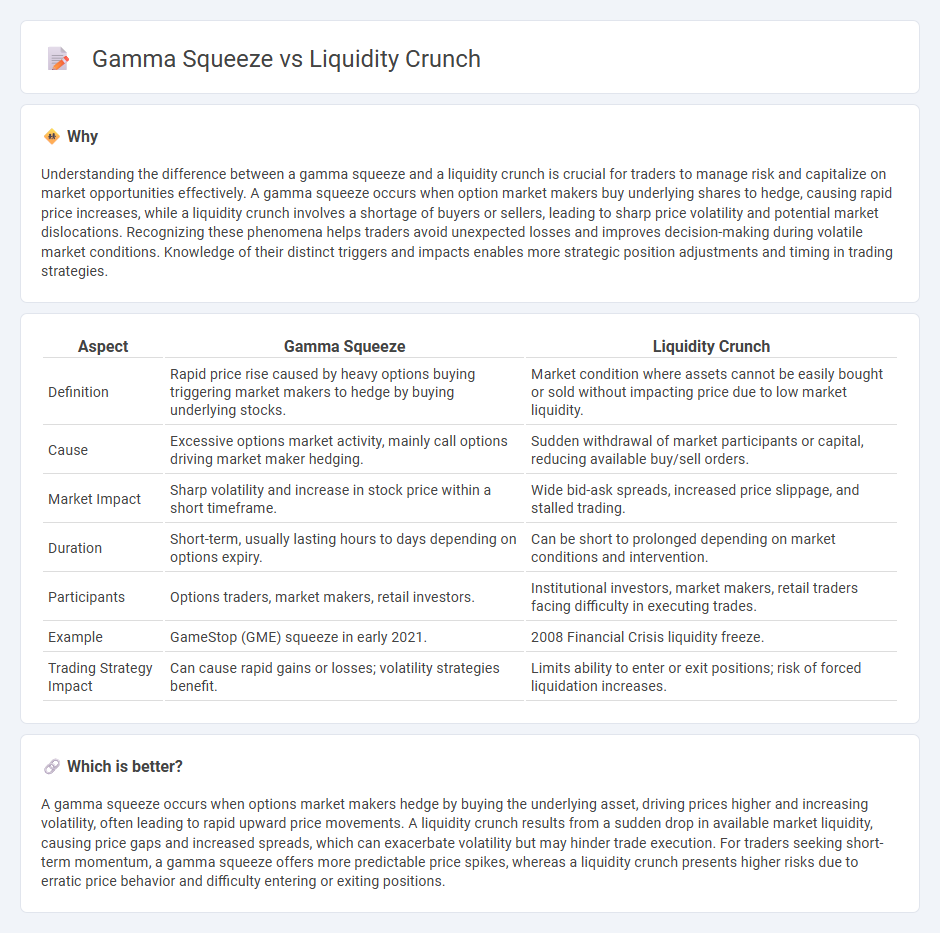
Understanding the difference between a gamma squeeze and a liquidity crunch is crucial for traders to manage risk and capitalize on market opportunities effectively. A gamma squeeze occurs when option market makers buy underlying shares to hedge, causing rapid price increases, while a liquidity crunch involves a shortage of buyers or sellers, leading to sharp price volatility and potential market dislocations. Recognizing these phenomena helps traders avoid unexpected losses and improves decision-making during volatile market conditions. Knowledge of their distinct triggers and impacts enables more strategic position adjustments and timing in trading strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gamma Squeeze | Liquidity Crunch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid price rise caused by heavy options buying triggering market makers to hedge by buying underlying stocks. | Market condition where assets cannot be easily bought or sold without impacting price due to low market liquidity. |
| Cause | Excessive options market activity, mainly call options driving market maker hedging. | Sudden withdrawal of market participants or capital, reducing available buy/sell orders. |
| Market Impact | Sharp volatility and increase in stock price within a short timeframe. | Wide bid-ask spreads, increased price slippage, and stalled trading. |
| Duration | Short-term, usually lasting hours to days depending on options expiry. | Can be short to prolonged depending on market conditions and intervention. |
| Participants | Options traders, market makers, retail investors. | Institutional investors, market makers, retail traders facing difficulty in executing trades. |
| Example | GameStop (GME) squeeze in early 2021. | 2008 Financial Crisis liquidity freeze. |
| Trading Strategy Impact | Can cause rapid gains or losses; volatility strategies benefit. | Limits ability to enter or exit positions; risk of forced liquidation increases. |
Which is better?
A gamma squeeze occurs when options market makers hedge by buying the underlying asset, driving prices higher and increasing volatility, often leading to rapid upward price movements. A liquidity crunch results from a sudden drop in available market liquidity, causing price gaps and increased spreads, which can exacerbate volatility but may hinder trade execution. For traders seeking short-term momentum, a gamma squeeze offers more predictable price spikes, whereas a liquidity crunch presents higher risks due to erratic price behavior and difficulty entering or exiting positions.
Connection
A gamma squeeze occurs when market makers rapidly buy underlying shares to hedge options positions, driving up stock prices and increasing volatility. This surge in buying pressure can strain market liquidity, leading to a liquidity crunch as available shares become scarce and bid-ask spreads widen. The combination of heightened demand and reduced liquidity amplifies price swings, intensifying market instability during a gamma squeeze event.
Key Terms
Liquidity Crunch:
Liquidity crunch occurs when financial institutions or markets face a sudden shortage of liquid assets, impairing their ability to meet short-term obligations and causing widespread financial stress. This phenomenon often results from rapid withdrawals, credit freezes, or abrupt declines in asset prices, significantly impacting market stability and economic growth. Explore how liquidity crunches influence global markets and strategies to mitigate their risks.
Market Depth
Liquidity crunch occurs when market depth deteriorates significantly, causing fewer buy and sell orders at various price levels, which results in increased price volatility and wider bid-ask spreads. Gamma squeeze happens when options market makers hedge their positions by buying shares aggressively, leading to sharp price movements despite relatively stable intrinsic values, often exacerbating the reduced market depth. Explore further to understand how these phenomena impact trading strategies and risk management in modern financial markets.
Bid-Ask Spread
A liquidity crunch causes bid-ask spreads to widen significantly as market makers face difficulty in matching buy and sell orders, leading to decreased market efficiency and increased transaction costs. In contrast, a gamma squeeze, driven by aggressive options trading, often leads to rapid price movements but can either tighten or widen bid-ask spreads depending on how market makers hedge their positions. Explore more to understand the intricate impacts of liquidity crunches and gamma squeezes on bid-ask dynamics.
Source and External Links
Liquidity crisis - Wikipedia - A liquidity crisis is an acute shortage of liquidity, where assets cannot be easily converted to cash and borrowers face heightened loan costs, often causing market participants to sell assets below fundamental value and impeding interbank lending.
What Is Liquidity Crisis: Definition and Meaning | Capital.com - A liquidity crisis occurs when financial institutions lack enough cash or liquid assets to meet obligations, often leading to emergency asset sales or loans, typically triggered by poor management, loss of confidence, or unexpected shocks.
The Liquidity Crunch - The Hedge Fund Journal - Funding liquidity tightening raises collateral requirements and reduces market liquidity, causing asset prices to fall and margin spirals that exacerbate losses and force further asset sales.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com