Modular blockchains offer enhanced scalability and customization, enabling decentralized trading environments that reduce reliance on intermediaries compared to centralized exchanges. Centralized exchanges provide higher liquidity and faster transaction times but pose risks such as custody concerns and regulatory constraints. Explore the differences between modular blockchain trading and centralized exchanges to optimize your trading strategy.
Why it is important
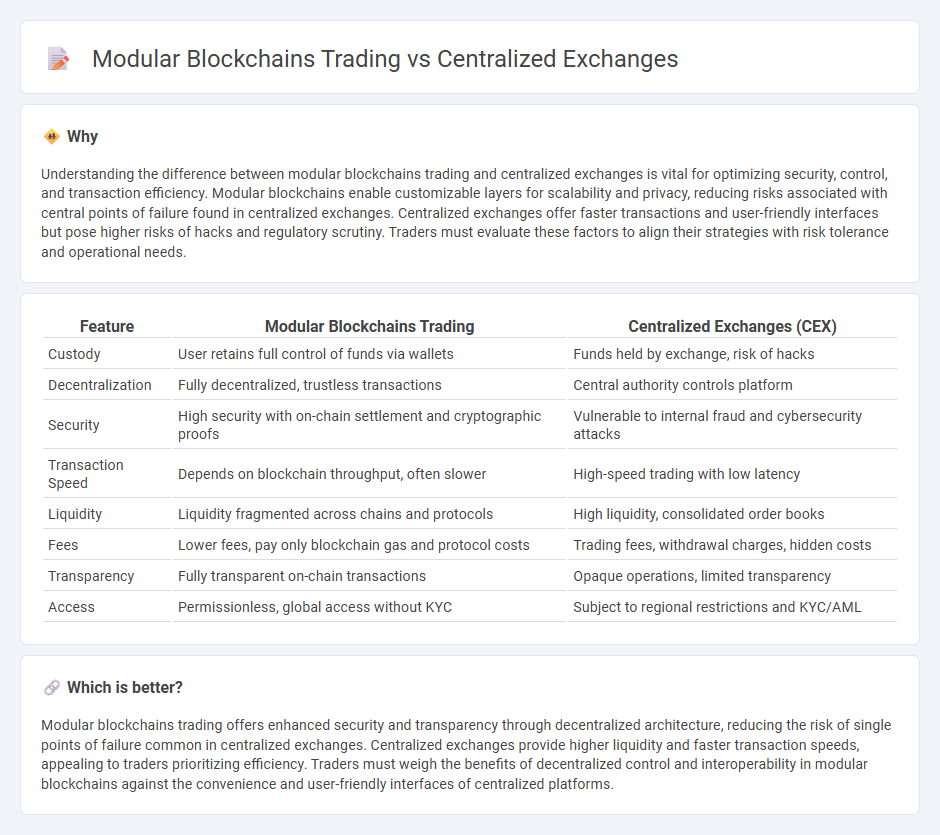
Understanding the difference between modular blockchains trading and centralized exchanges is vital for optimizing security, control, and transaction efficiency. Modular blockchains enable customizable layers for scalability and privacy, reducing risks associated with central points of failure found in centralized exchanges. Centralized exchanges offer faster transactions and user-friendly interfaces but pose higher risks of hacks and regulatory scrutiny. Traders must evaluate these factors to align their strategies with risk tolerance and operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Blockchains Trading | Centralized Exchanges (CEX) |
|---|---|---|
| Custody | User retains full control of funds via wallets | Funds held by exchange, risk of hacks |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized, trustless transactions | Central authority controls platform |
| Security | High security with on-chain settlement and cryptographic proofs | Vulnerable to internal fraud and cybersecurity attacks |
| Transaction Speed | Depends on blockchain throughput, often slower | High-speed trading with low latency |
| Liquidity | Liquidity fragmented across chains and protocols | High liquidity, consolidated order books |
| Fees | Lower fees, pay only blockchain gas and protocol costs | Trading fees, withdrawal charges, hidden costs |
| Transparency | Fully transparent on-chain transactions | Opaque operations, limited transparency |
| Access | Permissionless, global access without KYC | Subject to regional restrictions and KYC/AML |
Which is better?
Modular blockchains trading offers enhanced security and transparency through decentralized architecture, reducing the risk of single points of failure common in centralized exchanges. Centralized exchanges provide higher liquidity and faster transaction speeds, appealing to traders prioritizing efficiency. Traders must weigh the benefits of decentralized control and interoperability in modular blockchains against the convenience and user-friendly interfaces of centralized platforms.
Connection
Modular blockchains trading enhances scalability and customization by separating consensus, execution, and data availability layers, allowing decentralized finance applications to operate more efficiently. Centralized exchanges (CEXs) leverage this modular architecture to improve transaction speeds and liquidity management while maintaining user-friendly interfaces and high security standards. The integration between modular blockchain technology and CEXs creates a hybrid ecosystem that supports both on-chain asset settlement and off-chain order execution for optimal trading performance.
Key Terms
Custodial Trading
Centralized exchanges offer custodial trading where users' private keys and assets are managed by the platform, providing convenience but introducing counterparty risk. Modular blockchains with decentralized trading protocols enable users to retain control of their private keys, increasing security and transparency through on-chain order books and settlement. Explore the trade-offs between ease of use and asset custody to optimize your trading strategy.
Interoperability
Centralized exchanges dominate trading volume due to their user-friendly interfaces and high liquidity but often face limitations in cross-chain asset transfers. Modular blockchains enhance interoperability by allowing customized protocols and seamless communication between distinct blockchain networks, enabling more efficient and secure asset swaps. Explore how interoperability advancements in modular blockchain architectures are reshaping the future of decentralized trading.
Settlement Layers
Centralized exchanges provide fast transaction execution and liquidity but rely heavily on a single settlement layer, increasing risks of central points of failure. Modular blockchains separate execution, consensus, and settlement layers, enhancing scalability and security by distributing these functions across specialized layers. Explore how settlement layers redefine trading efficiency and security in blockchain ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Cryptocurrency Exchanges - Overview, Advantages, Top 10 - Centralized cryptocurrency exchanges (CEX) act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, operating with an order book system to match trades and earning through commissions and fees, with popular examples including Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, and KuCoin.
Centralized Crypto Exchanges Examined - Gemini - CEXs facilitate cryptocurrency trading for fiat and digital assets, providing security, regulatory compliance, and consumer protection, and remain the dominant infrastructure for over 95% of digital asset trades globally.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Crypto Exchanges - Centralized exchanges are user-friendly platforms suitable for beginner investors, operated by centralized entities such as Coinbase and Binance, in contrast to decentralized exchanges which offer different security trade-offs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com