Trading on modular blockchains benefits from enhanced scalability and specialized execution layers, enabling faster and more cost-effective transactions compared to traditional Layer 1 blockchains like Ethereum or Bitcoin. Modular architectures separate consensus, data availability, and execution, offering traders improved throughput and reduced latency, which is critical for high-frequency trading and complex decentralized finance strategies. Explore the differences in trading dynamics between modular and Layer 1 blockchains to optimize your investment approach.
Why it is important
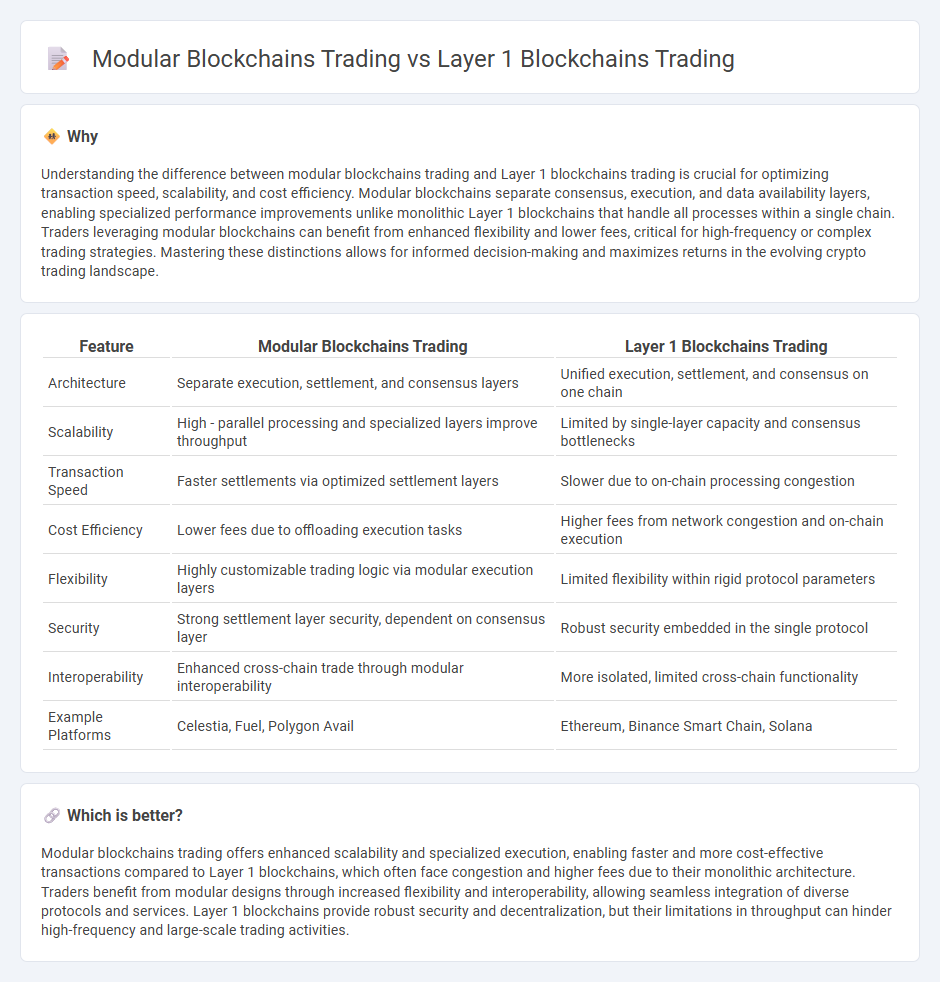
Understanding the difference between modular blockchains trading and Layer 1 blockchains trading is crucial for optimizing transaction speed, scalability, and cost efficiency. Modular blockchains separate consensus, execution, and data availability layers, enabling specialized performance improvements unlike monolithic Layer 1 blockchains that handle all processes within a single chain. Traders leveraging modular blockchains can benefit from enhanced flexibility and lower fees, critical for high-frequency or complex trading strategies. Mastering these distinctions allows for informed decision-making and maximizes returns in the evolving crypto trading landscape.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Blockchains Trading | Layer 1 Blockchains Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Separate execution, settlement, and consensus layers | Unified execution, settlement, and consensus on one chain |
| Scalability | High - parallel processing and specialized layers improve throughput | Limited by single-layer capacity and consensus bottlenecks |
| Transaction Speed | Faster settlements via optimized settlement layers | Slower due to on-chain processing congestion |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower fees due to offloading execution tasks | Higher fees from network congestion and on-chain execution |
| Flexibility | Highly customizable trading logic via modular execution layers | Limited flexibility within rigid protocol parameters |
| Security | Strong settlement layer security, dependent on consensus layer | Robust security embedded in the single protocol |
| Interoperability | Enhanced cross-chain trade through modular interoperability | More isolated, limited cross-chain functionality |
| Example Platforms | Celestia, Fuel, Polygon Avail | Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Solana |
Which is better?
Modular blockchains trading offers enhanced scalability and specialized execution, enabling faster and more cost-effective transactions compared to Layer 1 blockchains, which often face congestion and higher fees due to their monolithic architecture. Traders benefit from modular designs through increased flexibility and interoperability, allowing seamless integration of diverse protocols and services. Layer 1 blockchains provide robust security and decentralization, but their limitations in throughput can hinder high-frequency and large-scale trading activities.
Connection
Modular blockchains trading enhances liquidity and interoperability by allowing seamless integration with Layer 1 blockchains, facilitating faster and more scalable trading experiences. Layer 1 blockchains provide the fundamental security and consensus mechanisms, while modular blockchains optimize transaction processing and data availability, boosting trading efficiency. This synergy creates robust trading ecosystems capable of handling high volumes and complex financial instruments securely.
Key Terms
Throughput
Layer 1 blockchains typically manage all blockchain functions within a single layer, often resulting in throughput limitations due to on-chain congestion and consensus constraints. Modular blockchains separate execution, consensus, and data availability layers, significantly enhancing throughput by enabling parallel processing and scalability. Explore further to understand how modular designs are revolutionizing high-throughput blockchain trading environments.
Composability
Layer 1 blockchains offer integrated security and optimized throughput for decentralized applications, but often face limitations in composability across different chains. Modular blockchains enhance composability by separating consensus, execution, and data availability layers, enabling seamless interoperability and scalability for complex DeFi ecosystems. Explore how composability advancements in modular architectures revolutionize trading strategies and blockchain interactions.
Interoperability
Layer 1 blockchains operate independently with limited interoperability, often requiring complex bridges for asset transfers that introduce security risks and latency. Modular blockchains enhance interoperability by separating consensus, data availability, and execution layers, enabling seamless cross-chain communication and improved scalability. Explore the future of blockchain connectivity to understand how modular designs transform decentralized trading ecosystems.
Source and External Links
What Is Layer 1 in Blockchain? - Built In - Layer 1 blockchains are fundamental base networks executing all on-chain transactions, with top examples like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Algorand, and Cardano, each employing different consensus mechanisms and offering varied speeds and functionalities.
Top Layer 1 Coins by Market Cap - Kraken - Layer 1 blockchains such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, and Cardano enable decentralized applications and transactions, with trading involving coins secured by proof of work or proof of stake consensus mechanisms.
Top Layer 1 (L1) Coins by Market Cap | CoinGecko - The Layer 1 market cap is approximately $3.22 trillion, involving autonomous chains where transactions are executed and confirmed, with high trading volumes indicating active market trading of Layer 1 blockchain coins.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com