Gamma scalping involves adjusting options positions to profit from changes in volatility by managing the gamma, which measures the rate of change of delta in response to underlying price movements. Delta hedging focuses on neutralizing the directional risk of an options position by maintaining a delta-neutral portfolio, often through frequent rebalancing of the underlying asset. Explore the detailed strategies and benefits of gamma scalping versus delta hedging to optimize your trading performance.
Why it is important
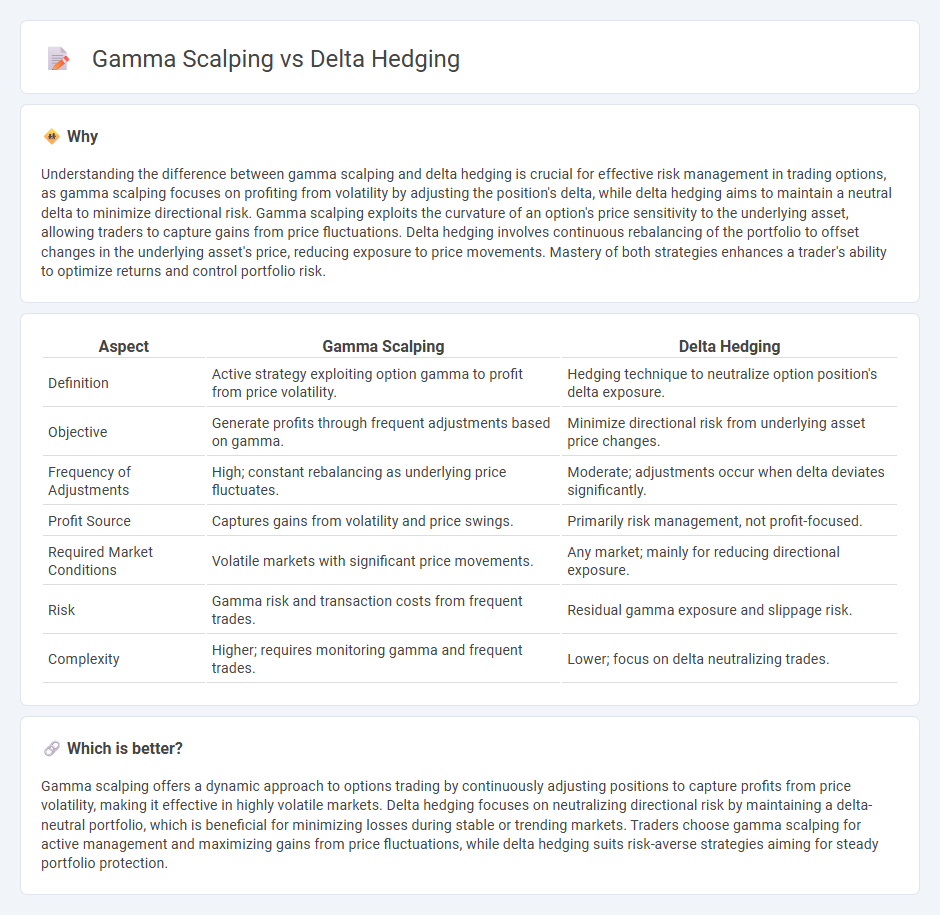
Understanding the difference between gamma scalping and delta hedging is crucial for effective risk management in trading options, as gamma scalping focuses on profiting from volatility by adjusting the position's delta, while delta hedging aims to maintain a neutral delta to minimize directional risk. Gamma scalping exploits the curvature of an option's price sensitivity to the underlying asset, allowing traders to capture gains from price fluctuations. Delta hedging involves continuous rebalancing of the portfolio to offset changes in the underlying asset's price, reducing exposure to price movements. Mastery of both strategies enhances a trader's ability to optimize returns and control portfolio risk.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gamma Scalping | Delta Hedging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active strategy exploiting option gamma to profit from price volatility. | Hedging technique to neutralize option position's delta exposure. |
| Objective | Generate profits through frequent adjustments based on gamma. | Minimize directional risk from underlying asset price changes. |
| Frequency of Adjustments | High; constant rebalancing as underlying price fluctuates. | Moderate; adjustments occur when delta deviates significantly. |
| Profit Source | Captures gains from volatility and price swings. | Primarily risk management, not profit-focused. |
| Required Market Conditions | Volatile markets with significant price movements. | Any market; mainly for reducing directional exposure. |
| Risk | Gamma risk and transaction costs from frequent trades. | Residual gamma exposure and slippage risk. |
| Complexity | Higher; requires monitoring gamma and frequent trades. | Lower; focus on delta neutralizing trades. |
Which is better?
Gamma scalping offers a dynamic approach to options trading by continuously adjusting positions to capture profits from price volatility, making it effective in highly volatile markets. Delta hedging focuses on neutralizing directional risk by maintaining a delta-neutral portfolio, which is beneficial for minimizing losses during stable or trending markets. Traders choose gamma scalping for active management and maximizing gains from price fluctuations, while delta hedging suits risk-averse strategies aiming for steady portfolio protection.
Connection
Gamma scalping and delta hedging are interconnected strategies used in options trading to manage portfolio risk and maintain a neutral market position. Delta hedging involves adjusting the position to keep the portfolio's delta close to zero, minimizing exposure to small price movements of the underlying asset. Gamma scalping complements this by exploiting the changes in delta due to price volatility, enabling traders to buy low and sell high, thereby profiting from market fluctuations while maintaining a delta-neutral stance.
Key Terms
Delta
Delta hedging involves adjusting a portfolio to maintain a neutral delta, minimizing risk from price movements in the underlying asset. Gamma scalping complements delta hedging by capitalizing on changes in gamma to adjust hedge positions dynamically, optimizing profits through frequent rebalancing. Explore deeper insights into managing option Greeks and risk strategies to enhance trading performance.
Gamma
Gamma represents the rate of change of an option's delta relative to the underlying asset price, making it a crucial measure for managing risk in options trading. Gamma scalping involves actively adjusting positions to capitalize on gamma fluctuations, unlike delta hedging, which solely targets neutralizing delta. Explore further how gamma-focused strategies optimize option portfolios for dynamic market conditions.
Rebalancing
Delta hedging involves continuously adjusting a portfolio to maintain a neutral delta, minimizing risk from price movements in the underlying asset. Gamma scalping focuses on exploiting changes in gamma by frequently rebalancing options positions to capture profits from volatility. Explore the intricacies of delta hedging and gamma scalping strategies to enhance your trading approach.
Source and External Links
Delta Hedging Explained (Visual Guide w/ Examples) - Delta hedging is a trading strategy used to balance positive and negative delta exposures so that their net effect is zero, reducing directional risk by offsetting positions through the purchase or sale of underlying shares to neutralize delta.
Delta Hedging - Overview, How It Works, Pros and Cons - Delta hedging reduces directional risk by using options and buying or selling underlying assets to achieve a delta-neutral portfolio, often requiring continuous rebalancing to maintain the hedge against price movements.
Delta neutral - Wikipedia - Delta hedging is the process of maintaining a portfolio's delta close to zero, so that its value remains stable despite small price changes in the underlying asset by offsetting positive and negative delta components.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com