Funding rate arbitrage exploits the difference in funding rates between perpetual futures and spot markets to generate risk-free profits by borrowing low-cost assets and entering opposite positions. Calendar spreads involve taking simultaneous long and short positions on futures contracts with different expiration dates to capitalize on price discrepancies over time. Explore these strategies further to understand their risk profiles and potential returns in trading.
Why it is important
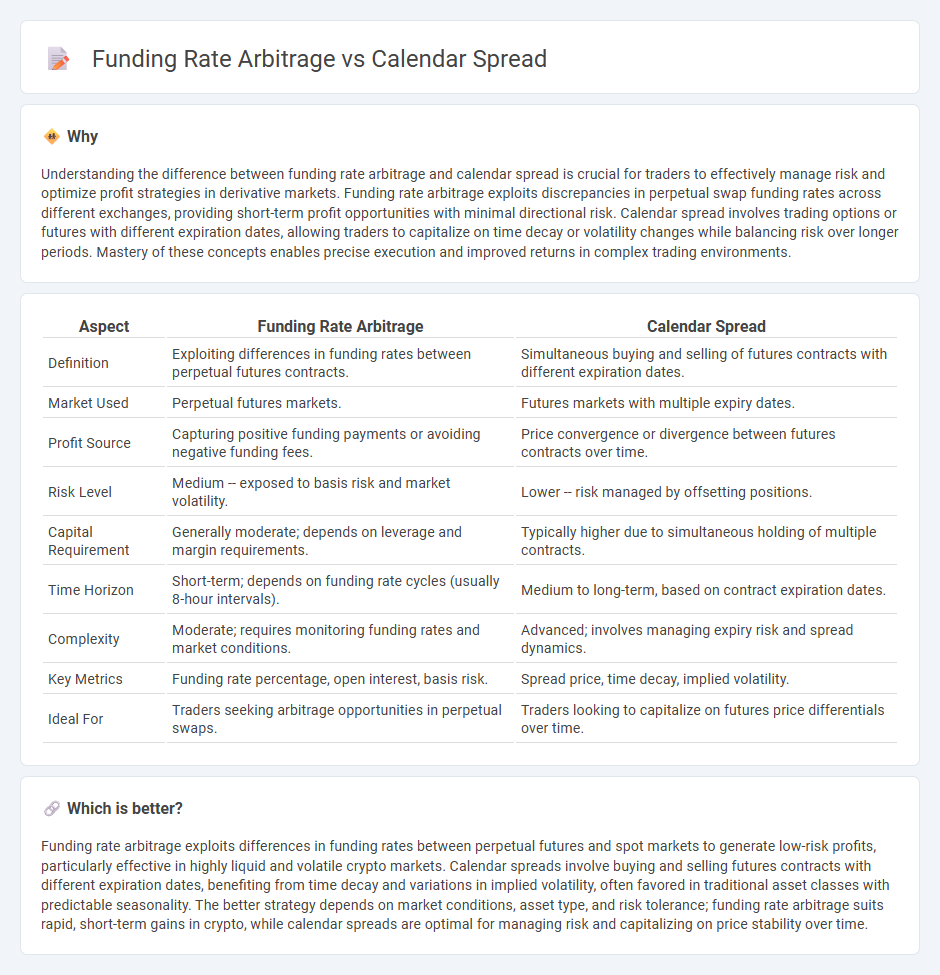
Understanding the difference between funding rate arbitrage and calendar spread is crucial for traders to effectively manage risk and optimize profit strategies in derivative markets. Funding rate arbitrage exploits discrepancies in perpetual swap funding rates across different exchanges, providing short-term profit opportunities with minimal directional risk. Calendar spread involves trading options or futures with different expiration dates, allowing traders to capitalize on time decay or volatility changes while balancing risk over longer periods. Mastery of these concepts enables precise execution and improved returns in complex trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Funding Rate Arbitrage | Calendar Spread |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting differences in funding rates between perpetual futures contracts. | Simultaneous buying and selling of futures contracts with different expiration dates. |
| Market Used | Perpetual futures markets. | Futures markets with multiple expiry dates. |
| Profit Source | Capturing positive funding payments or avoiding negative funding fees. | Price convergence or divergence between futures contracts over time. |
| Risk Level | Medium -- exposed to basis risk and market volatility. | Lower -- risk managed by offsetting positions. |
| Capital Requirement | Generally moderate; depends on leverage and margin requirements. | Typically higher due to simultaneous holding of multiple contracts. |
| Time Horizon | Short-term; depends on funding rate cycles (usually 8-hour intervals). | Medium to long-term, based on contract expiration dates. |
| Complexity | Moderate; requires monitoring funding rates and market conditions. | Advanced; involves managing expiry risk and spread dynamics. |
| Key Metrics | Funding rate percentage, open interest, basis risk. | Spread price, time decay, implied volatility. |
| Ideal For | Traders seeking arbitrage opportunities in perpetual swaps. | Traders looking to capitalize on futures price differentials over time. |
Which is better?
Funding rate arbitrage exploits differences in funding rates between perpetual futures and spot markets to generate low-risk profits, particularly effective in highly liquid and volatile crypto markets. Calendar spreads involve buying and selling futures contracts with different expiration dates, benefiting from time decay and variations in implied volatility, often favored in traditional asset classes with predictable seasonality. The better strategy depends on market conditions, asset type, and risk tolerance; funding rate arbitrage suits rapid, short-term gains in crypto, while calendar spreads are optimal for managing risk and capitalizing on price stability over time.
Connection
Funding rate arbitrage exploits price differences between perpetual futures and spot markets by taking opposite positions to capture funding payments, while calendar spread trading involves simultaneously buying and selling futures contracts with different expiration dates to benefit from changes in the spread. Both strategies leverage the cost of carry and market inefficiencies in futures pricing, using derivatives to capitalize on mispricings linked to funding rates across time. Understanding the relationship between funding rate fluctuations and inter-month spreads enables traders to optimize arbitrage opportunities in cryptocurrency and traditional futures markets.
Key Terms
Expiration dates
Calendar spreads exploit differences in option or futures prices with varying expiration dates to capture time decay benefits, typically involving near-month and far-month contracts. Funding rate arbitrage targets discrepancies in perpetual swap funding rates across exchanges, executed continuously without fixed expiration constraints. Explore deeper insights on expiration date strategies and their impact on these trading techniques here.
Interest rate differentials
Calendar spread strategies exploit interest rate differentials by simultaneously entering long and short positions in futures contracts with varying expirations, aiming to capture the price discrepancies caused by differing rates over time. Funding rate arbitrage capitalizes on the periodic payments between perpetual futures and spot prices, profiting from disparities in short-term interest rate expectations embedded in funding rates. Explore deeper insights into how interest rate differentials impact these trading strategies to enhance portfolio returns.
Contango/Backwardation
Calendar spread strategies capitalize on the price difference between near-term and longer-term futures contracts, benefiting from contango when longer-dated contracts trade at a premium. Funding rate arbitrage exploits the periodic payments between perpetual futures traders, profiting when funding rates diverge due to market sentiment shifts like backwardation, where spot prices exceed futures prices. Explore detailed insights on optimizing profits through these market conditions by diving deeper into contango and backwardation dynamics.
Source and External Links
Calendar spread - Wikipedia - A calendar spread is an options or futures trading strategy involving buying and selling contracts with the same strike price but different expiration dates, typically buying a longer-term option and selling a near-term option to profit from differences in implied volatility and time decay.
What is a Calendar Spread Option? - tastylive - A calendar spread is a low-risk, directionally neutral options strategy that profits primarily from the passage of time and volatility changes by simultaneously buying a longer-dated option and selling a shorter-dated option with the same strike.
Option Calendar Spreads - CME Group - Calendar spreads involve selling a near-term option and buying a longer-term option of the same strike and type to capitalize on expected low volatility and stable markets until the near-term expiration.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com