Market microstructure analyzes the mechanisms and processes through which securities are traded, focusing on order types, bid-ask spreads, and price formation. Latency arbitrage exploits time delays in market data transmission to gain profits by executing trades faster than competitors. Explore how these concepts shape modern trading strategies and market efficiency.
Why it is important
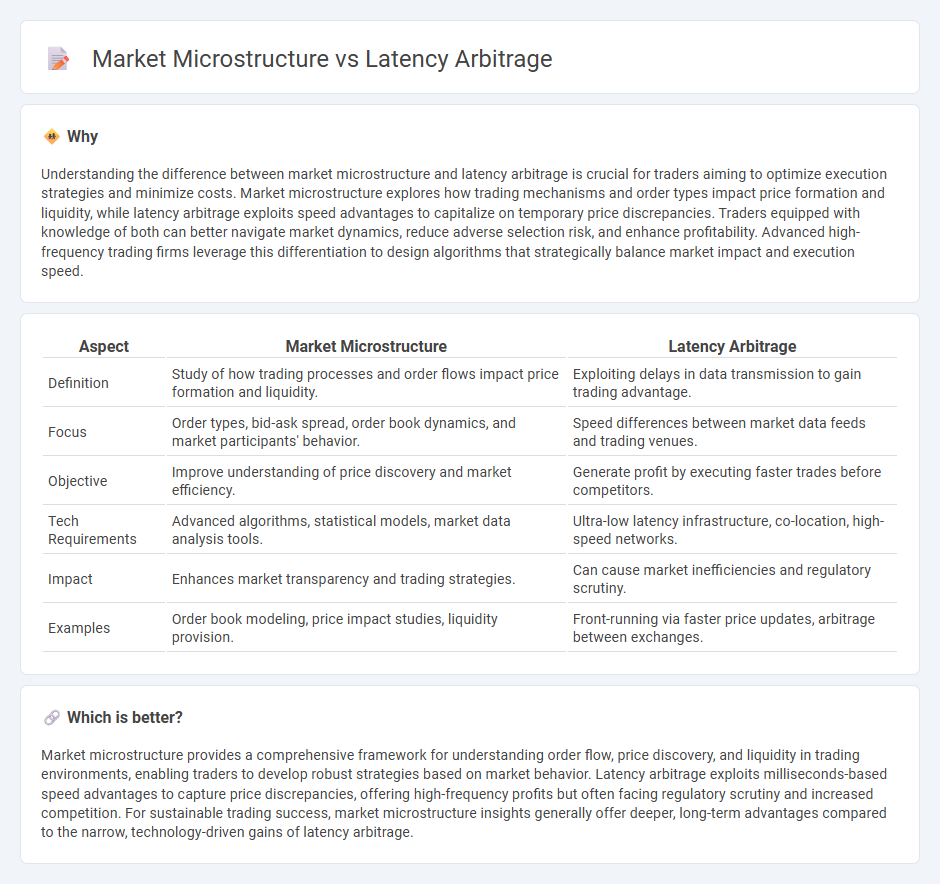
Understanding the difference between market microstructure and latency arbitrage is crucial for traders aiming to optimize execution strategies and minimize costs. Market microstructure explores how trading mechanisms and order types impact price formation and liquidity, while latency arbitrage exploits speed advantages to capitalize on temporary price discrepancies. Traders equipped with knowledge of both can better navigate market dynamics, reduce adverse selection risk, and enhance profitability. Advanced high-frequency trading firms leverage this differentiation to design algorithms that strategically balance market impact and execution speed.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Market Microstructure | Latency Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of how trading processes and order flows impact price formation and liquidity. | Exploiting delays in data transmission to gain trading advantage. |
| Focus | Order types, bid-ask spread, order book dynamics, and market participants' behavior. | Speed differences between market data feeds and trading venues. |
| Objective | Improve understanding of price discovery and market efficiency. | Generate profit by executing faster trades before competitors. |
| Tech Requirements | Advanced algorithms, statistical models, market data analysis tools. | Ultra-low latency infrastructure, co-location, high-speed networks. |
| Impact | Enhances market transparency and trading strategies. | Can cause market inefficiencies and regulatory scrutiny. |
| Examples | Order book modeling, price impact studies, liquidity provision. | Front-running via faster price updates, arbitrage between exchanges. |
Which is better?
Market microstructure provides a comprehensive framework for understanding order flow, price discovery, and liquidity in trading environments, enabling traders to develop robust strategies based on market behavior. Latency arbitrage exploits milliseconds-based speed advantages to capture price discrepancies, offering high-frequency profits but often facing regulatory scrutiny and increased competition. For sustainable trading success, market microstructure insights generally offer deeper, long-term advantages compared to the narrow, technology-driven gains of latency arbitrage.
Connection
Market microstructure examines the processes and mechanisms behind price formation and order execution in financial markets, closely influencing the opportunities for latency arbitrage. Latency arbitrage exploits small time delays in information dissemination and trade execution, capitalizing on the speed differences between high-frequency traders. Understanding the intricate details of order book dynamics and trade matching systems is essential for identifying and leveraging latency arbitrage strategies within market microstructure.
Key Terms
**Latency Arbitrage:**
Latency arbitrage exploits time delays in market data dissemination to execute trades before slower participants can react, capitalizing on price discrepancies across trading venues. This strategy relies heavily on cutting-edge technology, co-location services, and ultra-low latency networks to gain microsecond advantages. Explore how latency arbitrage reshapes trading dynamics and market fairness.
Speed Advantage
Latency arbitrage exploits millisecond differences in trade execution speeds, capitalizing on delayed market data to gain profit before others react. Market microstructure examines how information flow, order types, and trading mechanisms influence price formation and liquidity. Explore deeper insights into how speed advantages reshape trading strategies in modern markets.
Order Routing
Latency arbitrage exploits speed advantages in order routing to capitalize on price inefficiencies before others can react. Market microstructure studies how order routing mechanisms, including order matching and queue priority, influence price discovery and liquidity. Explore further to understand how advancements in order routing technology impact trading strategies and market fairness.
Source and External Links
Latency Arbitrage, Market Fragmentation, and Efficiency: A Two-Market Model - Latency arbitrage is a high-frequency trading strategy where traders use advantages in access and response time to profit from price differences between fragmented markets occurring due to information delays, which can reduce market efficiency and liquidity.
Latency Arbitrage in Forex Trading: easy profits? Not really. - This trading method exploits milliseconds-long discrepancies in price caused by transmission delays between markets, requiring extremely low-latency connections and technology to identify and execute profitable trades.
What Is Latency Arbitrage in Forex Trading? - B2PRIME - Latency arbitrage exploits time-delay differences between brokers or exchanges, viewed controversially as "toxic flow" by many brokers who try to prevent it through technology and rules, raising legal and ethical concerns about market manipulation and fairness.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com