Flash loans offer immediate, uncollateralized borrowing for arbitrage and liquidations, enabling traders to capitalize on market inefficiencies within a single transaction block. Staking involves locking cryptocurrency assets in a blockchain network to earn rewards or validate transactions, supporting network security and providing passive income. Discover how these distinct trading strategies can enhance your crypto portfolio by exploring their mechanisms and benefits.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between flash loans and staking is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and managing risk effectively. Flash loans enable traders to borrow assets instantly without collateral for arbitrage or liquidation opportunities, while staking involves locking up tokens to earn rewards and support network security. Confusing these can lead to missed profit opportunities or unintended exposure to market volatility. Mastery of both concepts empowers traders to leverage decentralized finance (DeFi) tools efficiently and securely.
Comparison Table
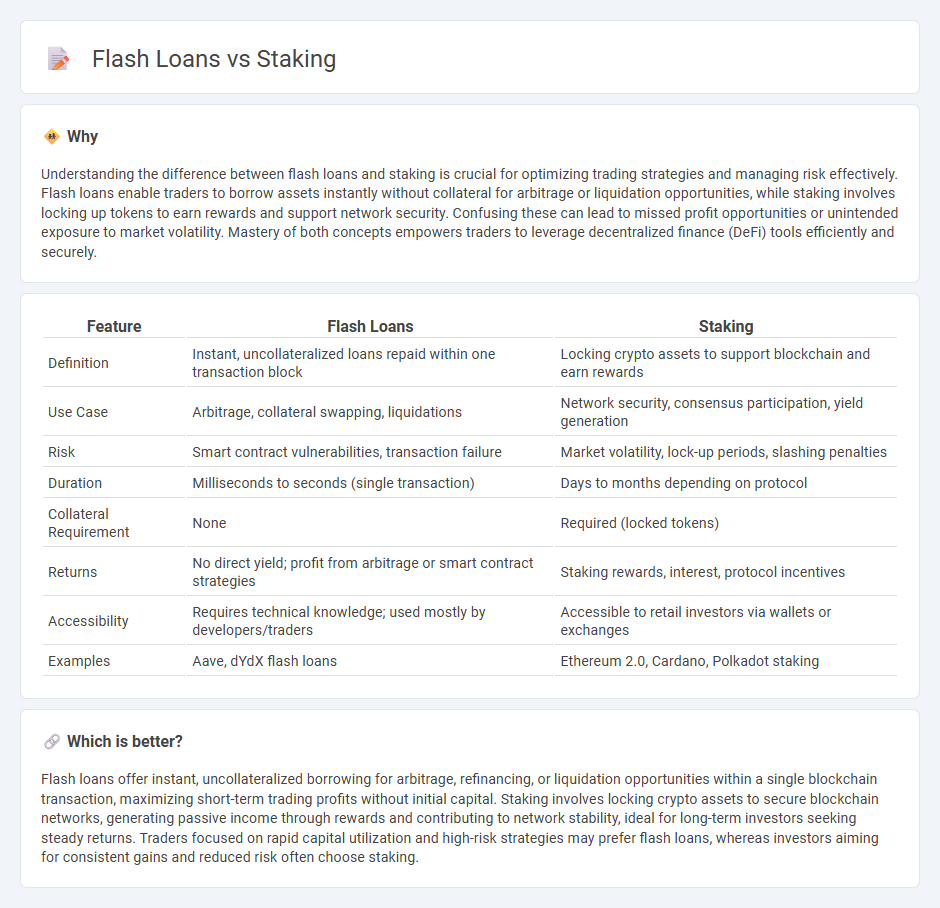
| Feature | Flash Loans | Staking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instant, uncollateralized loans repaid within one transaction block | Locking crypto assets to support blockchain and earn rewards |
| Use Case | Arbitrage, collateral swapping, liquidations | Network security, consensus participation, yield generation |
| Risk | Smart contract vulnerabilities, transaction failure | Market volatility, lock-up periods, slashing penalties |
| Duration | Milliseconds to seconds (single transaction) | Days to months depending on protocol |
| Collateral Requirement | None | Required (locked tokens) |
| Returns | No direct yield; profit from arbitrage or smart contract strategies | Staking rewards, interest, protocol incentives |
| Accessibility | Requires technical knowledge; used mostly by developers/traders | Accessible to retail investors via wallets or exchanges |
| Examples | Aave, dYdX flash loans | Ethereum 2.0, Cardano, Polkadot staking |
Which is better?
Flash loans offer instant, uncollateralized borrowing for arbitrage, refinancing, or liquidation opportunities within a single blockchain transaction, maximizing short-term trading profits without initial capital. Staking involves locking crypto assets to secure blockchain networks, generating passive income through rewards and contributing to network stability, ideal for long-term investors seeking steady returns. Traders focused on rapid capital utilization and high-risk strategies may prefer flash loans, whereas investors aiming for consistent gains and reduced risk often choose staking.
Connection
Flash loans enable instant, uncollateralized borrowing within a single transaction, allowing traders to leverage staking positions by quickly acquiring assets without upfront capital. Staking these borrowed assets can generate rewards or liquidity, enhancing yield opportunities while temporarily boosting available holdings. This synergy between flash loans and staking facilitates efficient capital utilization and strategic trading in decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems.
Key Terms
Yield
Staking yields are generated by locking cryptocurrency assets to support network security and operations, resulting in predictable, long-term rewards often ranging from 5% to 20% annually. Flash loans offer rapid, uncollateralized borrowing within a single transaction, leveraging arbitrage opportunities or yield farming to potentially capture high, but highly volatile, returns. Explore our detailed comparison to understand how staking's steady income contrasts with the dynamic, high-risk strategies of flash loans.
Collateral
Staking involves locking collateral, typically native tokens, to secure a blockchain network and earn rewards, promoting long-term commitment and network stability. Flash loans use no collateral but require repayment within a single transaction, enabling risk-free arbitrage and quick liquidity without upfront capital. Explore the detailed mechanics and risks associated with staking and flash loans to better understand their unique roles in decentralized finance.
Arbitrage
Staking involves locking up cryptocurrency to earn rewards over time, while flash loans are uncollateralized loans used to execute arbitrage opportunities within a single blockchain transaction. Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets, where flash loans provide quick capital to amplify profits without upfront investment, contrasting with the long-term, reward-based nature of staking. Explore further to understand how these DeFi tools revolutionize arbitrage strategies.
Source and External Links
What is crypto staking and how does it work? - Fidelity Investments - Crypto staking is the process of validating blockchain transactions through a proof-of-stake mechanism, where users lock a minimum number of crypto tokens to be randomly selected as validators who propose new blocks and earn rewards while ensuring network security.
Staking - Solana - Staking on Solana involves delegating tokens to validators to increase their voting power, helping the network reach consensus while the token owner retains control over their tokens and earns rewards proportional to the size of their stake.
What is staking? - Coinbase - Staking allows cryptocurrency holders to earn rewards by actively helping run a blockchain network, typically by locking their crypto assets to secure and maintain the network without lending them out.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com