Algorithmic arbitrage utilizes computer algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across various financial instruments and markets with high-speed execution, enhancing efficiency in trade operations. Index arbitrage focuses on exploiting price differences between stock indices and their constituent securities, capitalizing on mispricings for profit. Explore further to understand the distinct methodologies and advantages of each arbitrage strategy.
Why it is important
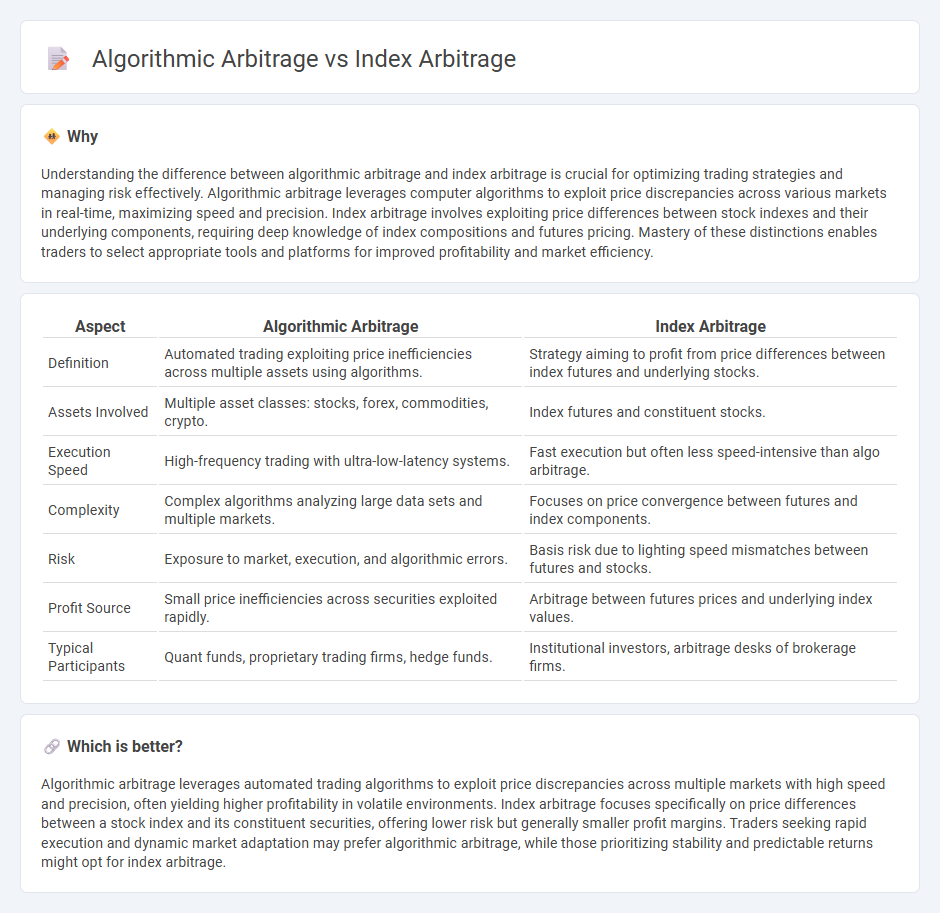
Understanding the difference between algorithmic arbitrage and index arbitrage is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and managing risk effectively. Algorithmic arbitrage leverages computer algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across various markets in real-time, maximizing speed and precision. Index arbitrage involves exploiting price differences between stock indexes and their underlying components, requiring deep knowledge of index compositions and futures pricing. Mastery of these distinctions enables traders to select appropriate tools and platforms for improved profitability and market efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Arbitrage | Index Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated trading exploiting price inefficiencies across multiple assets using algorithms. | Strategy aiming to profit from price differences between index futures and underlying stocks. |
| Assets Involved | Multiple asset classes: stocks, forex, commodities, crypto. | Index futures and constituent stocks. |
| Execution Speed | High-frequency trading with ultra-low-latency systems. | Fast execution but often less speed-intensive than algo arbitrage. |
| Complexity | Complex algorithms analyzing large data sets and multiple markets. | Focuses on price convergence between futures and index components. |
| Risk | Exposure to market, execution, and algorithmic errors. | Basis risk due to lighting speed mismatches between futures and stocks. |
| Profit Source | Small price inefficiencies across securities exploited rapidly. | Arbitrage between futures prices and underlying index values. |
| Typical Participants | Quant funds, proprietary trading firms, hedge funds. | Institutional investors, arbitrage desks of brokerage firms. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic arbitrage leverages automated trading algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across multiple markets with high speed and precision, often yielding higher profitability in volatile environments. Index arbitrage focuses specifically on price differences between a stock index and its constituent securities, offering lower risk but generally smaller profit margins. Traders seeking rapid execution and dynamic market adaptation may prefer algorithmic arbitrage, while those prioritizing stability and predictable returns might opt for index arbitrage.
Connection
Algorithmic arbitrage uses advanced computer algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across multiple markets simultaneously, enhancing speed and accuracy in trading decisions. Index arbitrage focuses on capitalizing on price differences between an index and its constituent stocks, requiring rapid execution and data analysis, often achieved through algorithmic strategies. The synergy between these two lies in algorithmic arbitrage providing the technological framework that enables efficient and timely index arbitrage opportunities.
Key Terms
Index Futures
Index arbitrage exploits price differences between stock indices and index futures to capture risk-free profits. Algorithmic arbitrage employs automated trading systems using complex algorithms to identify and execute trades across multiple markets, enhancing speed and efficiency in index futures arbitrage. Discover how sophisticated algorithms are transforming index futures trading strategies with increased precision and market responsiveness.
Automated Execution
Index arbitrage exploits price differences between index futures and underlying stocks, leveraging automated execution systems for rapid trade synchronization. Algorithmic arbitrage employs complex algorithms to identify and execute trades across multiple markets and asset classes with minimal latency. Explore detailed strategies and technology behind automated execution in arbitrage to enhance trading performance.
Price Discrepancy
Index arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between index futures and the underlying asset basket, enabling traders to profit from temporary mispricings in the market. Algorithmic arbitrage uses advanced algorithms to identify and capitalize on price inefficiencies across multiple markets and instruments with high-speed execution. Discover deeper insights into how each strategy leverages price discrepancy for optimal trading outcomes.
Source and External Links
Index Arbitrage - Quantra by QuantInsti - Index arbitrage is a strategy that exploits price discrepancies between a stock index and its futures contract by taking opposite positions to profit from price convergence, often involving simultaneous buying of stocks and selling futures or vice versa.
Index arbitrage - Wikipedia - Index arbitrage involves exploiting deviations between the market price of an index-tracking product (like futures or ETFs) and the underlying components, with arbitrageurs buying undervalued components while selling overvalued index derivatives or vice versa to capture price differentials.
What is Stock Index Arbitrage? Definition and Examples - Groww - Index arbitrage is a trading method that profits from differences between an index and its related futures contract, relying on the concept of "fair value" which accounts for spot price plus carrying cost, and is typically done when futures trade significantly away from fair value.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com