Dark pool aggregation consolidates large, non-public trading venues to provide traders with enhanced liquidity and reduced market impact, while iceberg orders break large trades into smaller visible portions to minimize signaling risk on public exchanges. These trading strategies cater to institutional investors seeking discretion and efficiency in executing substantial orders. Explore the differences and benefits of dark pool aggregation versus iceberg orders to optimize your trading approach.
Why it is important
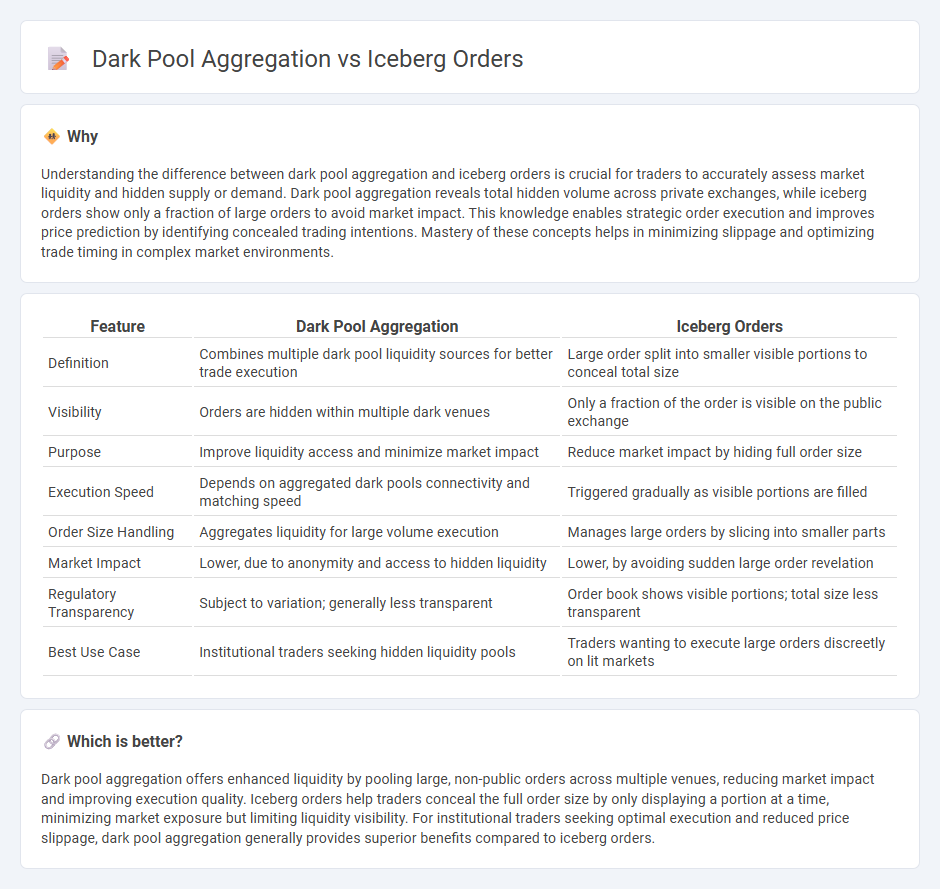
Understanding the difference between dark pool aggregation and iceberg orders is crucial for traders to accurately assess market liquidity and hidden supply or demand. Dark pool aggregation reveals total hidden volume across private exchanges, while iceberg orders show only a fraction of large orders to avoid market impact. This knowledge enables strategic order execution and improves price prediction by identifying concealed trading intentions. Mastery of these concepts helps in minimizing slippage and optimizing trade timing in complex market environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dark Pool Aggregation | Iceberg Orders |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines multiple dark pool liquidity sources for better trade execution | Large order split into smaller visible portions to conceal total size |
| Visibility | Orders are hidden within multiple dark venues | Only a fraction of the order is visible on the public exchange |
| Purpose | Improve liquidity access and minimize market impact | Reduce market impact by hiding full order size |
| Execution Speed | Depends on aggregated dark pools connectivity and matching speed | Triggered gradually as visible portions are filled |
| Order Size Handling | Aggregates liquidity for large volume execution | Manages large orders by slicing into smaller parts |
| Market Impact | Lower, due to anonymity and access to hidden liquidity | Lower, by avoiding sudden large order revelation |
| Regulatory Transparency | Subject to variation; generally less transparent | Order book shows visible portions; total size less transparent |
| Best Use Case | Institutional traders seeking hidden liquidity pools | Traders wanting to execute large orders discreetly on lit markets |
Which is better?
Dark pool aggregation offers enhanced liquidity by pooling large, non-public orders across multiple venues, reducing market impact and improving execution quality. Iceberg orders help traders conceal the full order size by only displaying a portion at a time, minimizing market exposure but limiting liquidity visibility. For institutional traders seeking optimal execution and reduced price slippage, dark pool aggregation generally provides superior benefits compared to iceberg orders.
Connection
Dark pool aggregation consolidates large, non-public trading orders from multiple dark pools, providing traders with enhanced market liquidity and reduced price impact. Iceberg orders, which reveal only a fraction of the total order size to the market, complement dark pool aggregation by enabling traders to discreetly execute large trades without signaling their full intent. The synergy between dark pool aggregation and iceberg orders facilitates efficient execution of substantial transactions while minimizing market disruption and information leakage.
Key Terms
Order Book Visibility
Iceberg orders enhance order book visibility by displaying only a fraction of the total order size, concealing the full volume while signaling market intent. Dark pool aggregation hides orders completely from public view, aggregating liquidity off-exchange to minimize market impact and maintain anonymity. Explore how these strategies impact transparency and execution quality in modern trading environments.
Hidden Liquidity
Iceberg orders split large trades into smaller visible portions while keeping the full order size hidden, enabling traders to execute large volumes without revealing total intent, thus preserving hidden liquidity. Dark pool aggregation consolidates these hidden and non-displayed orders from multiple venues, providing a comprehensive view of liquidity typically unseen on public order books. Explore how combining iceberg strategies and dark pool aggregation enhances access to hidden liquidity for optimized trading execution.
Trade Execution
Iceberg orders allow traders to execute large trades by breaking them into smaller visible chunks, minimizing market impact and price slippage. Dark pool aggregation consolidates liquidity from multiple private venues, enhancing trade execution anonymity and access to hidden liquidity pools. Explore how combining these strategies can optimize execution efficiency in modern trading environments.
Source and External Links
Iceberg Order - Overview, How It Works, and Example - An iceberg order is a large order broken into smaller chunks to hide the full size from the market and reduce price impact during execution, commonly used by institutional traders.
Iceberg Orders - Kraken Support - Iceberg orders reveal only a small visible portion of the total limit order at a time to prevent market impact, with the hidden portion revealed incrementally as the visible part fills.
What are Iceberg Orders? - Bookmap - Iceberg orders help large traders execute sizable buys or sells by splitting them into multiple smaller limit orders, minimizing market price disruption and hiding true order size.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com