Volatility harvesting leverages fluctuations in asset prices to systematically generate returns through frequent, low-risk trades, capitalizing on market inefficiencies. Swing trading focuses on capturing short- to medium-term gains by holding positions over several days or weeks, exploiting price momentum and technical patterns. Discover how these strategies differ and which aligns best with your investment goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between volatility harvesting and swing trading is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and managing risk effectively. Volatility harvesting focuses on exploiting price fluctuations within a range to generate consistent returns, while swing trading aims to capture larger price moves over days or weeks. Proper knowledge enables traders to tailor their approach according to market conditions and personal risk tolerance. This differentiation enhances decision-making and portfolio performance in dynamic financial markets.
Comparison Table
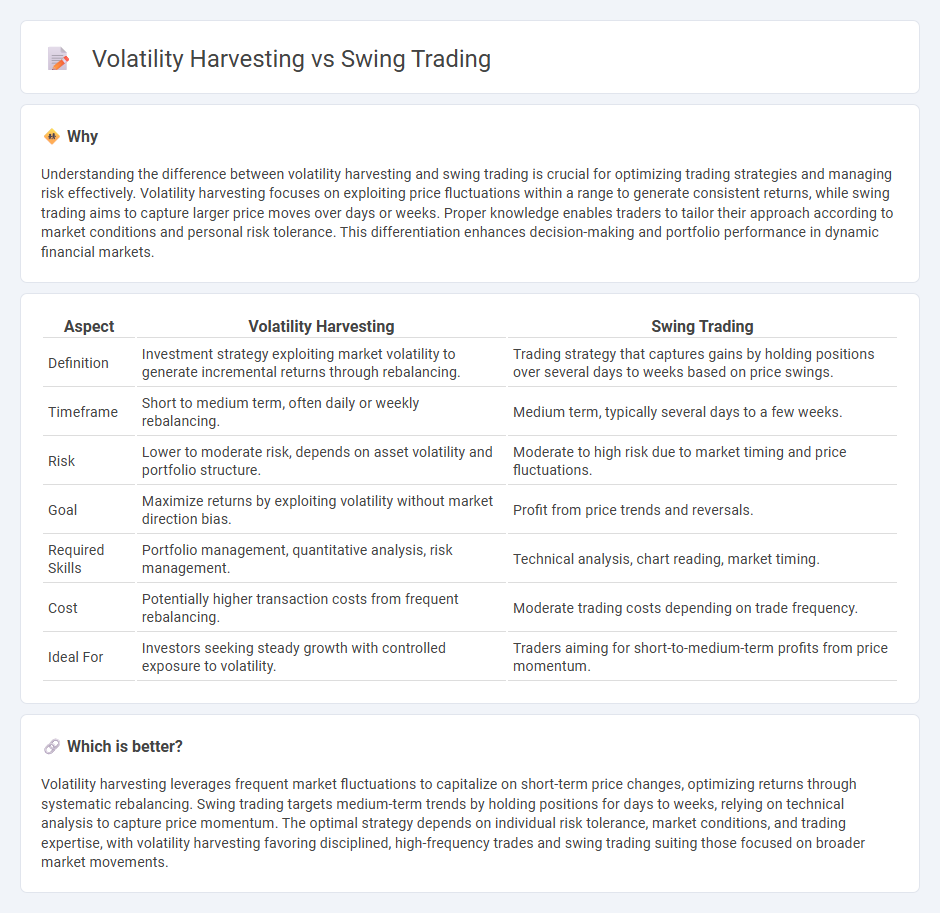
| Aspect | Volatility Harvesting | Swing Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment strategy exploiting market volatility to generate incremental returns through rebalancing. | Trading strategy that captures gains by holding positions over several days to weeks based on price swings. |
| Timeframe | Short to medium term, often daily or weekly rebalancing. | Medium term, typically several days to a few weeks. |
| Risk | Lower to moderate risk, depends on asset volatility and portfolio structure. | Moderate to high risk due to market timing and price fluctuations. |
| Goal | Maximize returns by exploiting volatility without market direction bias. | Profit from price trends and reversals. |
| Required Skills | Portfolio management, quantitative analysis, risk management. | Technical analysis, chart reading, market timing. |
| Cost | Potentially higher transaction costs from frequent rebalancing. | Moderate trading costs depending on trade frequency. |
| Ideal For | Investors seeking steady growth with controlled exposure to volatility. | Traders aiming for short-to-medium-term profits from price momentum. |
Which is better?
Volatility harvesting leverages frequent market fluctuations to capitalize on short-term price changes, optimizing returns through systematic rebalancing. Swing trading targets medium-term trends by holding positions for days to weeks, relying on technical analysis to capture price momentum. The optimal strategy depends on individual risk tolerance, market conditions, and trading expertise, with volatility harvesting favoring disciplined, high-frequency trades and swing trading suiting those focused on broader market movements.
Connection
Volatility harvesting leverages market price fluctuations to generate consistent returns by systematically rebalancing portfolios, which aligns closely with swing trading strategies that capitalize on short- to medium-term price swings in volatile assets. Both approaches rely on identifying and exploiting periods of increased market volatility to enhance profit potential while managing risk through timely entry and exit points. Integrating volatility harvesting techniques into swing trading can optimize trade timing and position sizing, improving overall portfolio performance.
Key Terms
Holding Period
Swing trading typically involves holding positions for several days to weeks, aiming to capture short- to medium-term price movements in volatile markets. Volatility harvesting leverages frequent rebalancing within shorter holding periods to capitalize on fluctuating volatility and enhance portfolio returns. Explore detailed strategies and optimal holding periods to maximize gains in both approaches.
Price Swings
Swing trading capitalizes on short- to medium-term price swings in assets, aiming to capture gains during market momentum shifts within days to weeks. Volatility harvesting leverages price fluctuations by systematically buying low and selling high, optimizing returns through consistent exploitation of market volatility patterns. Explore detailed strategies to effectively harness price swings for improved trading outcomes.
Mean Reversion
Swing trading exploits price oscillations within a trend, capitalizing on short- to medium-term mean reversion patterns to enter and exit positions profitably. Volatility harvesting leverages market fluctuations by systematically rebalancing portfolios to capture volatility-induced gains, relying on the statistical property of mean reversion to generate consistent returns. Discover how integrating mean reversion principles can enhance strategies in both swing trading and volatility harvesting.
Source and External Links
Swing trading - Wikipedia - Swing trading is a speculative strategy where traders hold assets for days to profit from price swings, using objective rules and technical or fundamental analysis to time entries and exits without needing perfect timing for gains.
Swing trading: A complete guide for investors | TD Direct Investing - Swing trading involves profiting from short-term price changes by buying dips and shorting rises, appealing to trend-spotters who hold positions from days to weeks based on technical and fundamental analysis.
Swing Trading Stocks: Strategies and Indicators - Charles Schwab - Swing traders focus on short-term price swings with the broader trend, using tools such as support, resistance, chart patterns, moving averages, and oscillators to decide when to enter and exit trades.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com