High frequency trading (HFT) leverages advanced algorithms and high-speed data networks to execute thousands of trades within milliseconds, capitalizing on minute market inefficiencies. Discretionary trading relies on human judgment and decision-making to assess market conditions and execute trades based on experience and intuition. Explore the key differences and advantages of each approach in the evolving landscape of financial markets.
Why it is important
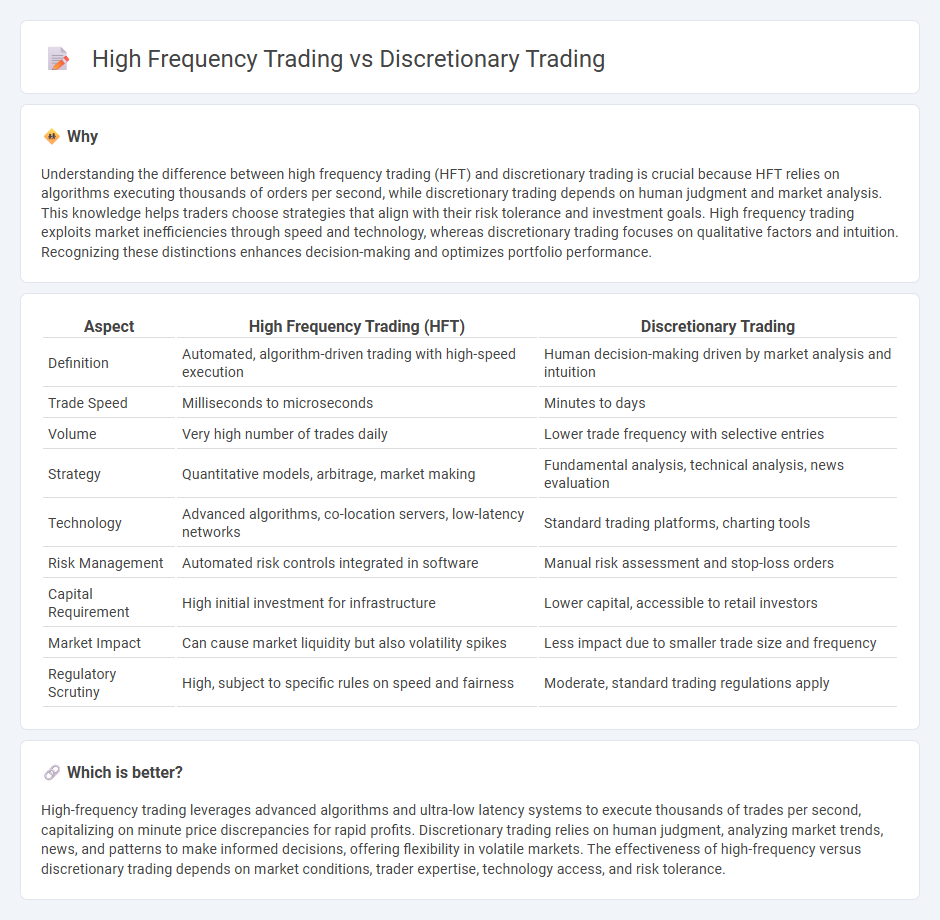
Understanding the difference between high frequency trading (HFT) and discretionary trading is crucial because HFT relies on algorithms executing thousands of orders per second, while discretionary trading depends on human judgment and market analysis. This knowledge helps traders choose strategies that align with their risk tolerance and investment goals. High frequency trading exploits market inefficiencies through speed and technology, whereas discretionary trading focuses on qualitative factors and intuition. Recognizing these distinctions enhances decision-making and optimizes portfolio performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | High Frequency Trading (HFT) | Discretionary Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated, algorithm-driven trading with high-speed execution | Human decision-making driven by market analysis and intuition |
| Trade Speed | Milliseconds to microseconds | Minutes to days |
| Volume | Very high number of trades daily | Lower trade frequency with selective entries |
| Strategy | Quantitative models, arbitrage, market making | Fundamental analysis, technical analysis, news evaluation |
| Technology | Advanced algorithms, co-location servers, low-latency networks | Standard trading platforms, charting tools |
| Risk Management | Automated risk controls integrated in software | Manual risk assessment and stop-loss orders |
| Capital Requirement | High initial investment for infrastructure | Lower capital, accessible to retail investors |
| Market Impact | Can cause market liquidity but also volatility spikes | Less impact due to smaller trade size and frequency |
| Regulatory Scrutiny | High, subject to specific rules on speed and fairness | Moderate, standard trading regulations apply |
Which is better?
High-frequency trading leverages advanced algorithms and ultra-low latency systems to execute thousands of trades per second, capitalizing on minute price discrepancies for rapid profits. Discretionary trading relies on human judgment, analyzing market trends, news, and patterns to make informed decisions, offering flexibility in volatile markets. The effectiveness of high-frequency versus discretionary trading depends on market conditions, trader expertise, technology access, and risk tolerance.
Connection
High frequency trading (HFT) and discretionary trading intersect through their influence on market liquidity and price discovery. While HFT uses algorithmic models to execute large volumes of trades at millisecond speeds, discretionary trading relies on human judgment and market analysis to make strategic decisions. The interaction between these trading styles shapes volatility and trading opportunities across financial markets.
Key Terms
Human Judgment
Discretionary trading hinges on human judgment, relying on traders' experience, intuition, and real-time decision-making to navigate market complexities. High-frequency trading (HFT) uses algorithms and automated systems to execute trades at lightning speed, minimizing human involvement and focusing on statistical arbitrage and market microstructure. Explore deeper insights on how human judgment shapes trading strategies and the evolving role of technology in market dynamics.
Algorithmic Execution
Discretionary trading relies on human judgment and intuition in executing trades, often incorporating market insights and discretionary adjustments, whereas high frequency trading (HFT) utilizes complex algorithms and ultra-fast execution to capitalize on minute price discrepancies within milliseconds. Algorithmic execution in HFT is designed to optimize order placement, reduce market impact, and exploit latency advantages, contrasting with the flexible and adaptive nature of discretionary strategies. Explore the intricacies of algorithmic execution to understand which trading style best suits your investment goals.
Trade Frequency
Discretionary trading involves human decision-making with a relatively lower trade frequency, often executed based on market analysis, intuition, or specific strategies. High-frequency trading (HFT) relies on automated algorithms executing thousands to millions of trades per second to capitalize on very small price discrepancies. Explore the differences in trade frequency and their impacts on market dynamics in more detail.
Source and External Links
What is discretionary trading? | FBS Glossary - Discretionary trading relies on a trader's intuition and understanding of the market, allowing modification of trading rules based on current conditions to adapt quickly and maximize profit, but it depends heavily on the trader's judgment and experience.
Mechanical Trading Strategies Vs. Discretionary Trading Strategies - Discretionary trading strategies involve decision-based trading where traders choose trades based on market conditions and their judgment, allowing flexibility to adjust profit targets and stop losses in response to volatility.
Discretionary Trading: Strategies for Savvy Investors - Discretionary trading combines market analysis with intuition, emphasizing the importance of blending personal insight with historical validation and risk management to maintain a trading edge.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com