Penny jump and order matching are key mechanisms in trading that influence market price movements and liquidity. Penny jump involves adjusting bid or ask prices by minimal increments, often one cent, to gain price priority, while order matching is the process of pairing buy and sell orders based on price and time priority in an exchange. Explore how these concepts impact trading strategies and market efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between penny jump and order matching is crucial for traders to optimize execution strategies and minimize slippage costs in fast-moving markets. Penny jump involves price increments of one cent, impacting bid-ask spreads and order priority, while order matching determines how trades are paired, affecting liquidity and fill rates. Accurate knowledge of these concepts enables traders to better anticipate price movements and improve trade timing. Mastery of penny jump and order matching dynamics enhances profitability by ensuring optimal order placement and execution efficiency.
Comparison Table
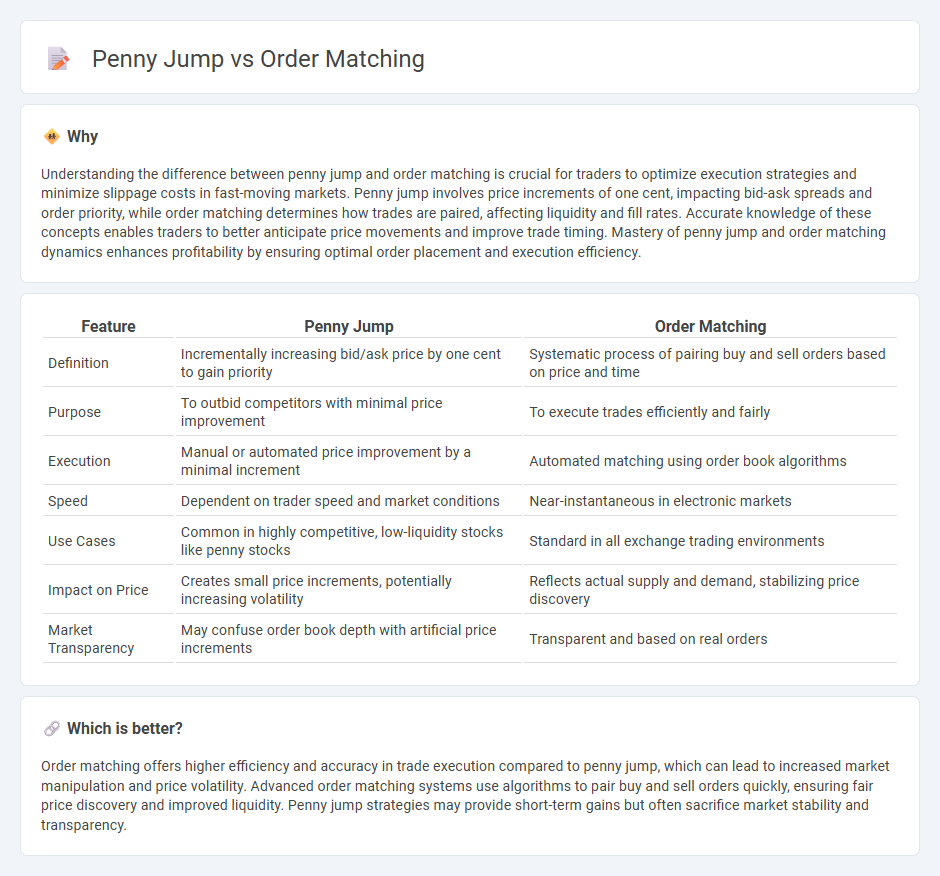
| Feature | Penny Jump | Order Matching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incrementally increasing bid/ask price by one cent to gain priority | Systematic process of pairing buy and sell orders based on price and time |
| Purpose | To outbid competitors with minimal price improvement | To execute trades efficiently and fairly |
| Execution | Manual or automated price improvement by a minimal increment | Automated matching using order book algorithms |
| Speed | Dependent on trader speed and market conditions | Near-instantaneous in electronic markets |
| Use Cases | Common in highly competitive, low-liquidity stocks like penny stocks | Standard in all exchange trading environments |
| Impact on Price | Creates small price increments, potentially increasing volatility | Reflects actual supply and demand, stabilizing price discovery |
| Market Transparency | May confuse order book depth with artificial price increments | Transparent and based on real orders |
Which is better?
Order matching offers higher efficiency and accuracy in trade execution compared to penny jump, which can lead to increased market manipulation and price volatility. Advanced order matching systems use algorithms to pair buy and sell orders quickly, ensuring fair price discovery and improved liquidity. Penny jump strategies may provide short-term gains but often sacrifice market stability and transparency.
Connection
Penny jump refers to the smallest possible price increment in a trading system, typically one cent, which influences the execution of trades by creating tight bid-ask spreads. Order matching algorithms use these increments to pair buy and sell orders efficiently, ensuring that trades occur at the best available prices within the penny jump constraints. This connection enhances market liquidity and price discovery by enabling rapid and precise matching of orders at minimal price differences.
Key Terms
**Order Matching:**
Order matching is a core process in financial markets where buy and sell orders are paired based on price and time priority, ensuring efficient trade execution. This mechanism prioritizes the best available prices and maintains market liquidity by continuously updating the order book. Discover how order matching impacts market dynamics and trading strategies.
Price-Time Priority
Order matching relies on price-time priority, where orders are executed based on the best available price and, if prices are equal, the earliest order receives priority, ensuring fairness in trade execution. Penny jump allows traders to improve their order's execution priority by minimally increasing or decreasing their price, which can disrupt the strict price-time priority by enabling price improvement strategies. Explore deeper insights into how these mechanisms impact market liquidity and execution efficiency for better trading strategies.
Order Book
Order matching in an order book entails pairing buy and sell orders based on price and time priority, ensuring execution at the best available price. Penny jumping occurs when traders place orders slightly better than existing bids or offers to gain priority in the order book queue, often leading to increased market competition and narrower spreads. Explore the dynamics of order book management to understand the impact of these strategies on market liquidity and price discovery.
Source and External Links
How does order matching work when I trade alternative assets on Public? - Orders are matched when buy (bid) and sell (ask) prices are equal or cross, prioritized first by best price and then by time submitted, meaning earlier orders at the same price get matched first.
Order matching system: Explained - The core of an order matching system is the matching algorithm, commonly using price-time priority (best price first, then earliest order) or pro-rata (priority by order size) to pair buy and sell orders fairly and efficiently.
Electronic Trading and Order Matching System Basics - Strike - Electronic order matching follows steps including order placement, validation, queuing in the order book, price determination, and matching using a price-time priority, where orders with the best price and earliest timestamp get matched first, ensuring transparency and efficient execution.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com