Liquidity sweeps involve strategic market orders designed to target and absorb available liquidity across multiple price levels, minimizing slippage and optimizing trade execution. Front running is an unethical practice where traders exploit advanced knowledge of pending orders to gain an unfair advantage, often leading to increased market volatility and higher costs for other investors. Explore the intricacies of liquidity sweeps and front running to enhance your trading strategies and protect your investments.
Why it is important
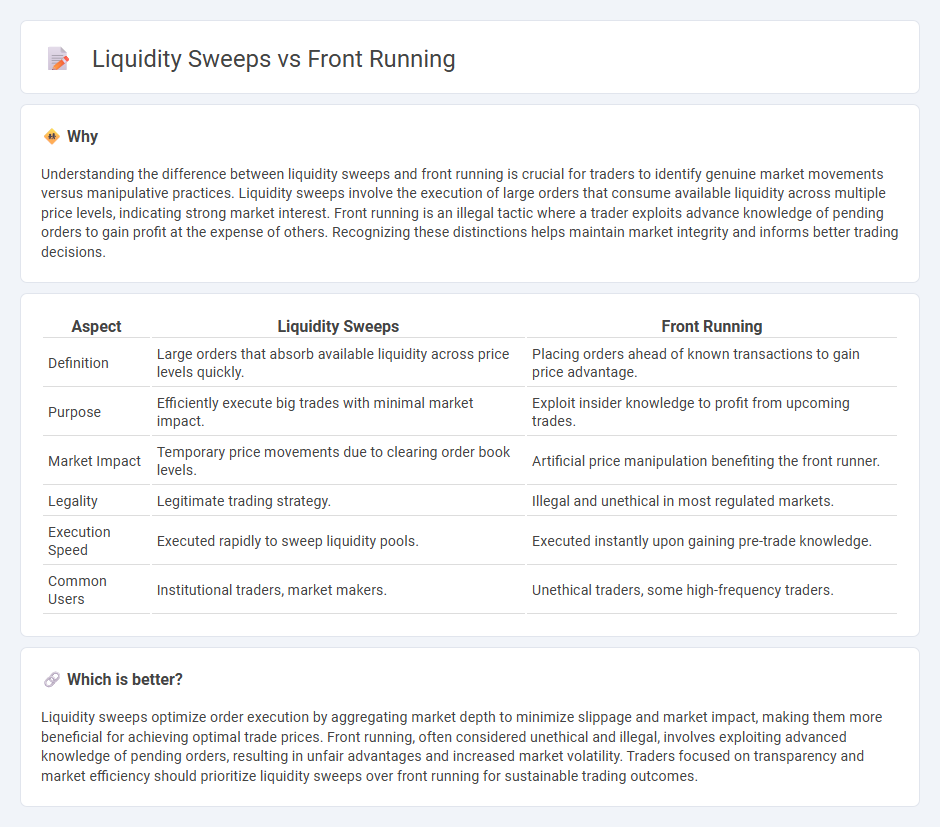
Understanding the difference between liquidity sweeps and front running is crucial for traders to identify genuine market movements versus manipulative practices. Liquidity sweeps involve the execution of large orders that consume available liquidity across multiple price levels, indicating strong market interest. Front running is an illegal tactic where a trader exploits advance knowledge of pending orders to gain profit at the expense of others. Recognizing these distinctions helps maintain market integrity and informs better trading decisions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Liquidity Sweeps | Front Running |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large orders that absorb available liquidity across price levels quickly. | Placing orders ahead of known transactions to gain price advantage. |
| Purpose | Efficiently execute big trades with minimal market impact. | Exploit insider knowledge to profit from upcoming trades. |
| Market Impact | Temporary price movements due to clearing order book levels. | Artificial price manipulation benefiting the front runner. |
| Legality | Legitimate trading strategy. | Illegal and unethical in most regulated markets. |
| Execution Speed | Executed rapidly to sweep liquidity pools. | Executed instantly upon gaining pre-trade knowledge. |
| Common Users | Institutional traders, market makers. | Unethical traders, some high-frequency traders. |
Which is better?
Liquidity sweeps optimize order execution by aggregating market depth to minimize slippage and market impact, making them more beneficial for achieving optimal trade prices. Front running, often considered unethical and illegal, involves exploiting advanced knowledge of pending orders, resulting in unfair advantages and increased market volatility. Traders focused on transparency and market efficiency should prioritize liquidity sweeps over front running for sustainable trading outcomes.
Connection
Liquidity sweeps involve large orders that absorb available market liquidity, creating an opportunity for front running, where traders anticipate these sizable trades to execute ahead and profit from subsequent price movements. Front running exploits the temporary information asymmetry caused by liquidity sweeps, often leading to increased market volatility and altered price dynamics. This connection highlights the importance of robust market surveillance to detect and mitigate predatory trading practices affecting fair market conditions.
Key Terms
Order Flow
Front running exploits advance knowledge of pending orders to trade ahead and capitalize on price movements, often impacting market fairness. Liquidity sweeps aggressively consume multiple price levels in the order book to trigger stop orders and awaken hidden liquidity, resulting in rapid price shifts. Explore the nuances of order flow strategies to better understand their influence on trading dynamics and market efficiency.
Execution Speed
Front running exploits execution speed by placing orders just before large trades to profit from price movements, often leveraging high-frequency trading algorithms. Liquidity sweeps prioritize rapid order execution to capture fragmented liquidity across multiple venues, reducing slippage and market impact. Explore further to understand how execution speed shapes competitive trading strategies and market efficiency.
Market Impact
Front running exploits advance knowledge of pending orders, causing significant market impact by driving price changes before the original trade executes. Liquidity sweeps aggressively consume available liquidity across multiple price levels, leading to sharp price movements and increased volatility. Explore more to understand how these tactics affect market efficiency and trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Front Running Explained: What Is It, Examples, Is It Legal? - Front running is when a broker trades a financial asset using non-public information about a large upcoming trade that will influence the asset's price, profiting by trading ahead of the client's order, which is illegal and unethical.
Front running - Wikipedia - Front running, also called tailgating, is a form of market manipulation where a trader or broker trades securities in advance of a large pending transaction based on nonpublic knowledge, profiting at the expense of customers or the market, and is prohibited.
Front Running Definition - CoinMarketCap - Front running is placing a transaction ahead in a queue when knowing about a future transaction, common in crypto and traditional markets and can include various attack methods like displacement or insertion to exploit transaction timing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com