Paper trading platforms simulate real market conditions, allowing traders to practice strategies without financial risk by using virtual funds and real-time data. Automated trading systems execute pre-programmed trading instructions based on algorithms, enhancing speed and reducing emotional bias in decision-making. Explore the pros and cons of each approach to optimize your trading strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between paper trading platforms and automated trading systems is crucial for developing effective trading strategies and mitigating financial risks. Paper trading simulates market conditions without real capital, allowing traders to practice and refine their techniques, while automated trading systems execute trades based on pre-set algorithms in real-time markets, potentially maximizing efficiency and emotion-free decisions. Knowledge of both enables traders to transition smoothly from strategy testing to live trading with greater confidence. Proper evaluation of platform reliability, execution speed, and algorithm performance determines trading success and capital preservation.
Comparison Table
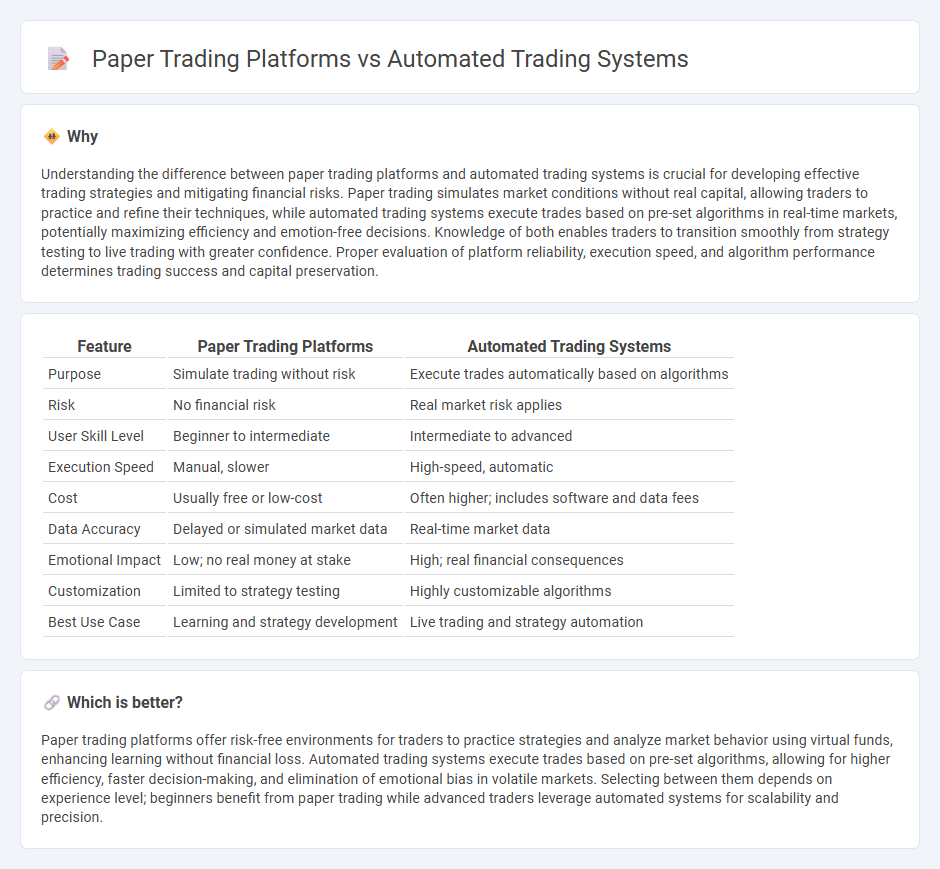
| Feature | Paper Trading Platforms | Automated Trading Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Simulate trading without risk | Execute trades automatically based on algorithms |
| Risk | No financial risk | Real market risk applies |
| User Skill Level | Beginner to intermediate | Intermediate to advanced |
| Execution Speed | Manual, slower | High-speed, automatic |
| Cost | Usually free or low-cost | Often higher; includes software and data fees |
| Data Accuracy | Delayed or simulated market data | Real-time market data |
| Emotional Impact | Low; no real money at stake | High; real financial consequences |
| Customization | Limited to strategy testing | Highly customizable algorithms |
| Best Use Case | Learning and strategy development | Live trading and strategy automation |
Which is better?
Paper trading platforms offer risk-free environments for traders to practice strategies and analyze market behavior using virtual funds, enhancing learning without financial loss. Automated trading systems execute trades based on pre-set algorithms, allowing for higher efficiency, faster decision-making, and elimination of emotional bias in volatile markets. Selecting between them depends on experience level; beginners benefit from paper trading while advanced traders leverage automated systems for scalability and precision.
Connection
Paper trading platforms simulate real market conditions, allowing traders to test automated trading systems without financial risk. Automated trading systems execute pre-programmed strategies based on real-time data, and paper trading helps refine these algorithms by providing performance feedback in a risk-free environment. Integrating paper trading with automated systems enhances strategy development, enabling optimization before live deployment.
Key Terms
Algorithmic Execution
Automated trading systems use algorithmic execution to execute trades at high speed and accuracy based on predefined criteria, significantly reducing human error and emotional bias. Paper trading platforms simulate these algorithmic strategies without real capital, providing a risk-free environment for testing and refining execution algorithms. Explore the nuances between these systems to optimize your trading strategy and performance.
Backtesting
Automated trading systems leverage advanced algorithms to execute real trades, enabling precise backtesting with historical data to refine strategies and minimize risks. Paper trading platforms simulate market conditions without financial exposure, allowing traders to test strategies in a risk-free environment but often lacking the execution speed and slippage insights of real trading. Explore comprehensive comparisons and detailed analyses to optimize your backtesting approach effectively.
Simulated Orders
Automated trading systems execute real-time trades using algorithms, while paper trading platforms simulate orders to test strategies without financial risk. Simulated orders provide a risk-free environment to evaluate performance, order execution speed, and market reaction before deploying actual capital. Explore detailed comparisons to understand the benefits and limitations of both approaches.
Source and External Links
Automated trading system - Wikipedia - An automated trading system (ATS) is a computer program that automatically creates and submits buy and sell orders to market exchanges based on predefined trading strategies using technical analysis or advanced computations, widely used by investment banks, hedge funds, and private investors, accounting for 70-80% of market transactions.
Automated Trading Systems - Overview, How They Work, ... - Corporate Finance Institute - Automated trading systems employ algorithmic trading to execute orders based on programmed entry and exit rules derived from technical indicators or complex mathematical models, allowing investors a hands-off approach and removing emotional bias from trading.
Automated trading systems - Purple Trading - Automated trading systems, also called trading robots or Expert Advisors, autonomously analyze technical data, open and close positions, and manage risk (stop loss/take profit), providing faster execution and multitasking advantages over human traders.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com