Quantitative backtesting involves applying statistical models to historical market data to evaluate trading strategies' performance and risk metrics. Forward testing, or paper trading, simulates strategy execution in live market conditions without real capital, capturing real-time market dynamics and slippage. Explore deeper insights on optimizing trading systems with quantitative backtesting and forward testing techniques.
Why it is important
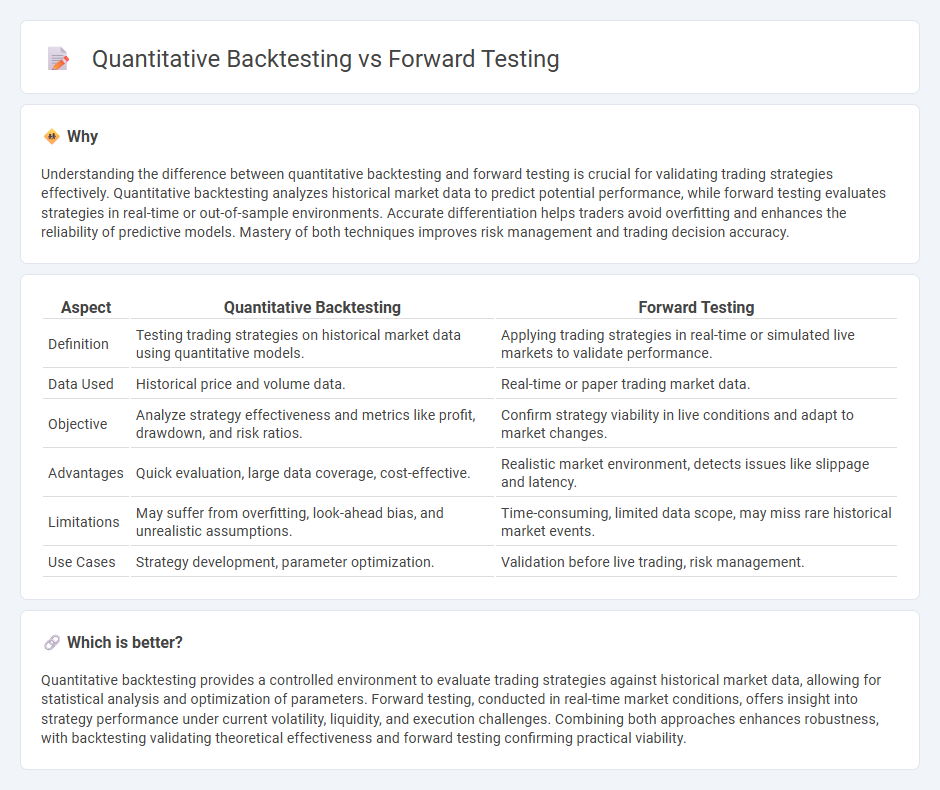
Understanding the difference between quantitative backtesting and forward testing is crucial for validating trading strategies effectively. Quantitative backtesting analyzes historical market data to predict potential performance, while forward testing evaluates strategies in real-time or out-of-sample environments. Accurate differentiation helps traders avoid overfitting and enhances the reliability of predictive models. Mastery of both techniques improves risk management and trading decision accuracy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Backtesting | Forward Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Testing trading strategies on historical market data using quantitative models. | Applying trading strategies in real-time or simulated live markets to validate performance. |
| Data Used | Historical price and volume data. | Real-time or paper trading market data. |
| Objective | Analyze strategy effectiveness and metrics like profit, drawdown, and risk ratios. | Confirm strategy viability in live conditions and adapt to market changes. |
| Advantages | Quick evaluation, large data coverage, cost-effective. | Realistic market environment, detects issues like slippage and latency. |
| Limitations | May suffer from overfitting, look-ahead bias, and unrealistic assumptions. | Time-consuming, limited data scope, may miss rare historical market events. |
| Use Cases | Strategy development, parameter optimization. | Validation before live trading, risk management. |
Which is better?
Quantitative backtesting provides a controlled environment to evaluate trading strategies against historical market data, allowing for statistical analysis and optimization of parameters. Forward testing, conducted in real-time market conditions, offers insight into strategy performance under current volatility, liquidity, and execution challenges. Combining both approaches enhances robustness, with backtesting validating theoretical effectiveness and forward testing confirming practical viability.
Connection
Quantitative backtesting evaluates trading strategies using historical data to identify potential performance and risk metrics. Forward testing applies these strategies in live or simulated real-time environments to validate backtesting results and assess adaptability to market conditions. Integrating both methods ensures robust strategy development by combining historical analysis with real-world verification.
Key Terms
Live Data
Forward testing evaluates trading strategies using live data to simulate real market conditions, ensuring robustness and adaptability. Quantitative backtesting relies on historical data and statistical models to assess strategy performance, which may not accurately reflect future market dynamics. Explore the advantages of forward testing and how it complements quantitative backtesting for more reliable trading decisions.
Historical Data
Forward testing evaluates trading strategies using out-of-sample data to simulate real-time market conditions, ensuring robustness beyond historical patterns. Quantitative backtesting relies on historical data to statistically measure strategy performance but may suffer from overfitting and look-ahead bias. Explore more in-depth comparisons to optimize your trading model validation process.
Strategy Validation
Forward testing simulates real-time trading by applying a strategy to new, unseen market data to validate its effectiveness under current conditions, minimizing overfitting risks common in quantitative backtesting. Quantitative backtesting rigorously evaluates strategies against historical datasets using statistical metrics, offering insights into potential performance but often susceptible to data snooping and curve fitting. Explore in-depth comparisons and best practices in strategy validation to enhance trading system reliability.
Source and External Links
Forward Testing of Trading Strategies - Forward testing, also known as paper trading or walk-forward testing, validates a trading strategy in real market conditions without risking real money, bridging theory and practice to build trader confidence before live trading.
Backtesting and Forward Testing in Algo Trading: Explained - Forward testing involves running a trading strategy in a demo or small real-money account to monitor and analyze its performance live, allowing traders to identify weaknesses and improve the strategy under real market conditions.
Forward testing effect - In psychology, the forward testing effect refers to how testing learned information enhances the learning and recall of new information, showing that testing itself improves memory beyond just repetition or restudy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com