Liquidity sweeps involve quick execution of large orders to capture available liquidity across multiple price levels, reducing market impact and revealing genuine supply or demand. Order book spoofing manipulates market perception by placing fake orders to create false demand or supply signals, aiming to deceive other traders before canceling these orders. Explore the key differences and implications of liquidity sweeps versus order book spoofing to enhance your trading strategy.
Why it is important
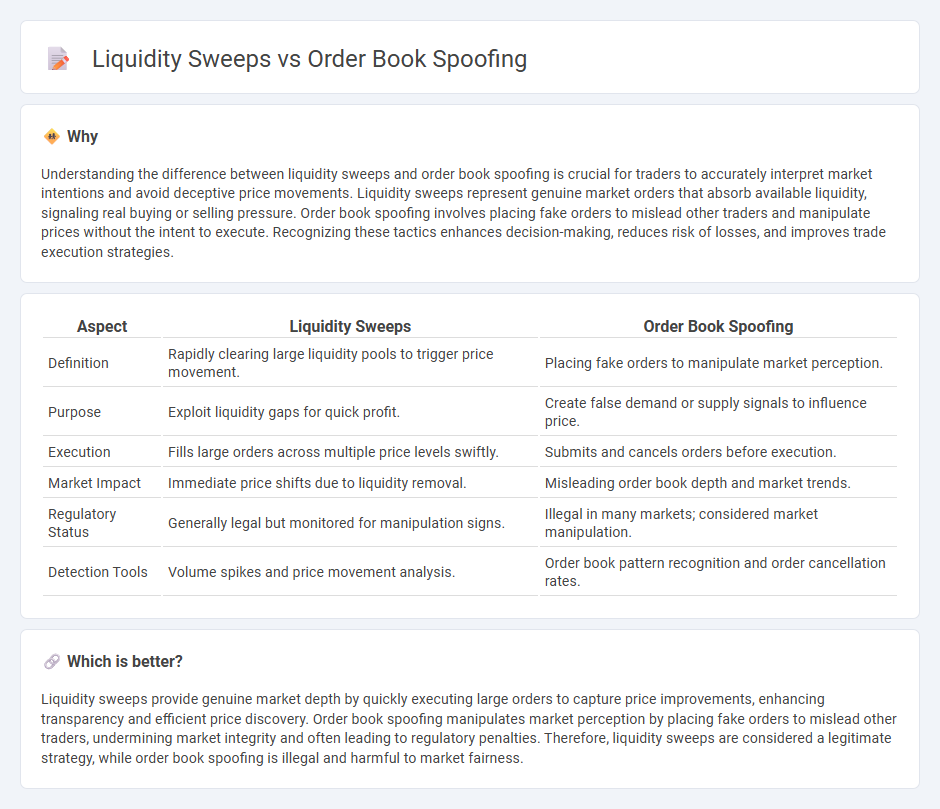
Understanding the difference between liquidity sweeps and order book spoofing is crucial for traders to accurately interpret market intentions and avoid deceptive price movements. Liquidity sweeps represent genuine market orders that absorb available liquidity, signaling real buying or selling pressure. Order book spoofing involves placing fake orders to mislead other traders and manipulate prices without the intent to execute. Recognizing these tactics enhances decision-making, reduces risk of losses, and improves trade execution strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Liquidity Sweeps | Order Book Spoofing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapidly clearing large liquidity pools to trigger price movement. | Placing fake orders to manipulate market perception. |
| Purpose | Exploit liquidity gaps for quick profit. | Create false demand or supply signals to influence price. |
| Execution | Fills large orders across multiple price levels swiftly. | Submits and cancels orders before execution. |
| Market Impact | Immediate price shifts due to liquidity removal. | Misleading order book depth and market trends. |
| Regulatory Status | Generally legal but monitored for manipulation signs. | Illegal in many markets; considered market manipulation. |
| Detection Tools | Volume spikes and price movement analysis. | Order book pattern recognition and order cancellation rates. |
Which is better?
Liquidity sweeps provide genuine market depth by quickly executing large orders to capture price improvements, enhancing transparency and efficient price discovery. Order book spoofing manipulates market perception by placing fake orders to mislead other traders, undermining market integrity and often leading to regulatory penalties. Therefore, liquidity sweeps are considered a legitimate strategy, while order book spoofing is illegal and harmful to market fairness.
Connection
Liquidity sweeps manipulate market depth by executing large orders to trigger stop-losses, creating artificial volatility that misleads traders. Order book spoofing complements this by placing fake orders to distort the perceived supply and demand before quickly canceling them. Both tactics exploit the order book's transparency to misguide trading decisions and gain unfair advantage.
Key Terms
Order Book Spoofing:
Order book spoofing involves placing large fake orders to manipulate market perception of supply and demand, misleading other traders without any intention of execution. This deceptive practice disrupts normal trading patterns and can lead to wrongful price movements, posing significant regulatory challenges in financial markets. Explore deeper insights into order book spoofing techniques and detection methods to understand its impact on market integrity.
Fake Orders
Order book spoofing involves placing fake orders to create a false impression of market demand or supply, misleading other traders about price movements. Liquidity sweeps execute large trades by quickly absorbing available liquidity, often triggering stop orders or price cascades, but without the intent of maintaining false orders. Explore the nuances and strategies behind these trading tactics to enhance market understanding.
Market Manipulation
Order book spoofing involves placing large fake orders to mislead traders about supply and demand, creating false market sentiment for manipulation. Liquidity sweeps rapidly consume available orders at various price levels, triggering price movements and exploiting short-term market inefficiencies. Learn more about how these practices distort prices and impact market integrity.
Source and External Links
Spoofing the order book: UK and US regulators take aim - Spoofing is a market manipulation tactic where a trader places large orders to move the price but has no intent to execute, quickly canceling them after profiting from price changes induced by the fake orders.
Crypto market spoofing: Identifying fake orders and their impact - Spoofing involves placing and canceling fake orders to mislead trading bots and other market participants into moving prices favorably for the spoofer who then executes a real trade.
Cracking the Spoofing Code: Inside the World of Market Manipulation - Spoofers create false market sentiment by placing large, deceptive orders to influence others' trading decisions and then cancel these orders to avoid execution, profiting from the artificial price movements they provoke.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com