Perpetual contracts offer traders indefinite exposure to an asset without an expiration date, relying on a funding rate mechanism to anchor prices close to spot markets. Forward contracts are customized agreements between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specified price on a future date, commonly used for hedging purposes with fixed settlement terms. Explore the differences in risk profiles, liquidity, and use cases to better understand which contract suits your trading strategy.
Why it is important
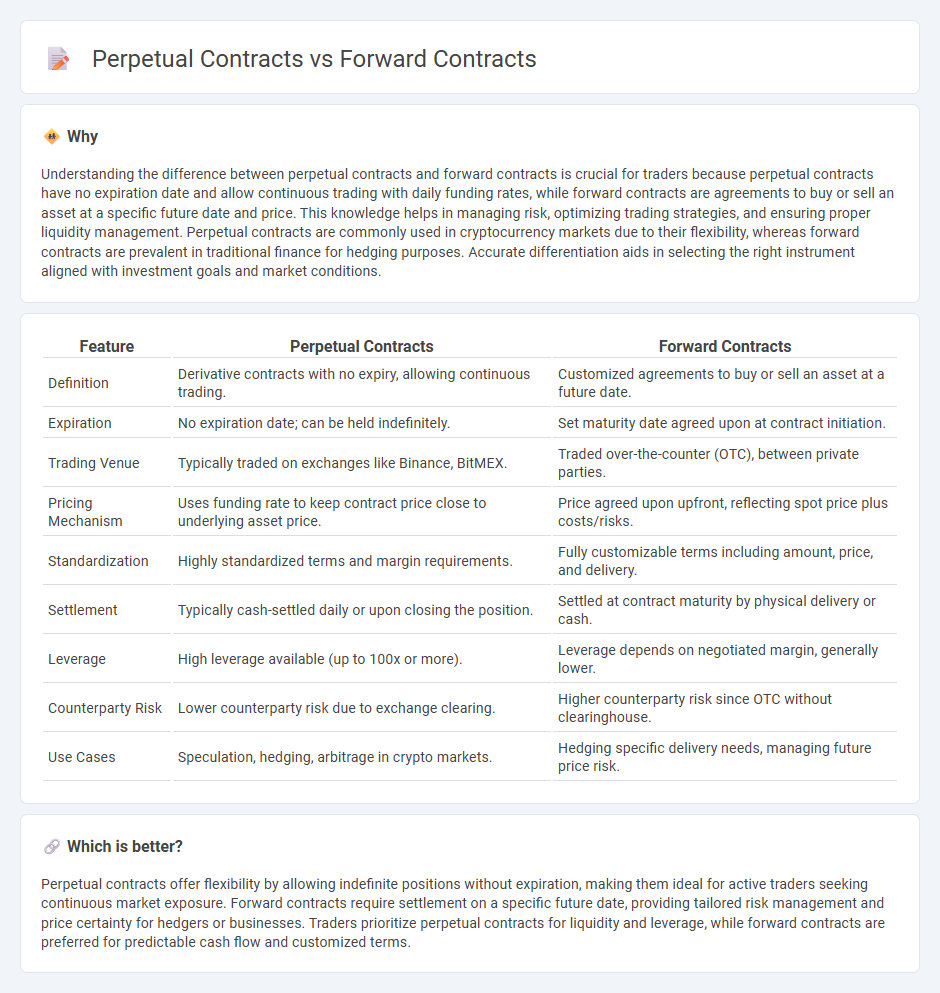
Understanding the difference between perpetual contracts and forward contracts is crucial for traders because perpetual contracts have no expiration date and allow continuous trading with daily funding rates, while forward contracts are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a specific future date and price. This knowledge helps in managing risk, optimizing trading strategies, and ensuring proper liquidity management. Perpetual contracts are commonly used in cryptocurrency markets due to their flexibility, whereas forward contracts are prevalent in traditional finance for hedging purposes. Accurate differentiation aids in selecting the right instrument aligned with investment goals and market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Perpetual Contracts | Forward Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Derivative contracts with no expiry, allowing continuous trading. | Customized agreements to buy or sell an asset at a future date. |
| Expiration | No expiration date; can be held indefinitely. | Set maturity date agreed upon at contract initiation. |
| Trading Venue | Typically traded on exchanges like Binance, BitMEX. | Traded over-the-counter (OTC), between private parties. |
| Pricing Mechanism | Uses funding rate to keep contract price close to underlying asset price. | Price agreed upon upfront, reflecting spot price plus costs/risks. |
| Standardization | Highly standardized terms and margin requirements. | Fully customizable terms including amount, price, and delivery. |
| Settlement | Typically cash-settled daily or upon closing the position. | Settled at contract maturity by physical delivery or cash. |
| Leverage | High leverage available (up to 100x or more). | Leverage depends on negotiated margin, generally lower. |
| Counterparty Risk | Lower counterparty risk due to exchange clearing. | Higher counterparty risk since OTC without clearinghouse. |
| Use Cases | Speculation, hedging, arbitrage in crypto markets. | Hedging specific delivery needs, managing future price risk. |
Which is better?
Perpetual contracts offer flexibility by allowing indefinite positions without expiration, making them ideal for active traders seeking continuous market exposure. Forward contracts require settlement on a specific future date, providing tailored risk management and price certainty for hedgers or businesses. Traders prioritize perpetual contracts for liquidity and leverage, while forward contracts are preferred for predictable cash flow and customized terms.
Connection
Perpetual contracts and forward contracts are connected through their role in derivative trading, allowing investors to speculate on asset prices without owning the underlying asset. Perpetual contracts offer continuous, margin-based trading with no expiration date, while forward contracts set a fixed price for asset delivery at a future date, typically customized between parties. Both instruments facilitate price risk management and leverage, contributing to market liquidity and price discovery.
Key Terms
Expiry Date
Forward contracts have a fixed expiry date, which means the contract settles on a specific future date agreed upon by both parties. Perpetual contracts lack an expiry date, allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely without contract rollover, making them popular in cryptocurrency markets. Explore more to understand how expiry dates influence risk management and trading strategies.
Settlement
Forward contracts involve settlement at a predetermined future date with the delivery of the underlying asset or cash settlement based on the contract terms. Perpetual contracts do not have an expiry date, and their settlement is continuous through periodic funding payments exchanged between long and short positions to maintain price alignment with the underlying asset. Explore more to understand the implications of settlement differences on trading strategies and risk management.
Funding Rate
Forward contracts are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date, with no ongoing payments between parties. Perpetual contracts, often used in cryptocurrency trading, have no expiration and rely on the Funding Rate mechanism to anchor their price to the underlying asset's spot market. Explore in-depth insights on how Funding Rates influence perpetual contracts and risk management strategies.
Source and External Links
Forward Contract - Defined, How to Use, Example - A forward contract is a customized agreement between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date, often used to hedge against price volatility and typically settled by delivery or cash payment at expiration.
Forward contract - Wikipedia - Forward contracts are non-standardized OTC agreements with counterparty risk, differing from futures as they lack exchange trading, daily margining, and allow customization, often used to lock in prices without upfront cash flows.
Futures Contracts Compared to Forwards - CME Group - Forward contracts set terms for future delivery and payment on customized OTC contracts, typically used to hedge price risks for commodities or other assets, differing from standardized futures traded on exchanges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com