Gamma scalping involves actively managing options positions to capitalize on price fluctuations and maintain a delta-neutral stance, optimizing gains from volatility changes. Theta decay refers to the gradual loss of an option's time value as it approaches expiration, impacting the profitability of holding options over time. Discover more about how mastering the balance between gamma scalping and theta decay can enhance your trading strategy.
Why it is important
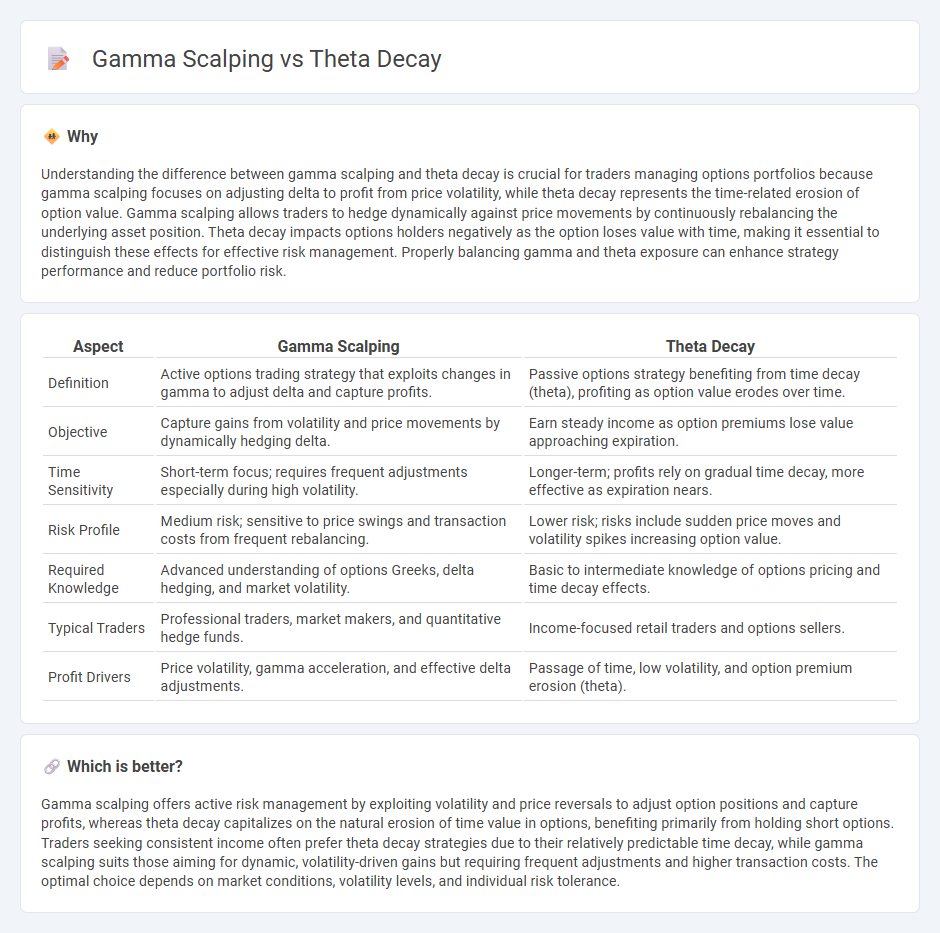
Understanding the difference between gamma scalping and theta decay is crucial for traders managing options portfolios because gamma scalping focuses on adjusting delta to profit from price volatility, while theta decay represents the time-related erosion of option value. Gamma scalping allows traders to hedge dynamically against price movements by continuously rebalancing the underlying asset position. Theta decay impacts options holders negatively as the option loses value with time, making it essential to distinguish these effects for effective risk management. Properly balancing gamma and theta exposure can enhance strategy performance and reduce portfolio risk.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gamma Scalping | Theta Decay |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active options trading strategy that exploits changes in gamma to adjust delta and capture profits. | Passive options strategy benefiting from time decay (theta), profiting as option value erodes over time. |
| Objective | Capture gains from volatility and price movements by dynamically hedging delta. | Earn steady income as option premiums lose value approaching expiration. |
| Time Sensitivity | Short-term focus; requires frequent adjustments especially during high volatility. | Longer-term; profits rely on gradual time decay, more effective as expiration nears. |
| Risk Profile | Medium risk; sensitive to price swings and transaction costs from frequent rebalancing. | Lower risk; risks include sudden price moves and volatility spikes increasing option value. |
| Required Knowledge | Advanced understanding of options Greeks, delta hedging, and market volatility. | Basic to intermediate knowledge of options pricing and time decay effects. |
| Typical Traders | Professional traders, market makers, and quantitative hedge funds. | Income-focused retail traders and options sellers. |
| Profit Drivers | Price volatility, gamma acceleration, and effective delta adjustments. | Passage of time, low volatility, and option premium erosion (theta). |
Which is better?
Gamma scalping offers active risk management by exploiting volatility and price reversals to adjust option positions and capture profits, whereas theta decay capitalizes on the natural erosion of time value in options, benefiting primarily from holding short options. Traders seeking consistent income often prefer theta decay strategies due to their relatively predictable time decay, while gamma scalping suits those aiming for dynamic, volatility-driven gains but requiring frequent adjustments and higher transaction costs. The optimal choice depends on market conditions, volatility levels, and individual risk tolerance.
Connection
Gamma scalping exploits option gamma to hedge delta-neutral portfolios, adjusting positions as the underlying asset price moves. Theta decay reflects the time decay of option premiums, causing option values to decrease as expiration approaches. Successful gamma scalping strategies manage theta decay by capturing profits from volatility while offsetting time decay losses in options trading.
Key Terms
Time Decay (Theta)
Theta decay refers to the gradual loss of an option's value as it approaches expiration, driven by the passage of time, which diminishes the extrinsic value of the option. Gamma scalping involves frequently adjusting a delta-neutral options position to capitalize on price movements, effectively managing gamma risk while offsetting time decay effects. Explore detailed strategies and risk management techniques to optimize option portfolios against theta decay and leverage gamma scalping benefits.
Options Delta
Theta decay measures the rate at which an option's extrinsic value decreases as expiration approaches, directly affecting the option's premium over time. Gamma scalping involves adjusting the underlying asset position to maintain a delta-neutral portfolio, capitalizing on gamma to offset losses from theta decay. Explore these strategies further to optimize your options trading performance.
Position Hedging
Theta decay measures the loss of an option's value as time passes, impacting position value daily. Gamma scalping involves actively managing delta exposure to benefit from price fluctuations, balancing position risk during market movements. Explore detailed strategies to optimize theta decay management and advanced gamma scalping techniques.
Source and External Links
What is the meaning of the term 'theta decay' and why does it happen? - Theta decay, or time decay, is the gradual reduction in an option's value as time passes, primarily affecting the option's extrinsic value because as expiration approaches, the time value and the potential for price movement decrease.
What is Theta in Options Trading & How Does it Work? - Theta (th) measures the one-day rate at which an option loses its time value, harming long option holders but benefiting short option sellers as options approach expiration and lose extrinsic value.
Option Theta Explained: Time Decay for Beginners - Theta quantifies daily option value loss due to time decay, accelerating as expiration nears, with at-the-money options experiencing the highest theta, making it crucial for traders to consider in strategy decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com