Risk reversal strategies involve buying a call option and selling a put option to capitalize on bullish market movements while managing downside risk. Collar strategies combine holding the underlying asset with buying a protective put and selling a call option, effectively limiting both potential losses and gains within a defined range. Explore the nuances of risk reversals and collars to enhance your trading risk management techniques.
Why it is important
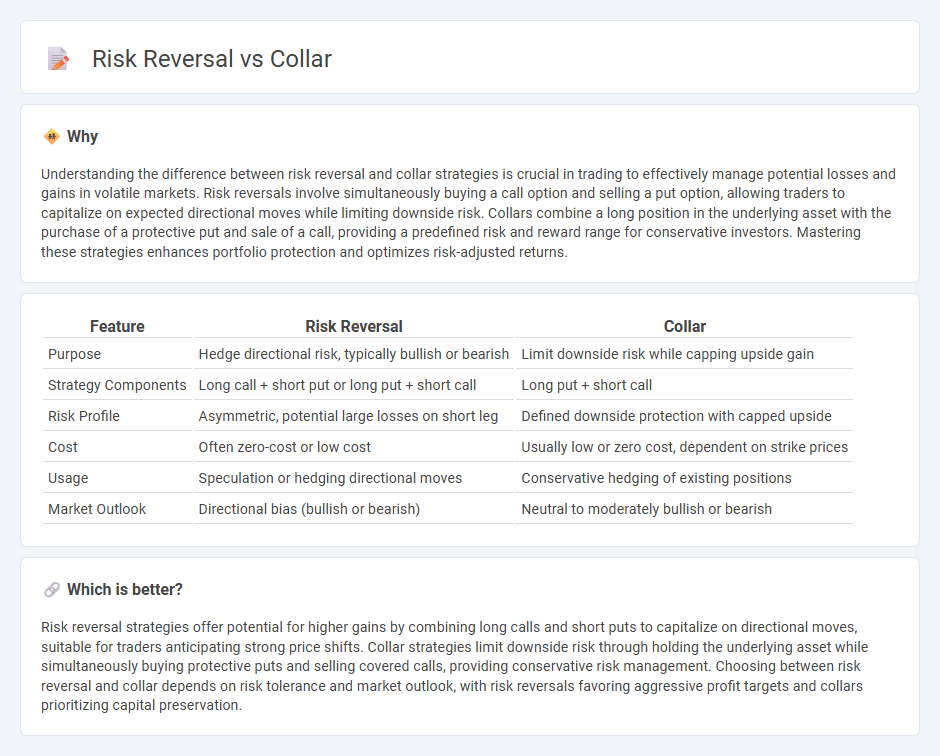
Understanding the difference between risk reversal and collar strategies is crucial in trading to effectively manage potential losses and gains in volatile markets. Risk reversals involve simultaneously buying a call option and selling a put option, allowing traders to capitalize on expected directional moves while limiting downside risk. Collars combine a long position in the underlying asset with the purchase of a protective put and sale of a call, providing a predefined risk and reward range for conservative investors. Mastering these strategies enhances portfolio protection and optimizes risk-adjusted returns.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Risk Reversal | Collar |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Hedge directional risk, typically bullish or bearish | Limit downside risk while capping upside gain |
| Strategy Components | Long call + short put or long put + short call | Long put + short call |
| Risk Profile | Asymmetric, potential large losses on short leg | Defined downside protection with capped upside |
| Cost | Often zero-cost or low cost | Usually low or zero cost, dependent on strike prices |
| Usage | Speculation or hedging directional moves | Conservative hedging of existing positions |
| Market Outlook | Directional bias (bullish or bearish) | Neutral to moderately bullish or bearish |
Which is better?
Risk reversal strategies offer potential for higher gains by combining long calls and short puts to capitalize on directional moves, suitable for traders anticipating strong price shifts. Collar strategies limit downside risk through holding the underlying asset while simultaneously buying protective puts and selling covered calls, providing conservative risk management. Choosing between risk reversal and collar depends on risk tolerance and market outlook, with risk reversals favoring aggressive profit targets and collars prioritizing capital preservation.
Connection
Risk reversal and collar strategies both involve options trading techniques used to hedge or manage risk in volatile markets. A risk reversal combines a long call and a short put to protect against unfavorable price movements, while a collar pairs a long underlying position with a protective put and a covered call, limiting downside risk and capping upside potential. Both strategies optimize risk management by balancing potential losses and gains through strategic option positions.
Key Terms
Options Strategy
A collar options strategy involves holding the underlying asset while simultaneously buying a protective put and selling a covered call to limit downside risk and cap upside potential. Risk reversal, on the other hand, entails buying a call option and selling a put option with different strike prices, aiming to benefit from directional price movements with limited upfront cost. Explore detailed comparisons and use cases of collar and risk reversal strategies to optimize portfolio risk management.
Protective Put (Collar)
A Protective Put, also known as a collar strategy, involves buying a put option while simultaneously holding the underlying asset to guard against downside risk, effectively setting a floor price for potential losses. Unlike risk reversals, which combine a long call and short put to create directional bias with limited risk, collars emphasize capital preservation and risk mitigation. Explore detailed examples and benefits of collars to better understand their role in portfolio protection.
Synthetic Position (Risk Reversal)
A synthetic position created by a risk reversal involves simultaneously buying a call and selling a put option, effectively replicating a long stock position with limited risk. Unlike a collar, which uses both options to cap potential loss and gain, a risk reversal emphasizes directional exposure with asymmetric risk and reward profiles. Explore the strategic use of risk reversals to optimize synthetic positions in volatile markets.
Source and External Links
Collar (clothing) - Wikipedia - A collar in clothing is the part of a shirt, dress, coat, or blouse that frames or fastens around the neck, with various types such as standing, turnover, and flat collars.
Collar - Wikipedia - The term "collar" can refer to human neckwear like clothing collars, clerical collars, and jewelry, as well as animal collars such as dog collars, tracking collars, and shock collars.
Original Designs Dog Collar - Lupine Pet - Lupine Pet offers durable, adjustable dog collars made with strong steel D-rings and custom side quick-release buckles, designed for everyday use and available in multiple sizes and designs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com