Dark pool prints offer traders access to large, anonymous order executions away from public exchanges, minimizing market impact and information leakage. Alternative trading systems (ATS) provide a regulated framework facilitating diverse trading venues, enhancing liquidity and price discovery through varied order types and matching algorithms. Explore how dark pool prints and ATS reshape trading strategies and market dynamics.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark pool prints and alternative trading systems is crucial for traders seeking transparency and price discovery. Dark pool prints represent large, non-public trades executed away from public exchanges, impacting market liquidity and price formation silently. Alternative trading systems (ATS) operate as regulated trading venues offering varied access and execution methods, influencing market efficiency and competition. Recognizing these differences helps traders optimize strategy, manage risk, and navigate market dynamics effectively.
Comparison Table
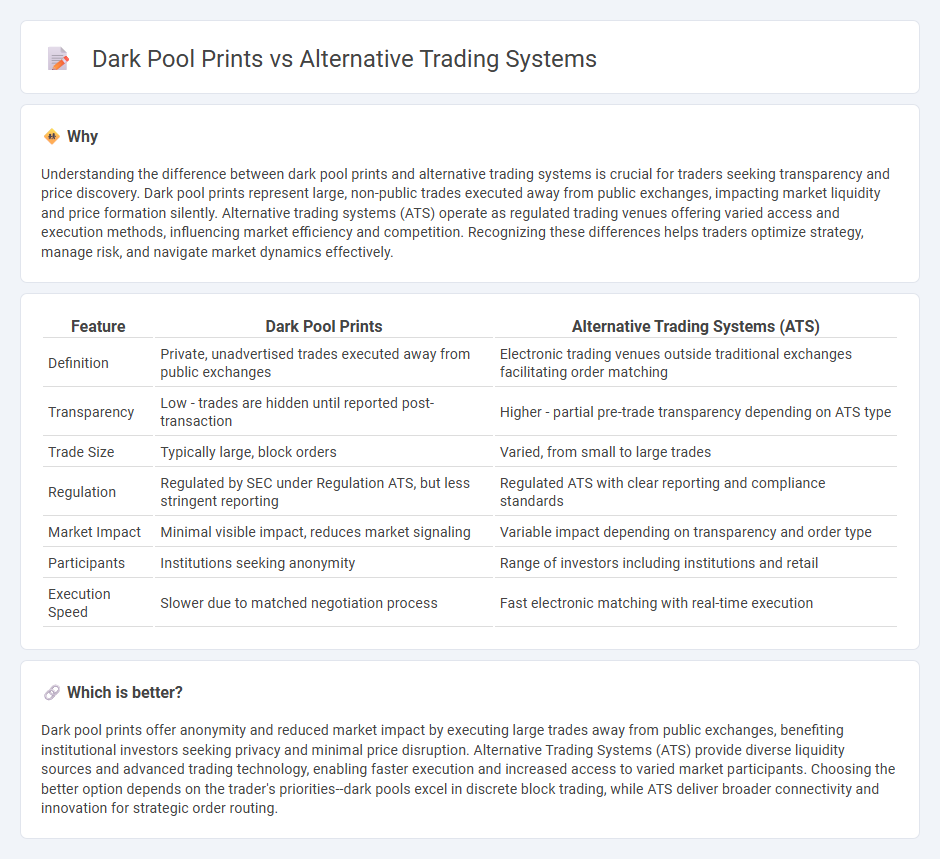
| Feature | Dark Pool Prints | Alternative Trading Systems (ATS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private, unadvertised trades executed away from public exchanges | Electronic trading venues outside traditional exchanges facilitating order matching |
| Transparency | Low - trades are hidden until reported post-transaction | Higher - partial pre-trade transparency depending on ATS type |
| Trade Size | Typically large, block orders | Varied, from small to large trades |
| Regulation | Regulated by SEC under Regulation ATS, but less stringent reporting | Regulated ATS with clear reporting and compliance standards |
| Market Impact | Minimal visible impact, reduces market signaling | Variable impact depending on transparency and order type |
| Participants | Institutions seeking anonymity | Range of investors including institutions and retail |
| Execution Speed | Slower due to matched negotiation process | Fast electronic matching with real-time execution |
Which is better?
Dark pool prints offer anonymity and reduced market impact by executing large trades away from public exchanges, benefiting institutional investors seeking privacy and minimal price disruption. Alternative Trading Systems (ATS) provide diverse liquidity sources and advanced trading technology, enabling faster execution and increased access to varied market participants. Choosing the better option depends on the trader's priorities--dark pools excel in discrete block trading, while ATS deliver broader connectivity and innovation for strategic order routing.
Connection
Dark pool prints represent large block trades executed within private venues, bypassing public exchanges to minimize market impact, a core function of alternative trading systems (ATS). ATS platforms facilitate these off-exchange transactions by providing anonymity and reduced transparency, which attracts institutional investors seeking to trade substantial volumes discreetly. The interplay between dark pool prints and ATS enhances liquidity fragmentation and influences price discovery in modern financial markets.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Alternative trading systems (ATS) provide transparent liquidity pools by displaying order books and facilitating order matching, differing from dark pool prints that conceal trade details until after execution to minimize market impact. ATS enhance price discovery through visible quotes and continuous trading, while dark pools primarily focus on minimizing information leakage for large block trades. Explore how these liquidity sources influence market dynamics and trading strategies for deeper insights.
Transparency
Alternative trading systems (ATS) offer regulated platforms for securities trading, providing greater transparency through pre-trade and post-trade disclosures, contrasting with dark pool prints where transactions occur privately without immediate public reporting. ATS enhance market efficiency by enabling price discovery and reducing information asymmetry, whereas dark pools prioritize anonymity to minimize market impact on large trades. Explore the nuances of transparency in trading venues to better understand their impact on market integrity.
Execution
Alternative Trading Systems (ATS) provide transparent marketplaces for executing trades with improved liquidity and reduced market impact, while dark pool prints offer access to large block trades away from public view to minimize price disruption. ATS platforms are regulated entities subject to reporting requirements, enabling participants to benefit from pre-trade transparency and competitive pricing. Explore how execution strategies vary between ATS and dark pool prints to optimize trading outcomes.
Source and External Links
Alternative Trading System (ATS) Regulation and Requirements - Alternative Trading Systems include types like Dark Pools, Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs), Crossing Networks, Broker-Dealers' Internal Systems, and Call Markets, each offering distinct trading features outside traditional exchanges such as anonymity, speed, and cost advantages.
Alternative Trading System (ATS) - Definition, Examples - An ATS is a trading venue in North America that enables trades outside traditional exchange hours, including private systems like dark pools and crossing networks, often used by institutional investors for large block trades with benefits like reduced market impact and anonymity.
Alternative trading system - Wikipedia - In the US and Canada, an ATS is a regulated non-exchange venue that matches buyers and sellers electronically or otherwise, serving as an alternative to exchanges, and includes systems like ECNs which are fully electronic and anonymous order matchers, important for trading large blocks without disturbing market prices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com