Quantitative momentum investing focuses on identifying stocks exhibiting strong price trends by analyzing historical price data and trading volumes through algorithmic models. Factor investing, on the other hand, targets specific attributes such as value, size, or quality by selecting securities based on fundamental financial metrics and risk factors. Explore further to understand how these strategies impact portfolio performance and risk management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quantitative momentum and factor investing is crucial for traders to optimize portfolio performance by identifying distinct market signals and risk exposures. Quantitative momentum focuses on assets exhibiting upward price trends, leveraging recent performance data to predict future returns. Factor investing targets systematic drivers like value, size, or volatility, aiming to capture long-term risk premia across diversified asset classes. Mastery of both approaches enables traders to tailor strategies that balance growth potential and risk management effectively.
Comparison Table
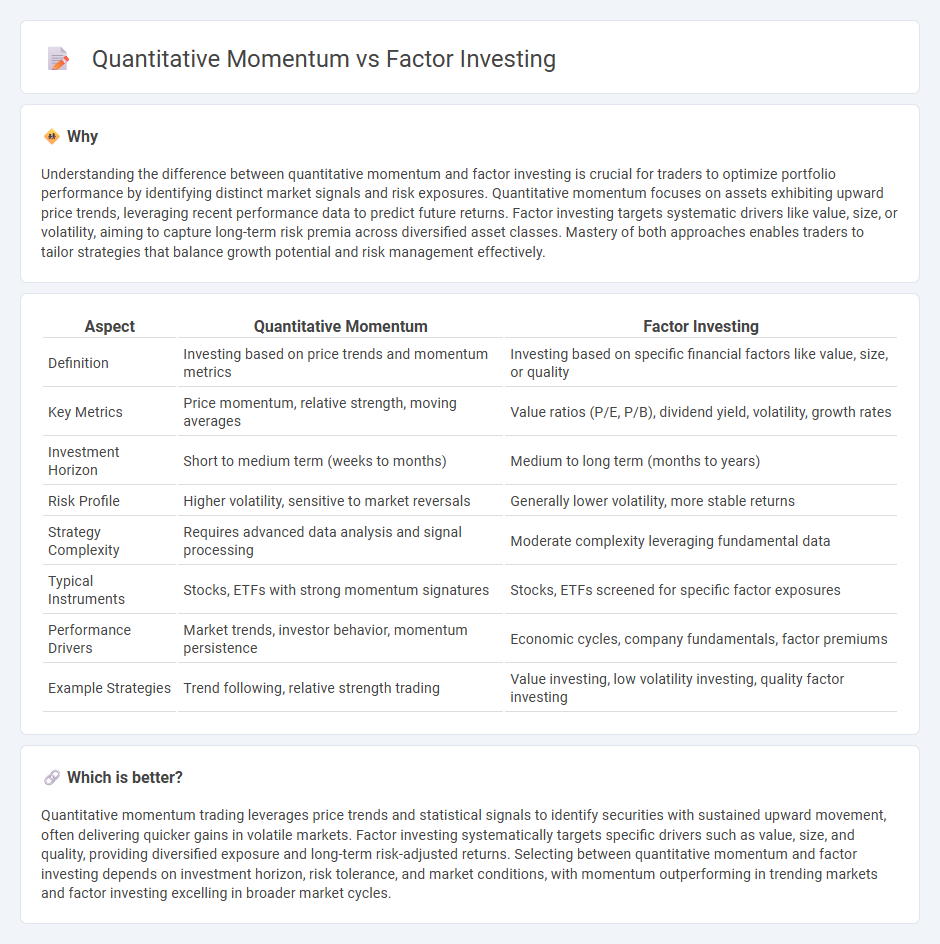
| Aspect | Quantitative Momentum | Factor Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investing based on price trends and momentum metrics | Investing based on specific financial factors like value, size, or quality |
| Key Metrics | Price momentum, relative strength, moving averages | Value ratios (P/E, P/B), dividend yield, volatility, growth rates |
| Investment Horizon | Short to medium term (weeks to months) | Medium to long term (months to years) |
| Risk Profile | Higher volatility, sensitive to market reversals | Generally lower volatility, more stable returns |
| Strategy Complexity | Requires advanced data analysis and signal processing | Moderate complexity leveraging fundamental data |
| Typical Instruments | Stocks, ETFs with strong momentum signatures | Stocks, ETFs screened for specific factor exposures |
| Performance Drivers | Market trends, investor behavior, momentum persistence | Economic cycles, company fundamentals, factor premiums |
| Example Strategies | Trend following, relative strength trading | Value investing, low volatility investing, quality factor investing |
Which is better?
Quantitative momentum trading leverages price trends and statistical signals to identify securities with sustained upward movement, often delivering quicker gains in volatile markets. Factor investing systematically targets specific drivers such as value, size, and quality, providing diversified exposure and long-term risk-adjusted returns. Selecting between quantitative momentum and factor investing depends on investment horizon, risk tolerance, and market conditions, with momentum outperforming in trending markets and factor investing excelling in broader market cycles.
Connection
Quantitative momentum and factor investing are connected through the systematic identification and exploitation of persistent market patterns using data-driven algorithms. Quantitative momentum strategies focus on assets exhibiting strong recent performance, while factor investing targets specific characteristics such as value, size, or quality that explain returns. Both approaches utilize statistical models to enhance portfolio returns by capturing risk premia and behavioral biases.
Key Terms
Alpha
Factor investing targets systematic sources of alpha by exploiting traditional risk factors such as value, size, and quality across diversified portfolios. Quantitative momentum strategies generate alpha by identifying and capitalizing on securities exhibiting persistent upward price trends through algorithmic analysis. Explore the nuances of each approach to enhance your understanding of alpha generation techniques.
Factor Exposure
Factor investing targets specific risk factors such as value, size, and quality to systematically capture long-term returns, while quantitative momentum focuses on identifying securities with strong price trends through data-driven models. Factor exposure in factor investing is explicit and aligned with economic rationales, whereas momentum relies on price action signals that often reflect investor behavior and market sentiment. Discover deeper insights into how these approaches manage factor exposure and optimize portfolio performance.
Momentum Signal
Momentum signal in factor investing captures stock price trends to identify securities with persistent performance, leveraging historical returns for predictive insights. Quantitative momentum strategies specifically harness advanced algorithms to analyze momentum signal strength over various timeframes, optimizing buy and sell decisions. Explore deeper insights into how momentum signals enhance portfolio returns and risk management in factor-based investing.
Source and External Links
What is Factor Investing? - NEPC - Factor investing aims to capture risk premiums associated with specific factors to achieve long-term excess returns and involves building diversified multi-factor portfolios to reduce risk and increase returns over time.
Guide to factor investing in equity markets - Robeco.com - Factor investing targets market segments with proven characteristics like value, momentum, low volatility, and quality, which have historically generated higher risk-adjusted returns than the market over decades.
What are factor based funds? | Vanguard - Factor-based funds actively tilt portfolios toward stock characteristics such as minimum volatility, value, momentum, and quality, aiming for long-term capital appreciation through a rules-based, transparent approach.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com