Microstructure trading focuses on the analysis of market mechanics, order flow, and price formation at the micro-level, leveraging algorithms and high-frequency data for precise execution. Discretionary trading relies on human judgment, intuition, and experience to make decisions based on broader market trends and fundamental analysis. Discover how each approach influences trading performance and risk management strategies.
Why it is important
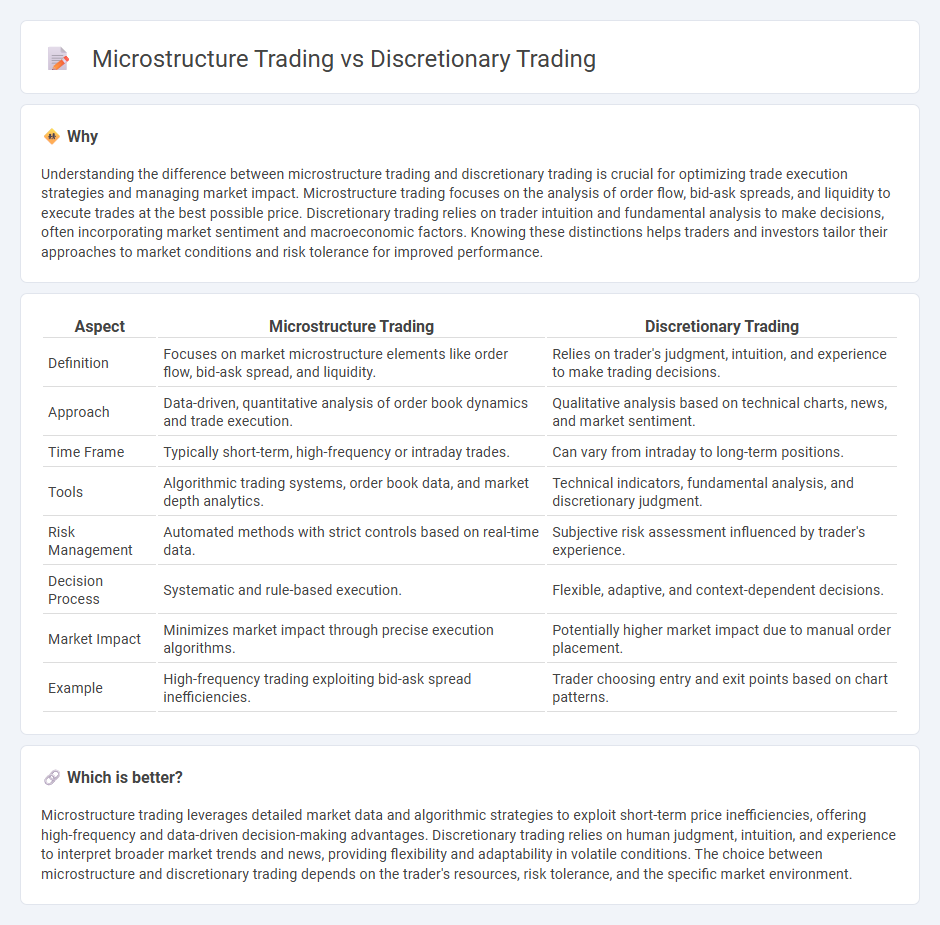
Understanding the difference between microstructure trading and discretionary trading is crucial for optimizing trade execution strategies and managing market impact. Microstructure trading focuses on the analysis of order flow, bid-ask spreads, and liquidity to execute trades at the best possible price. Discretionary trading relies on trader intuition and fundamental analysis to make decisions, often incorporating market sentiment and macroeconomic factors. Knowing these distinctions helps traders and investors tailor their approaches to market conditions and risk tolerance for improved performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microstructure Trading | Discretionary Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on market microstructure elements like order flow, bid-ask spread, and liquidity. | Relies on trader's judgment, intuition, and experience to make trading decisions. |
| Approach | Data-driven, quantitative analysis of order book dynamics and trade execution. | Qualitative analysis based on technical charts, news, and market sentiment. |
| Time Frame | Typically short-term, high-frequency or intraday trades. | Can vary from intraday to long-term positions. |
| Tools | Algorithmic trading systems, order book data, and market depth analytics. | Technical indicators, fundamental analysis, and discretionary judgment. |
| Risk Management | Automated methods with strict controls based on real-time data. | Subjective risk assessment influenced by trader's experience. |
| Decision Process | Systematic and rule-based execution. | Flexible, adaptive, and context-dependent decisions. |
| Market Impact | Minimizes market impact through precise execution algorithms. | Potentially higher market impact due to manual order placement. |
| Example | High-frequency trading exploiting bid-ask spread inefficiencies. | Trader choosing entry and exit points based on chart patterns. |
Which is better?
Microstructure trading leverages detailed market data and algorithmic strategies to exploit short-term price inefficiencies, offering high-frequency and data-driven decision-making advantages. Discretionary trading relies on human judgment, intuition, and experience to interpret broader market trends and news, providing flexibility and adaptability in volatile conditions. The choice between microstructure and discretionary trading depends on the trader's resources, risk tolerance, and the specific market environment.
Connection
Microstructure trading focuses on the detailed mechanics of order execution, bid-ask spreads, and price formation, providing granular market insights that inform discretionary trading decisions. Discretionary traders leverage microstructure analysis to time entries and exits more precisely by reacting to real-time liquidity and order flow dynamics. Combining these approaches enhances trade execution quality and risk management in volatile markets.
Key Terms
Decision-Making (Human Judgment vs. Algorithmic Execution)
Discretionary trading relies heavily on human judgment, leveraging traders' experience and intuition to make decisions in dynamic market conditions. Microstructure trading emphasizes algorithmic execution, using high-frequency data and order book signals to optimize trade timing and minimize market impact. Explore the intricacies of decision-making dynamics to understand how these approaches uniquely influence trading performance.
Market Orders (Execution Style)
Discretionary trading relies on trader judgment and real-time market insights to decide when and how to use market orders, often aiming for swift execution amid fluctuating prices. Microstructure trading analyzes the order book dynamics, bid-ask spreads, and liquidity to optimize market order placement, minimizing market impact and slippage. Explore deeper differences and execution strategies to enhance trading performance.
Order Flow (Market Microstructure Analysis)
Discretionary trading relies on trader intuition and judgment, while microstructure trading emphasizes detailed order flow analysis to understand market dynamics at the granular level. Order flow in market microstructure reveals real-time supply and demand through transaction data, offering insights into price formation and liquidity provision. Explore deeper into market microstructure and order flow strategies to enhance trading precision and decision-making.
Source and External Links
Systematic vs. Discretionary Trading Strategies - Traders Mastermind - Discretionary trading relies on a trader's judgment, experience, and intuition, allowing flexibility and real-time adaptability but is prone to emotional influence and inconsistency.
What Is Discretionary Trading and How Does It Differ ... - uTrade Algos - Discretionary trading is a manual trading approach using human judgment and market analysis, characterized by flexibility and slower execution compared to algorithmic trading, but more prone to emotional bias.
What is discretionary trading? | FBS Glossary - Discretionary trading allows traders to apply and modify rules according to current market conditions using intuition for quick decisions, offering high adaptability but requiring experience to avoid emotional pitfalls.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com