Penny jump and front-running are trading strategies that influence market dynamics differently; penny jump involves placing orders slightly above the current best bid or ask to capture small profits, while front-running entails executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending large trades to gain an unfair advantage. Both practices have significant implications for price discovery and market fairness, attracting regulatory scrutiny. Explore the nuances of penny jump versus front-running to better understand their impact on trading behavior and market integrity.
Why it is important
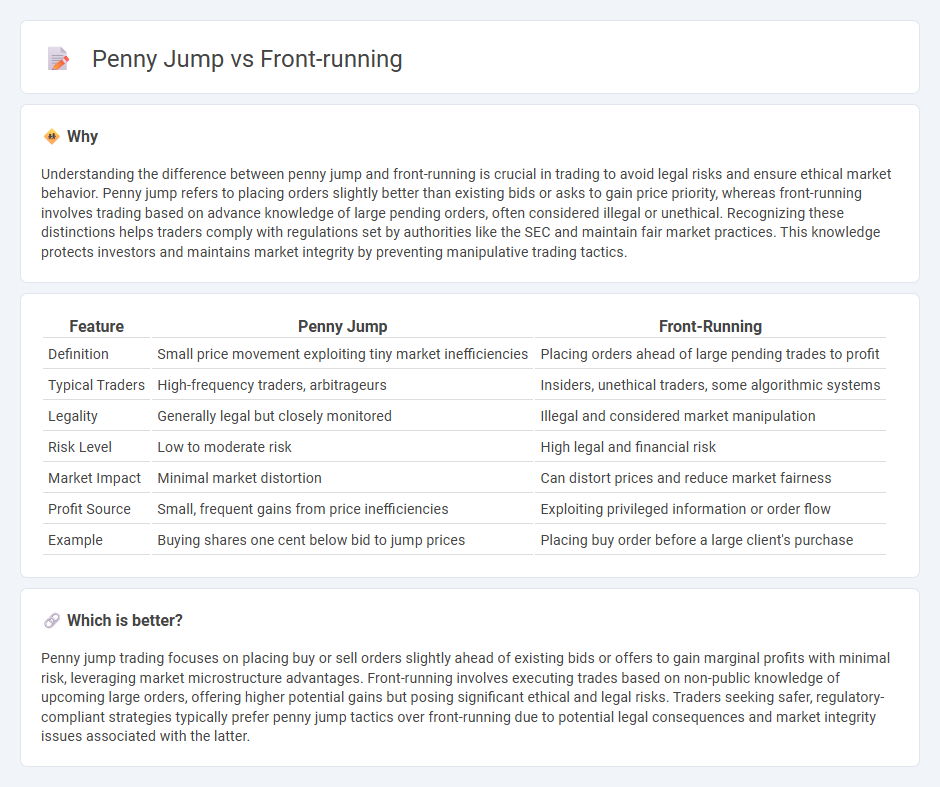
Understanding the difference between penny jump and front-running is crucial in trading to avoid legal risks and ensure ethical market behavior. Penny jump refers to placing orders slightly better than existing bids or asks to gain price priority, whereas front-running involves trading based on advance knowledge of large pending orders, often considered illegal or unethical. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders comply with regulations set by authorities like the SEC and maintain fair market practices. This knowledge protects investors and maintains market integrity by preventing manipulative trading tactics.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Penny Jump | Front-Running |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small price movement exploiting tiny market inefficiencies | Placing orders ahead of large pending trades to profit |
| Typical Traders | High-frequency traders, arbitrageurs | Insiders, unethical traders, some algorithmic systems |
| Legality | Generally legal but closely monitored | Illegal and considered market manipulation |
| Risk Level | Low to moderate risk | High legal and financial risk |
| Market Impact | Minimal market distortion | Can distort prices and reduce market fairness |
| Profit Source | Small, frequent gains from price inefficiencies | Exploiting privileged information or order flow |
| Example | Buying shares one cent below bid to jump prices | Placing buy order before a large client's purchase |
Which is better?
Penny jump trading focuses on placing buy or sell orders slightly ahead of existing bids or offers to gain marginal profits with minimal risk, leveraging market microstructure advantages. Front-running involves executing trades based on non-public knowledge of upcoming large orders, offering higher potential gains but posing significant ethical and legal risks. Traders seeking safer, regulatory-compliant strategies typically prefer penny jump tactics over front-running due to potential legal consequences and market integrity issues associated with the latter.
Connection
Penny jump and front-running are connected concepts in trading where penny jumping involves submitting a buy or sell order at a price slightly better than an existing order to gain execution priority, while front-running exploits the knowledge of a pending large order to trade ahead for profit. Both tactics leverage order book information to gain an advantage, often impacting market fairness and liquidity. Regulatory frameworks aim to detect and prevent these practices to ensure equitable trading environments.
Key Terms
Order Book
Front-running exploits advance knowledge of pending large orders to execute trades ahead, profiting from anticipated price movements in the order book. Penny jump involves placing orders slightly better than existing ones, improving order priority and capturing marginal gains by moving the best bid or ask by the smallest increment. Explore detailed strategies and impacts on market microstructure to understand these tactics deeply.
Execution Speed
Execution speed is critical in both front-running and penny jump strategies, where milliseconds can determine profitability. Front-running exploits knowledge of impending orders by executing trades mere moments before, leveraging ultra-low latency systems. Explore more about how advanced execution technologies impact these trading tactics.
Price Improvement
Price improvement strategies in trading highlight the differences between front-running and penny jump tactics. Front-running involves executing orders ahead of large, pending trades to capitalize on anticipated price moves, often leading to less favorable prices for the market. Penny jumping enhances price improvement by placing orders slightly better than the best bid or offer, encouraging tighter spreads and better execution; explore these strategies further to optimize your trading outcomes.
Source and External Links
Front Running Explained: What Is It, Examples, Is It Legal? -Front-running is when a broker trades a financial asset based on non-public information about a large upcoming trade that will affect the asset's price, allowing them to profit before executing the client's order; this practice is illegal and breaches fiduciary duties.
Front running - Wikipedia - Front running is the practice of trading securities ahead of a large pending transaction using advance, nonpublic knowledge, considered a form of market manipulation and illegal in many markets because it exploits private information at the expense of clients or the public.
Blockchain Front-Running: Risks and Protective Measures - In blockchain, front-running involves submitting a transaction with higher fees to get processed before a known large pending transaction for profit, with variants like back-running and displacement front-running posing risks to network fairness and performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com