Dark pools facilitate large block trades with minimal market impact by allowing anonymous transactions away from public exchanges, preserving confidentiality for institutional investors. Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) provide transparent, automated platforms connecting buyers and sellers, enabling real-time order matching and improved liquidity with greater market visibility. Explore how these trading venues shape modern financial markets and influence execution strategies.
Why it is important
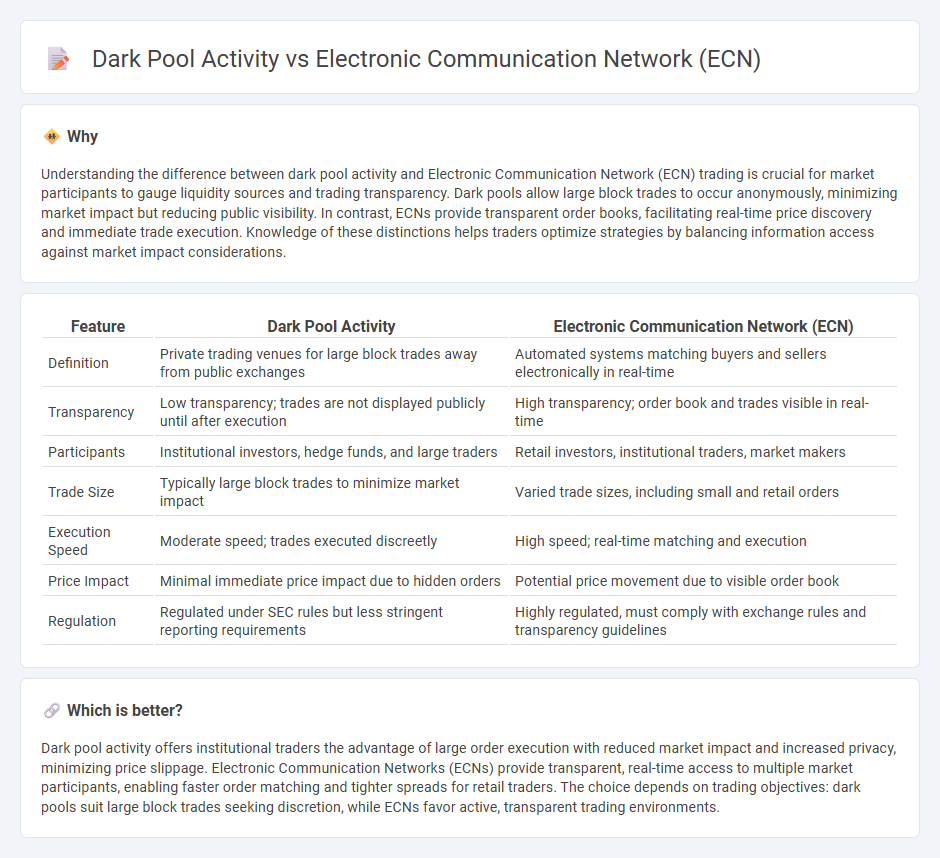
Understanding the difference between dark pool activity and Electronic Communication Network (ECN) trading is crucial for market participants to gauge liquidity sources and trading transparency. Dark pools allow large block trades to occur anonymously, minimizing market impact but reducing public visibility. In contrast, ECNs provide transparent order books, facilitating real-time price discovery and immediate trade execution. Knowledge of these distinctions helps traders optimize strategies by balancing information access against market impact considerations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dark Pool Activity | Electronic Communication Network (ECN) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private trading venues for large block trades away from public exchanges | Automated systems matching buyers and sellers electronically in real-time |
| Transparency | Low transparency; trades are not displayed publicly until after execution | High transparency; order book and trades visible in real-time |
| Participants | Institutional investors, hedge funds, and large traders | Retail investors, institutional traders, market makers |
| Trade Size | Typically large block trades to minimize market impact | Varied trade sizes, including small and retail orders |
| Execution Speed | Moderate speed; trades executed discreetly | High speed; real-time matching and execution |
| Price Impact | Minimal immediate price impact due to hidden orders | Potential price movement due to visible order book |
| Regulation | Regulated under SEC rules but less stringent reporting requirements | Highly regulated, must comply with exchange rules and transparency guidelines |
Which is better?
Dark pool activity offers institutional traders the advantage of large order execution with reduced market impact and increased privacy, minimizing price slippage. Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) provide transparent, real-time access to multiple market participants, enabling faster order matching and tighter spreads for retail traders. The choice depends on trading objectives: dark pools suit large block trades seeking discretion, while ECNs favor active, transparent trading environments.
Connection
Dark pool activity and Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) are connected through their roles in facilitating off-exchange trading, where large blocks of securities can be bought and sold with minimal market impact. Both platforms provide anonymity and liquidity to institutional traders by matching buy and sell orders away from public exchanges, thus helping to reduce price volatility and information leakage. The integration of ECNs with dark pools enhances execution efficiency, enabling faster order routing and improved price discovery in decentralized trading environments.
Key Terms
Order Transparency
Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) provide high order transparency by publicly displaying real-time bid and offer prices, enabling market participants to see available liquidity and trade intentions. Dark pools, conversely, operate with limited order transparency, allowing institutional investors to execute large trades anonymously without revealing order sizes or prices until after execution. Explore the intricate differences in order transparency between ECNs and dark pools to better understand their market impact and trading strategies.
Price Discovery
Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) facilitate transparent price discovery by matching buy and sell orders in real time on public order books, allowing market participants to see available liquidity and pricing. In contrast, dark pools operate as private trading venues where large orders are executed anonymously, minimizing market impact but reducing immediate price transparency and potentially delaying price formation. Explore more to understand how these trading mechanisms influence market efficiency and investor decision-making.
Counterparty Anonymity
Electronic Communication Networks (ECNs) offer transparent trading platforms where counterparty identities are visible, enhancing market efficiency and price discovery. In contrast, dark pools prioritize counterparty anonymity, enabling large institutional trades to execute without revealing participant identities, thus minimizing market impact. Explore deeper insights into how these contrasting approaches influence market dynamics and trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Electronic communication network - Wikipedia - An ECN is a computerized system accessed by electronic trading platforms that widely disseminate and match buy and sell orders of financial products such as stocks and currencies, allowing for lower transaction costs and order matching beyond traditional exchanges.
What is an electronic communication network (ECN)? - Databento - An ECN is an alternative trading system that facilitates direct, automated trading between buyers and sellers, often in OTC markets, distinguished from exchanges by settlement methods and order book structures.
What are ECNs? | ESCNS Trading Explained - Bookmap - ECNs automatically match buy and sell orders electronically, offering lower transaction costs, after-hours trading, and increased competition by giving clients access to order books outside standard exchange hours.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com