Order flow analysis reveals real-time market transactions by tracking buy and sell orders to predict price movements, offering deeper insights into supply and demand dynamics. Scalping focuses on executing numerous quick trades to capture small price changes, prioritizing speed and volume over prolonged market trends. Explore these strategies further to understand their unique benefits and applications in trading.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between order flow analysis and scalping is crucial for traders to choose the most effective strategy aligned with their risk tolerance and trading goals. Order flow analysis provides insights into market sentiment by examining the volume and type of orders, helping traders anticipate price movements. Scalping focuses on making quick, small profits from short-term price fluctuations, relying heavily on speed and precision. Mastering these concepts enhances decision-making accuracy and maximizes profit potential in fast-moving markets.
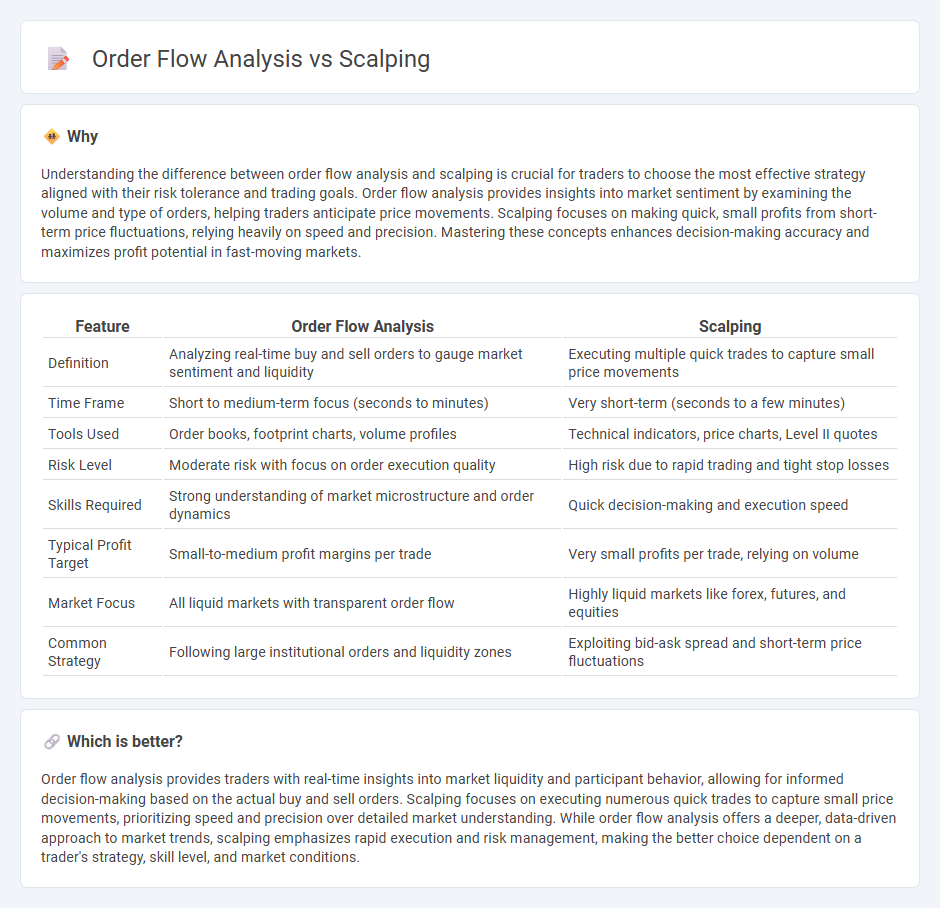
Comparison Table
| Feature | Order Flow Analysis | Scalping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzing real-time buy and sell orders to gauge market sentiment and liquidity | Executing multiple quick trades to capture small price movements |
| Time Frame | Short to medium-term focus (seconds to minutes) | Very short-term (seconds to a few minutes) |
| Tools Used | Order books, footprint charts, volume profiles | Technical indicators, price charts, Level II quotes |
| Risk Level | Moderate risk with focus on order execution quality | High risk due to rapid trading and tight stop losses |
| Skills Required | Strong understanding of market microstructure and order dynamics | Quick decision-making and execution speed |
| Typical Profit Target | Small-to-medium profit margins per trade | Very small profits per trade, relying on volume |
| Market Focus | All liquid markets with transparent order flow | Highly liquid markets like forex, futures, and equities |
| Common Strategy | Following large institutional orders and liquidity zones | Exploiting bid-ask spread and short-term price fluctuations |
Which is better?
Order flow analysis provides traders with real-time insights into market liquidity and participant behavior, allowing for informed decision-making based on the actual buy and sell orders. Scalping focuses on executing numerous quick trades to capture small price movements, prioritizing speed and precision over detailed market understanding. While order flow analysis offers a deeper, data-driven approach to market trends, scalping emphasizes rapid execution and risk management, making the better choice dependent on a trader's strategy, skill level, and market conditions.
Connection
Order flow analysis provides real-time market data that reveals the intentions of large traders, enabling scalpers to identify precise entry and exit points. Scalping relies on this detailed understanding of supply and demand dynamics to execute rapid trades with minimal risk. This connection enhances scalping strategies by improving timing and increasing profitability in highly volatile markets.
Key Terms
Timeframes
Scalping strategies typically operate on ultra-short timeframes, ranging from seconds to a few minutes, enabling traders to exploit rapid price movements for quick profits. Order flow analysis examines the detailed transactions within the order book, providing insights into market sentiment and liquidity at granular time intervals, often on tick or sub-second data. Explore deeper into how different timeframes impact trading decisions and optimize your approach with expert insights on scalping and order flow techniques.
Trade Volume
Scalping strategies rely heavily on rapid trade volume fluctuations to capture small price movements within seconds or minutes, emphasizing immediate market liquidity and momentum. Order flow analysis provides deeper insights into the true supply and demand by examining the quantity and speed of executed trades, revealing hidden buying or selling pressure beyond price action alone. Explore detailed methodologies to optimize your trading decisions based on trade volume nuances.
Liquidity
Scalping techniques prioritize rapid trade execution to exploit short-term price movements, heavily relying on liquidity levels to ensure quick entry and exit with minimal slippage. Order flow analysis provides a deeper understanding of market liquidity by examining bid-ask volumes, trade imbalances, and order book dynamics to anticipate price shifts more accurately. Discover how mastering liquidity through order flow analysis can enhance scalping strategies and improve trading performance.
Source and External Links
Scalping (Day Trading Technique) - Corporate Finance Institute - Scalping is a day trading strategy where investors buy and sell the same stock multiple times within a day to earn small profits on each trade, focusing on highly volatile stocks and quick turnover.
What is a scalping strategy in the stock market and how does it work? - Scalping is a fast-paced trading strategy that relies on technical analysis and indicators like moving averages and RSI to make quick trades aiming for small profits multiple times per day.
Scalping (trading) - Wikipedia - Scalping is a trading method involving rapid buying and selling to capture small price differences or arbitrage opportunities, often executed within seconds or minutes using high capital and leverage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com