Grid trading involves placing buy and sell orders at preset intervals around a target price, aiming to profit from market volatility. Dollar-cost averaging systematically invests a fixed amount at regular intervals, reducing the impact of market fluctuations on the purchase price. Explore detailed strategies to determine which approach suits your trading goals and risk tolerance.
Why it is important
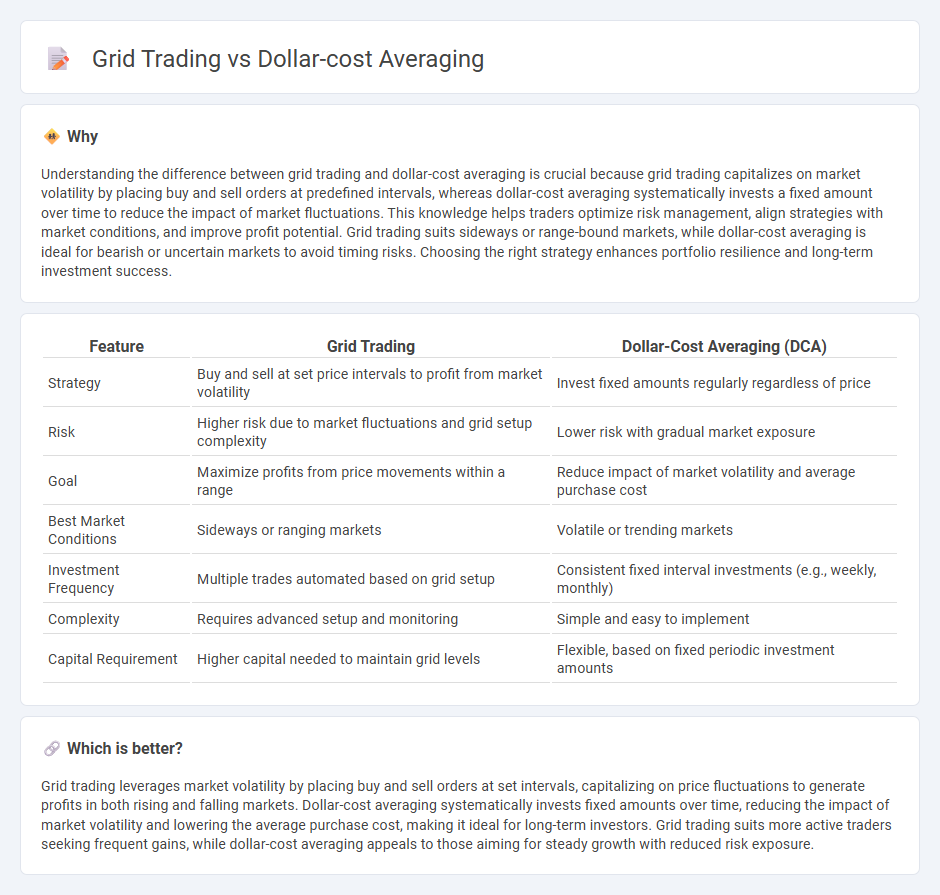
Understanding the difference between grid trading and dollar-cost averaging is crucial because grid trading capitalizes on market volatility by placing buy and sell orders at predefined intervals, whereas dollar-cost averaging systematically invests a fixed amount over time to reduce the impact of market fluctuations. This knowledge helps traders optimize risk management, align strategies with market conditions, and improve profit potential. Grid trading suits sideways or range-bound markets, while dollar-cost averaging is ideal for bearish or uncertain markets to avoid timing risks. Choosing the right strategy enhances portfolio resilience and long-term investment success.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Grid Trading | Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA) |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy | Buy and sell at set price intervals to profit from market volatility | Invest fixed amounts regularly regardless of price |
| Risk | Higher risk due to market fluctuations and grid setup complexity | Lower risk with gradual market exposure |
| Goal | Maximize profits from price movements within a range | Reduce impact of market volatility and average purchase cost |
| Best Market Conditions | Sideways or ranging markets | Volatile or trending markets |
| Investment Frequency | Multiple trades automated based on grid setup | Consistent fixed interval investments (e.g., weekly, monthly) |
| Complexity | Requires advanced setup and monitoring | Simple and easy to implement |
| Capital Requirement | Higher capital needed to maintain grid levels | Flexible, based on fixed periodic investment amounts |
Which is better?
Grid trading leverages market volatility by placing buy and sell orders at set intervals, capitalizing on price fluctuations to generate profits in both rising and falling markets. Dollar-cost averaging systematically invests fixed amounts over time, reducing the impact of market volatility and lowering the average purchase cost, making it ideal for long-term investors. Grid trading suits more active traders seeking frequent gains, while dollar-cost averaging appeals to those aiming for steady growth with reduced risk exposure.
Connection
Grid trading and dollar-cost averaging both utilize strategic buy and sell orders to capitalize on market fluctuations, aiming to optimize entry and exit points over time. Grid trading involves setting predefined price levels to execute multiple trades, while dollar-cost averaging systematically invests fixed amounts at regular intervals regardless of price. Together, these methods reduce the impact of market volatility and help traders build positions methodically while managing risk.
Key Terms
Entry strategy
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) involves investing a fixed amount at regular intervals regardless of price, reducing the impact of market volatility and avoiding the risk of market timing. Grid trading sets buy and sell orders at predefined intervals above and below a set price, capitalizing on market fluctuations through systematic entries and exits. Explore deeper insights and optimal entry tactics to enhance your trading strategy.
Position sizing
Position sizing in dollar-cost averaging (DCA) involves investing a fixed amount of capital at regular intervals, reducing the impact of market volatility through consistent, smaller purchases. In grid trading, position sizing adapts dynamically by placing buy and sell orders at predefined price levels, capitalizing on market fluctuations within a specific range. Explore detailed strategies and optimal position sizing techniques to enhance your trading performance.
Market volatility
Dollar-cost averaging mitigates market volatility by spreading investment over fixed intervals, reducing the impact of price fluctuations. Grid trading exploits volatility by placing buy and sell orders at predetermined price levels, capturing gains within market swings. Explore detailed strategies to optimize your trading approach under varying market conditions.
Source and External Links
What Is Dollar-Cost Averaging? - Dollar-cost averaging is the practice of investing a fixed dollar amount on a regular basis, regardless of the share price, which can reduce the average cost per share over time by buying more shares when prices are low and fewer when prices are high.
Dollar cost averaging - An investment strategy coined by Benjamin Graham where the investor invests the same dollar amount at regular intervals, buying more shares when prices are low, which decreases the average cost per share and avoids the need for market timing.
What is Dollar-Cost Averaging? - Dollar-cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount periodically to reduce the risk of investing a lump sum at a market high, encouraging disciplined investing and lowering the impact of market volatility on overall purchase cost.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com