Microstructure trading focuses on the granular dynamics of trading processes, analyzing order flows, bid-ask spreads, and price formation within markets to optimize execution strategies. Quantitative trading employs mathematical models and algorithms to identify trading opportunities based on statistical patterns and historical data. Explore the distinct methodologies and advantages of microstructure and quantitative trading to enhance your trading expertise.
Why it is important
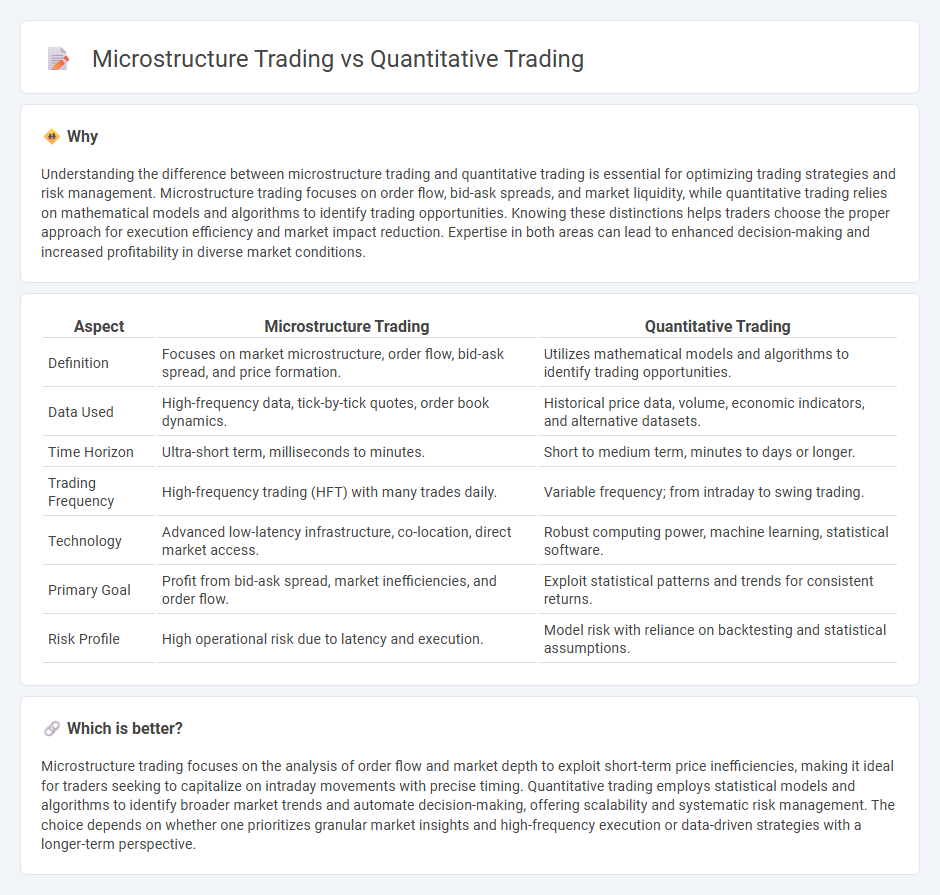
Understanding the difference between microstructure trading and quantitative trading is essential for optimizing trading strategies and risk management. Microstructure trading focuses on order flow, bid-ask spreads, and market liquidity, while quantitative trading relies on mathematical models and algorithms to identify trading opportunities. Knowing these distinctions helps traders choose the proper approach for execution efficiency and market impact reduction. Expertise in both areas can lead to enhanced decision-making and increased profitability in diverse market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microstructure Trading | Quantitative Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on market microstructure, order flow, bid-ask spread, and price formation. | Utilizes mathematical models and algorithms to identify trading opportunities. |
| Data Used | High-frequency data, tick-by-tick quotes, order book dynamics. | Historical price data, volume, economic indicators, and alternative datasets. |
| Time Horizon | Ultra-short term, milliseconds to minutes. | Short to medium term, minutes to days or longer. |
| Trading Frequency | High-frequency trading (HFT) with many trades daily. | Variable frequency; from intraday to swing trading. |
| Technology | Advanced low-latency infrastructure, co-location, direct market access. | Robust computing power, machine learning, statistical software. |
| Primary Goal | Profit from bid-ask spread, market inefficiencies, and order flow. | Exploit statistical patterns and trends for consistent returns. |
| Risk Profile | High operational risk due to latency and execution. | Model risk with reliance on backtesting and statistical assumptions. |
Which is better?
Microstructure trading focuses on the analysis of order flow and market depth to exploit short-term price inefficiencies, making it ideal for traders seeking to capitalize on intraday movements with precise timing. Quantitative trading employs statistical models and algorithms to identify broader market trends and automate decision-making, offering scalability and systematic risk management. The choice depends on whether one prioritizes granular market insights and high-frequency execution or data-driven strategies with a longer-term perspective.
Connection
Microstructure trading focuses on the detailed analysis of order flow, bid-ask spreads, and market depth to exploit short-term price inefficiencies. Quantitative trading employs algorithmic models that often integrate microstructure data to optimize trade execution and minimize market impact. Together, they enhance trading strategies by combining granular market insights with advanced statistical techniques.
Key Terms
Algorithmic Models
Quantitative trading employs algorithmic models to analyze large datasets and execute trades based on statistical patterns, aiming to maximize returns through automation and speed. Microstructure trading, however, focuses on the intricacies of market mechanics, such as order book dynamics and bid-ask spreads, to optimize trading strategies within the context of market microstructure theory. Explore deeper insights into how algorithmic models transform both quantitative and microstructure trading strategies for enhanced market efficiency.
Order Flow
Quantitative trading utilizes statistical models and algorithms to exploit market inefficiencies and optimize trade execution, relying heavily on historical price and volume data. Microstructure trading emphasizes order flow analysis, interpreting the real-time stream of buy and sell orders to understand market dynamics and liquidity. Explore in-depth strategies and tools that differentiate quantitative methods from microstructure trading techniques.
Market Liquidity
Quantitative trading leverages statistical models and algorithms to optimize market execution and liquidity access, while microstructure trading emphasizes the detailed dynamics of order flow and price formation at the bid-ask spread level. Market liquidity in quantitative trading is enhanced through high-frequency order book analysis and predictive order placement strategies, whereas microstructure trading analyzes the impact of trades on liquidity provision and price stability. Explore the intricate relationship between these approaches to better understand their impact on market liquidity.
Source and External Links
How To Become a Quantitative Trader in 4 Steps (With Skills) - Indeed - Quantitative traders, or quants, use mathematical models and large data analysis to identify and capitalize on profitable trading opportunities, with careers requiring creativity and strong quantitative skills and offering an average salary around $174,497 per year.
Quantitative analysis (finance) - Wikipedia - Quantitative analysis in finance involves applying mathematical and statistical methods to identify patterns, price derivatives, manage risks, and execute algorithmic trading, often done by quants at firms like Renaissance Technologies and D.E. Shaw.
Quantitative Trader - Jane Street - Jane Street is a quantitative trading firm focusing on technology-driven trading strategies where traders develop proprietary models, manage risk, and engage in millions of trades daily, with an emphasis on collaborative problem solving and programming skills.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com