A liquidity sweep is an advanced trading technique targeting multiple price levels to execute large orders without significantly impacting market prices. Market orders prioritize immediate execution at the best available price, often causing price slippage during high volatility. Explore the differences between liquidity sweeps and market orders to optimize your trading strategy effectively.
Why it is important
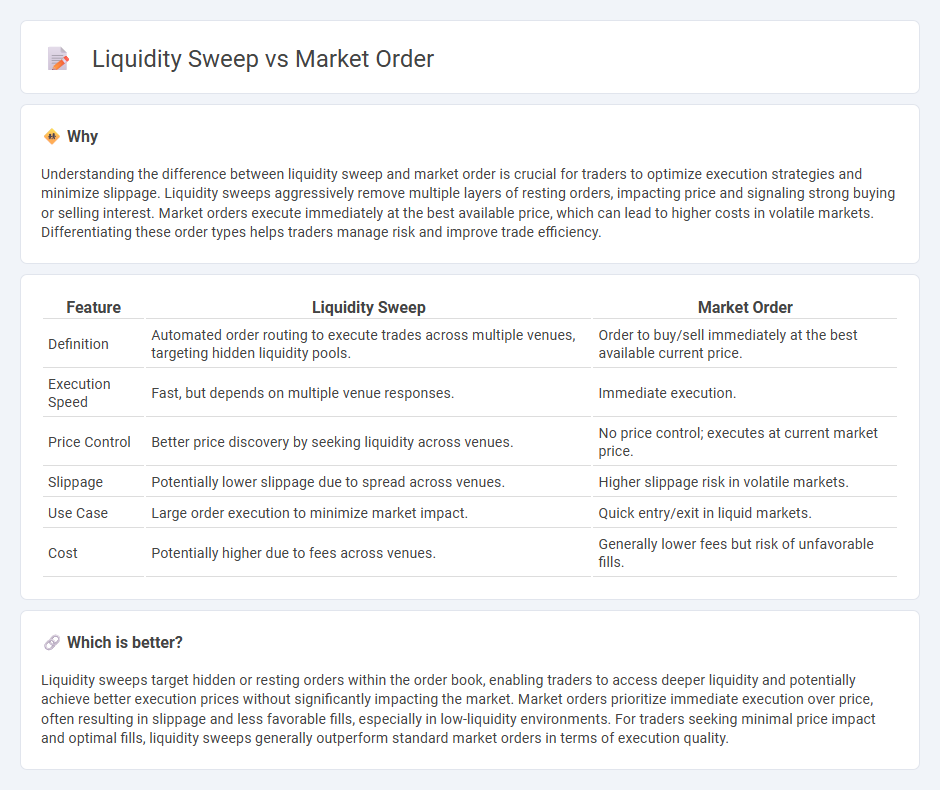
Understanding the difference between liquidity sweep and market order is crucial for traders to optimize execution strategies and minimize slippage. Liquidity sweeps aggressively remove multiple layers of resting orders, impacting price and signaling strong buying or selling interest. Market orders execute immediately at the best available price, which can lead to higher costs in volatile markets. Differentiating these order types helps traders manage risk and improve trade efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Liquidity Sweep | Market Order |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated order routing to execute trades across multiple venues, targeting hidden liquidity pools. | Order to buy/sell immediately at the best available current price. |
| Execution Speed | Fast, but depends on multiple venue responses. | Immediate execution. |
| Price Control | Better price discovery by seeking liquidity across venues. | No price control; executes at current market price. |
| Slippage | Potentially lower slippage due to spread across venues. | Higher slippage risk in volatile markets. |
| Use Case | Large order execution to minimize market impact. | Quick entry/exit in liquid markets. |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to fees across venues. | Generally lower fees but risk of unfavorable fills. |
Which is better?
Liquidity sweeps target hidden or resting orders within the order book, enabling traders to access deeper liquidity and potentially achieve better execution prices without significantly impacting the market. Market orders prioritize immediate execution over price, often resulting in slippage and less favorable fills, especially in low-liquidity environments. For traders seeking minimal price impact and optimal fills, liquidity sweeps generally outperform standard market orders in terms of execution quality.
Connection
Liquidity sweeps occur when a large market order rapidly consumes available liquidity across multiple price levels, causing significant price movements. Market orders are designed to execute immediately at the best available prices, which triggers liquidity sweeps by hitting resting limit orders on the order book. This connection highlights how aggressive market orders impact order book dynamics, leading to temporary liquidity depletion and potential price volatility.
Key Terms
Immediate Execution
A market order guarantees immediate execution by matching the best available prices on the order book, ensuring swift trade fulfillment regardless of price fluctuations. A liquidity sweep targets multiple layers of liquidity to quickly consume available volume across price levels, optimizing for rapid execution in volatile or illiquid markets. Explore the differences in execution strategies to enhance your trading efficiency and decision-making.
Order Book Depth
Market orders execute immediately against the best available prices in the order book, often consuming multiple levels of liquidity to fill the entire order. Liquidity sweeps aggressively target deeper layers of the order book, clearing out large quantities across multiple price points to capture or remove hidden liquidity. Explore the detailed mechanics and impact of these order types on market depth for better trading strategies.
Slippage
Market orders execute trades immediately at the best available price but are prone to slippage, especially in volatile or low-liquidity markets where the order can fill at a worse price than expected. Liquidity sweeps target multiple price levels to capture available liquidity, potentially reducing slippage by breaking up large orders into smaller parts and accessing deeper market depth. Explore how these strategies impact execution quality and slippage management in trading platforms.
Source and External Links
Market order - Robinhood - A market order is a request to buy or sell a stock immediately at the next available price, prioritizing fast execution over price certainty, with no guarantee of execution at a specific price.
Mastering the Order Types: Market Orders - Charles Schwab - A market order is an order to buy or sell a security at the best available current price, offering quick execution but not guaranteeing a specific price.
Market Order - Overview, How It is Placed - Corporate Finance Institute - Market orders are requests to buy or sell securities at the best available current price, executed quickly and reliably, especially in highly traded stocks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com