Pair trading involves simultaneously buying and selling two correlated assets to exploit price inefficiencies, while day trading focuses on rapid buying and selling of individual assets within a single trading day to capitalize on short-term price movements. Pair trading minimizes market risk through hedging, whereas day trading demands quick decision-making and rigorous market analysis. Explore more to understand which strategy aligns best with your trading goals and risk tolerance.
Why it is important
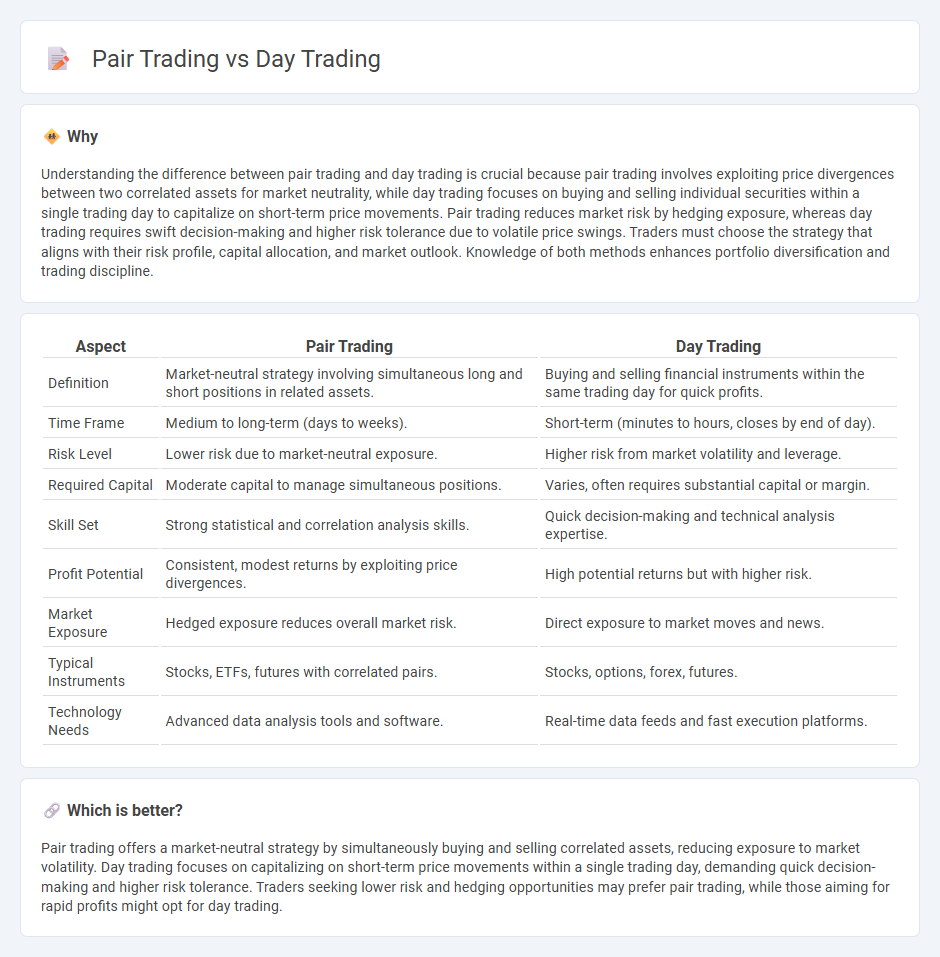
Understanding the difference between pair trading and day trading is crucial because pair trading involves exploiting price divergences between two correlated assets for market neutrality, while day trading focuses on buying and selling individual securities within a single trading day to capitalize on short-term price movements. Pair trading reduces market risk by hedging exposure, whereas day trading requires swift decision-making and higher risk tolerance due to volatile price swings. Traders must choose the strategy that aligns with their risk profile, capital allocation, and market outlook. Knowledge of both methods enhances portfolio diversification and trading discipline.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Pair Trading | Day Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market-neutral strategy involving simultaneous long and short positions in related assets. | Buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day for quick profits. |
| Time Frame | Medium to long-term (days to weeks). | Short-term (minutes to hours, closes by end of day). |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to market-neutral exposure. | Higher risk from market volatility and leverage. |
| Required Capital | Moderate capital to manage simultaneous positions. | Varies, often requires substantial capital or margin. |
| Skill Set | Strong statistical and correlation analysis skills. | Quick decision-making and technical analysis expertise. |
| Profit Potential | Consistent, modest returns by exploiting price divergences. | High potential returns but with higher risk. |
| Market Exposure | Hedged exposure reduces overall market risk. | Direct exposure to market moves and news. |
| Typical Instruments | Stocks, ETFs, futures with correlated pairs. | Stocks, options, forex, futures. |
| Technology Needs | Advanced data analysis tools and software. | Real-time data feeds and fast execution platforms. |
Which is better?
Pair trading offers a market-neutral strategy by simultaneously buying and selling correlated assets, reducing exposure to market volatility. Day trading focuses on capitalizing on short-term price movements within a single trading day, demanding quick decision-making and higher risk tolerance. Traders seeking lower risk and hedging opportunities may prefer pair trading, while those aiming for rapid profits might opt for day trading.
Connection
Pair trading and day trading intersect through their reliance on short-term market movements and price discrepancies between assets. Pair trading involves simultaneously buying and selling two correlated securities to capitalize on relative price changes, while day trading focuses on executing multiple trades within a single trading session to exploit intraday volatility. Both strategies require advanced technical analysis, real-time data, and strict risk management to maximize profits and minimize losses.
Key Terms
**Day Trading:**
Day trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day, aiming to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations. Traders use technical analysis, real-time data, and rapid execution to exploit market volatility while minimizing overnight risk exposure. Explore more about effective strategies and tools to enhance your day trading success.
Intraday
Day trading focuses on buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations, leveraging high liquidity and volatility. Pair trading, an intraday market-neutral strategy, involves simultaneously buying one asset and shorting another correlated asset to exploit relative price movements while minimizing market risk. Discover the key tactics and tools to master intraday trading strategies by exploring our comprehensive guides.
Volatility
Day trading capitalizes on rapid price fluctuations within a single trading day, relying heavily on high volatility to generate quick profits from short-term market movements. Pair trading involves simultaneously buying one asset and selling another correlated asset, aiming to exploit relative price volatility while minimizing market risk through hedging. Explore more about how volatility impacts these strategies and which suits your trading style best.
Source and External Links
Day trading - Day trading is the practice of buying and selling a financial instrument within the same trading day to capitalize on short-term price movements, with all positions closed before market close to avoid overnight risk; pattern day traders who execute four or more day trades in five business days must maintain a minimum equity of $25,000 in their account.
Day Trading Guide - Day trading is a short-term investment strategy involving multiple trades in stocks, futures, forex, or cryptocurrencies within the same day using technical analysis and specific trading strategies like momentum or contrarian trading for profit.
What are the rules for day trading? - Day trading involves opening and closing a position within a single day and traders classified as pattern day traders must follow special margin requirements, including maintaining at least $25,000 minimum equity in their account per FINRA regulations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com