Market microstructure examines the processes and outcomes of exchanging assets, focusing on price formation, order types, and information flow within trading venues. Algorithmic trading utilizes automated systems to execute orders at high speed, optimizing execution strategies based on market microstructure insights and real-time data. Discover how understanding market microstructure enhances algorithmic trading efficiency and reduces transaction costs.
Why it is important
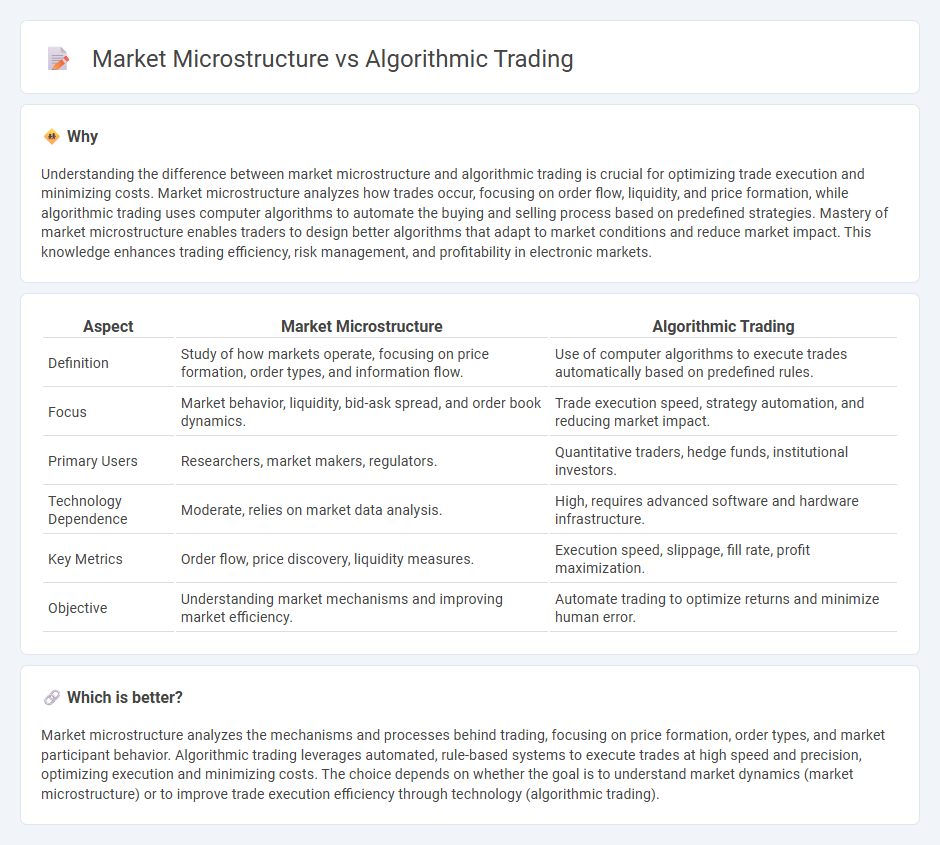
Understanding the difference between market microstructure and algorithmic trading is crucial for optimizing trade execution and minimizing costs. Market microstructure analyzes how trades occur, focusing on order flow, liquidity, and price formation, while algorithmic trading uses computer algorithms to automate the buying and selling process based on predefined strategies. Mastery of market microstructure enables traders to design better algorithms that adapt to market conditions and reduce market impact. This knowledge enhances trading efficiency, risk management, and profitability in electronic markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Market Microstructure | Algorithmic Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of how markets operate, focusing on price formation, order types, and information flow. | Use of computer algorithms to execute trades automatically based on predefined rules. |
| Focus | Market behavior, liquidity, bid-ask spread, and order book dynamics. | Trade execution speed, strategy automation, and reducing market impact. |
| Primary Users | Researchers, market makers, regulators. | Quantitative traders, hedge funds, institutional investors. |
| Technology Dependence | Moderate, relies on market data analysis. | High, requires advanced software and hardware infrastructure. |
| Key Metrics | Order flow, price discovery, liquidity measures. | Execution speed, slippage, fill rate, profit maximization. |
| Objective | Understanding market mechanisms and improving market efficiency. | Automate trading to optimize returns and minimize human error. |
Which is better?
Market microstructure analyzes the mechanisms and processes behind trading, focusing on price formation, order types, and market participant behavior. Algorithmic trading leverages automated, rule-based systems to execute trades at high speed and precision, optimizing execution and minimizing costs. The choice depends on whether the goal is to understand market dynamics (market microstructure) or to improve trade execution efficiency through technology (algorithmic trading).
Connection
Market microstructure studies the processes and rules that govern trading mechanisms and price formation, which directly influence the design and execution of algorithmic trading strategies. Algorithmic trading leverages microstructure insights such as order book dynamics, bid-ask spreads, and transaction costs to optimize trade execution and minimize market impact. Advanced algorithms analyze high-frequency data and microstructure patterns to make real-time decisions, enhancing liquidity provision and market efficiency.
Key Terms
Algorithmic Trading:
Algorithmic trading leverages complex mathematical models and high-speed data processing to execute trades at optimal prices and volumes, significantly reducing human intervention and errors. This trading strategy relies heavily on real-time market data, order book dynamics, and latency-sensitive algorithms to capitalize on short-term market inefficiencies. Explore how advanced algorithmic systems transform trading efficiency and market liquidity by delving deeper into this innovative field.
Execution Algorithms
Execution algorithms leverage market microstructure insights to optimize trade execution by minimizing market impact and transaction costs. They analyze order book dynamics, liquidity, and price trends to make real-time decisions for order slicing, timing, and routing. Discover how execution algorithms transform trading strategies by integrating advanced market microstructure models.
Backtesting
Algorithmic trading relies heavily on backtesting to evaluate strategies against historical market data, ensuring robustness before live deployment. Market microstructure provides insights into order book dynamics and execution costs, crucial for refining backtesting accuracy and minimizing slippage. Explore in-depth how integrating market microstructure enhances algorithmic backtesting precision and trading performance.
Source and External Links
What is Algorithmic Trading and How Do You Get Started? - IG - Algorithmic trading uses computer code to execute trades based on set rules like price movements, employing strategies such as price action, technical analysis, or a combination, useful for high-frequency trading and risk management.
Algorithmic Trading - Definition, Example, Pros, Cons - It involves automated trading decisions programmed with preset rules, such as a moving average strategy, often executing large trades incrementally to avoid market price distortion.
Algorithmic trading - Wikipedia - Algorithmic trading automates order execution with pre-programmed instructions and has evolved with machine learning techniques like deep reinforcement learning and directional change algorithms that adapt dynamically to market conditions for improved trade timing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com