Quantitative signals leverage algorithmic models and historical data patterns to identify profitable trading opportunities with precision. Correlation arbitrage exploits pricing inefficiencies between correlated assets to generate consistent returns while minimizing market risk. Explore deeper insights into how these strategies optimize portfolio performance in dynamic markets.
Why it is important
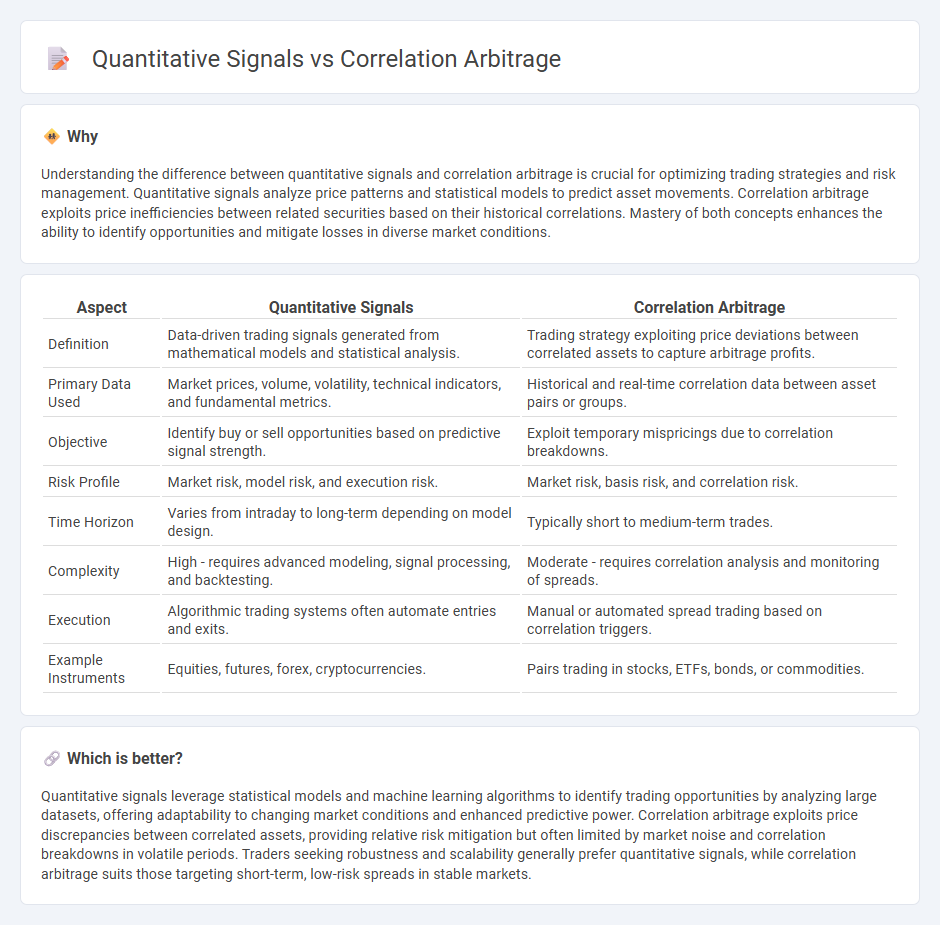
Understanding the difference between quantitative signals and correlation arbitrage is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and risk management. Quantitative signals analyze price patterns and statistical models to predict asset movements. Correlation arbitrage exploits price inefficiencies between related securities based on their historical correlations. Mastery of both concepts enhances the ability to identify opportunities and mitigate losses in diverse market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Signals | Correlation Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data-driven trading signals generated from mathematical models and statistical analysis. | Trading strategy exploiting price deviations between correlated assets to capture arbitrage profits. |
| Primary Data Used | Market prices, volume, volatility, technical indicators, and fundamental metrics. | Historical and real-time correlation data between asset pairs or groups. |
| Objective | Identify buy or sell opportunities based on predictive signal strength. | Exploit temporary mispricings due to correlation breakdowns. |
| Risk Profile | Market risk, model risk, and execution risk. | Market risk, basis risk, and correlation risk. |
| Time Horizon | Varies from intraday to long-term depending on model design. | Typically short to medium-term trades. |
| Complexity | High - requires advanced modeling, signal processing, and backtesting. | Moderate - requires correlation analysis and monitoring of spreads. |
| Execution | Algorithmic trading systems often automate entries and exits. | Manual or automated spread trading based on correlation triggers. |
| Example Instruments | Equities, futures, forex, cryptocurrencies. | Pairs trading in stocks, ETFs, bonds, or commodities. |
Which is better?
Quantitative signals leverage statistical models and machine learning algorithms to identify trading opportunities by analyzing large datasets, offering adaptability to changing market conditions and enhanced predictive power. Correlation arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between correlated assets, providing relative risk mitigation but often limited by market noise and correlation breakdowns in volatile periods. Traders seeking robustness and scalability generally prefer quantitative signals, while correlation arbitrage suits those targeting short-term, low-risk spreads in stable markets.
Connection
Quantitative signals play a crucial role in correlation arbitrage by identifying statistical relationships between related assets to exploit pricing inefficiencies. These signals, derived from mathematical models and algorithms, help traders execute strategies that capitalize on deviations in asset correlations. Harnessing robust quantitative signals enhances the precision and profitability of correlation arbitrage in dynamic financial markets.
Key Terms
**Correlation Arbitrage:**
Correlation arbitrage exploits statistical relationships between asset prices to generate profits by identifying mispricings in correlated securities, often using pairs trading or basket strategies. It relies on advanced models to detect deviations from historical correlation patterns, enabling traders to capitalize on mean-reversion dynamics. Explore how correlation arbitrage strategies can enhance portfolio diversification and risk-adjusted returns further.
Cointegration
Correlation arbitrage exploits price relationships between assets to identify mispricings, relying on statistical correlations that may be unstable over time. Quantitative signals using cointegration focus on identifying pairs or groups of assets whose prices share a long-term equilibrium relationship, providing more robust and persistent predictive power in arbitrage strategies. Explore more about how cointegration enhances quantitative models and improves arbitrage outcomes in financial markets.
Statistical Arbitrage
Correlation arbitrage exploits price relationships between related securities to profit from temporary divergences, relying heavily on statistical models to identify mispricings. Quantitative signals in statistical arbitrage incorporate various data inputs--price momentum, mean reversion, and volatility measures--to construct predictive models that guide trade execution. Explore the nuances of statistical arbitrage strategies to enhance your understanding of market inefficiencies and systematic trading approaches.
Source and External Links
Correlation Matrix Clustering for Statistical Arbitrage Portfolios - SSRN - Correlation arbitrage uses clustering methods on the correlation matrix of stock returns to build mean-reverting portfolios, generating statistically significant returns by exploiting residual market correlations within clusters of stocks.
Statistical Arbitrage - CFA, FRM, and Actuarial Exams Study Notes - Correlation arbitrage often involves pairs trading where two historically correlated stocks are traded when their price relationship deviates, under the assumption that prices will revert to their long-term average.
Statistical arbitrage - Wikipedia - Statistical arbitrage, including correlation arbitrage, relies on mean reversion across portfolios of many stocks matched by sector and region, using statistical tools to minimize risk and exploit short-term pricing inefficiencies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com