Liquidity sweeps aggressively target available liquidity across multiple price levels to execute large orders swiftly, minimizing market impact and slippage. Limit orders, conversely, specify a maximum or minimum price for execution, offering control over trade entry or exit but potentially facing partial fills or delays. Explore the strategic differences between liquidity sweeps and limit orders to optimize trading performance.
Why it is important
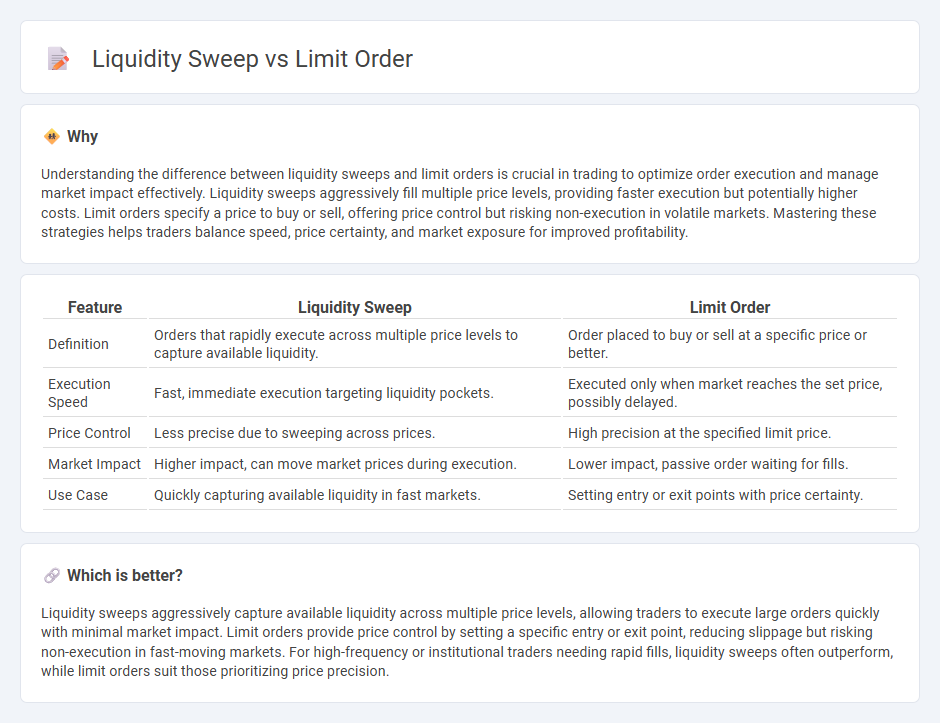
Understanding the difference between liquidity sweeps and limit orders is crucial in trading to optimize order execution and manage market impact effectively. Liquidity sweeps aggressively fill multiple price levels, providing faster execution but potentially higher costs. Limit orders specify a price to buy or sell, offering price control but risking non-execution in volatile markets. Mastering these strategies helps traders balance speed, price certainty, and market exposure for improved profitability.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Liquidity Sweep | Limit Order |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Orders that rapidly execute across multiple price levels to capture available liquidity. | Order placed to buy or sell at a specific price or better. |
| Execution Speed | Fast, immediate execution targeting liquidity pockets. | Executed only when market reaches the set price, possibly delayed. |
| Price Control | Less precise due to sweeping across prices. | High precision at the specified limit price. |
| Market Impact | Higher impact, can move market prices during execution. | Lower impact, passive order waiting for fills. |
| Use Case | Quickly capturing available liquidity in fast markets. | Setting entry or exit points with price certainty. |
Which is better?
Liquidity sweeps aggressively capture available liquidity across multiple price levels, allowing traders to execute large orders quickly with minimal market impact. Limit orders provide price control by setting a specific entry or exit point, reducing slippage but risking non-execution in fast-moving markets. For high-frequency or institutional traders needing rapid fills, liquidity sweeps often outperform, while limit orders suit those prioritizing price precision.
Connection
Liquidity sweep strategies actively capture available liquidity in the market by executing market orders that consume limit orders on the order book. Limit orders, placed by traders to buy or sell at specific prices, provide the liquidity that liquidity sweep algorithms target for swift execution. The interaction between liquidity sweeps and limit orders facilitates efficient price discovery and ensures smoother market operations.
Key Terms
Order execution
Limit orders specify a maximum purchase price or a minimum sale price, ensuring precise control over trade execution but potentially missing opportunities in fast-moving markets. Liquidity sweeps aggressively target available liquidity across multiple price levels, prioritizing rapid execution over specific price control by filling large orders quickly. Explore more about optimizing order execution strategies to enhance trading efficiency.
Price control
Limit orders allow precise price control by setting a specific execution price, ensuring trades occur only at desired levels. Liquidity sweeps prioritize speed over price, rapidly executing orders across multiple price points to capture available liquidity, often resulting in less predictable costs. Explore deeper insights on price control strategies in trading to optimize execution outcomes.
Market impact
Limit orders minimize market impact by specifying a price ceiling or floor, preventing unexpected price swings and preserving market stability. Liquidity sweeps aggressively consume available liquidity across multiple price levels, often causing significant short-term market impact and price disruptions. Explore further to understand how these order types influence trading strategies and market behavior.
Source and External Links
What is a Limit Order in Stocks: Examples & Types - SoFi - A limit order lets investors buy or sell securities at a specified price or better, providing price protection and allowing trades to execute only at the desired price level or more favorable ones, and can remain open until filled or canceled.
Understanding Market, Limit, and Stop Orders - YouTube - A limit order specifies a price to buy or sell that must be met for the trade to execute, but there is no guarantee the order will fill if the price is not reached.
Limit Orders: Types, Risks and Advantages - Charles Schwab - A limit order sets a maximum purchase price or minimum sale price, controlling execution price but not guaranteeing immediate or any execution, useful especially in volatile markets or extended trading hours.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com