Quantitative signals utilize mathematical models and algorithms to identify trading opportunities based on price patterns, volume, and other market data. Factor investing focuses on targeting specific investment drivers such as value, momentum, or quality to enhance portfolio returns and manage risk. Explore the nuances and benefits of both approaches to optimize your trading strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quantitative signals and factor investing is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and risk management. Quantitative signals use algorithmic data patterns to generate short-term trade decisions, while factor investing focuses on long-term exposure to specific drivers like value, momentum, or size. This distinction allows traders to tailor portfolios based on either high-frequency data or fundamental economic factors, improving performance and diversification. Mastery of both approaches enhances adaptability in volatile markets and aligns investment with individual risk profiles.
Comparison Table
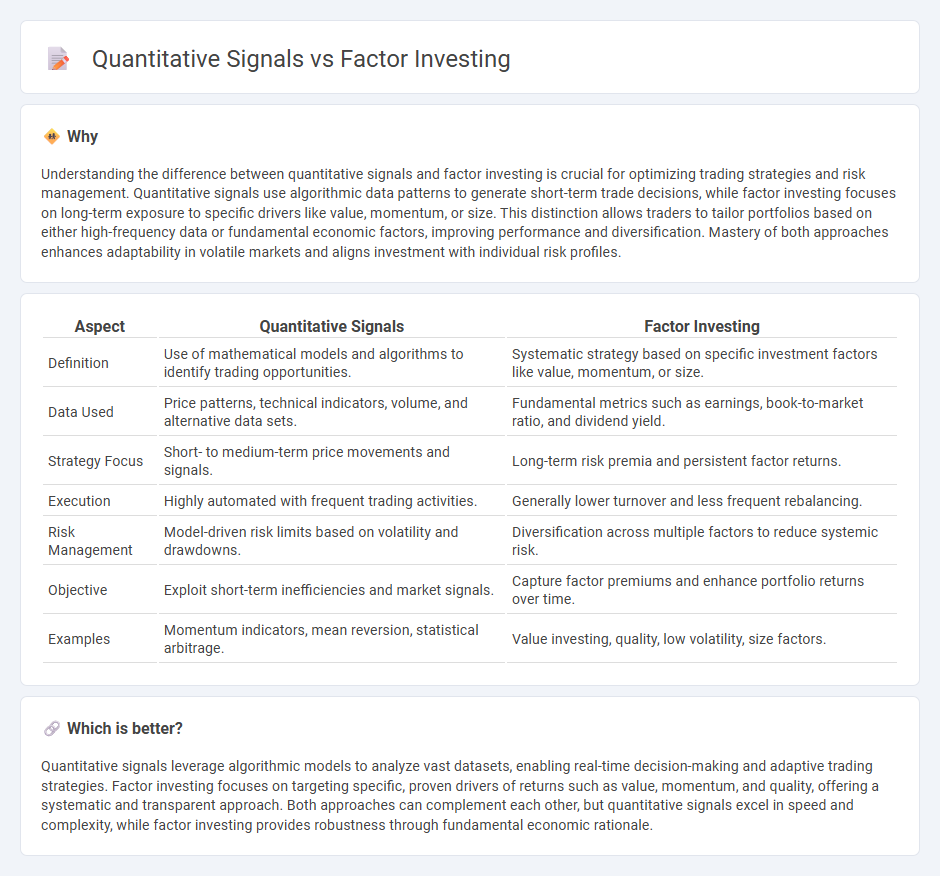
| Aspect | Quantitative Signals | Factor Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of mathematical models and algorithms to identify trading opportunities. | Systematic strategy based on specific investment factors like value, momentum, or size. |
| Data Used | Price patterns, technical indicators, volume, and alternative data sets. | Fundamental metrics such as earnings, book-to-market ratio, and dividend yield. |
| Strategy Focus | Short- to medium-term price movements and signals. | Long-term risk premia and persistent factor returns. |
| Execution | Highly automated with frequent trading activities. | Generally lower turnover and less frequent rebalancing. |
| Risk Management | Model-driven risk limits based on volatility and drawdowns. | Diversification across multiple factors to reduce systemic risk. |
| Objective | Exploit short-term inefficiencies and market signals. | Capture factor premiums and enhance portfolio returns over time. |
| Examples | Momentum indicators, mean reversion, statistical arbitrage. | Value investing, quality, low volatility, size factors. |
Which is better?
Quantitative signals leverage algorithmic models to analyze vast datasets, enabling real-time decision-making and adaptive trading strategies. Factor investing focuses on targeting specific, proven drivers of returns such as value, momentum, and quality, offering a systematic and transparent approach. Both approaches can complement each other, but quantitative signals excel in speed and complexity, while factor investing provides robustness through fundamental economic rationale.
Connection
Quantitative signals leverage statistical models and historical data to identify market patterns, forming the foundation for factor investing strategies that target specific drivers of returns such as value, momentum, and quality. Factor investing systematically exploits these signals by selecting securities exhibiting desired characteristics, enhancing portfolio performance through diversification and risk management. The synergy between quantitative signals and factor investing enables more objective, data-driven decision-making in trading, reducing emotional biases.
Key Terms
Factor Investing:
Factor investing leverages systematic strategies targeting specific attributes like value, momentum, or quality to enhance portfolio returns and manage risk. By identifying and exploiting persistent drivers of returns based on economic rationale and empirical evidence, factor investing seeks to generate alpha with greater transparency and durability compared to purely data-driven quantitative signals. Discover more about how factor investing can optimize your investment strategy and risk management.
Value
Value investing emphasizes selecting stocks that appear undervalued based on fundamental metrics like low price-to-earnings or price-to-book ratios, aiming to capture long-term market outperformance. Quantitative signals for value leverage algorithmic analysis of extensive financial data, identifying complex patterns beyond traditional valuation ratios to optimize stock selection and timing. Explore how blending factor investing principles with advanced quantitative methods can enhance portfolio construction and risk-adjusted returns.
Momentum
Momentum factor investing capitalizes on the tendency of assets with recent strong performance to continue outperforming in the near term, using historical price trends as a key quantitative signal. Quantitative signals in momentum strategies analyze price momentum through metrics like relative strength and moving averages to identify buy or sell opportunities systematically. Explore more to understand how momentum-driven factor investing integrates advanced quantitative models for optimized portfolio returns.
Source and External Links
What is Factor Investing? - NEPC - Factor investing aims to capture risk premiums from specific factors to achieve long-term excess returns and enhanced diversification by building balanced multi-factor portfolios tailored to clients' goals.
Guide to factor investing in equity markets - Robeco - Factor investing involves targeting market segments with characteristics like value, momentum, low volatility, and quality, which have historically generated higher risk-adjusted returns than the general market over decades.
What are factor based funds? | Vanguard - Factor-based funds actively tilt portfolios toward targeted stock characteristics such as value, momentum, quality, and low volatility, offering investors rules-based exposure to factors with long-term potential benefits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com