Flash loans enable traders to borrow large sums instantly without collateral, executing complex arbitrage or liquidation strategies within a single transaction. Spot trading involves direct buying and selling of assets at current market prices, offering straightforward ownership transfer and immediate settlement. Explore the advantages and risks of flash loans versus spot trading to optimize your trading strategy.
Why it is important
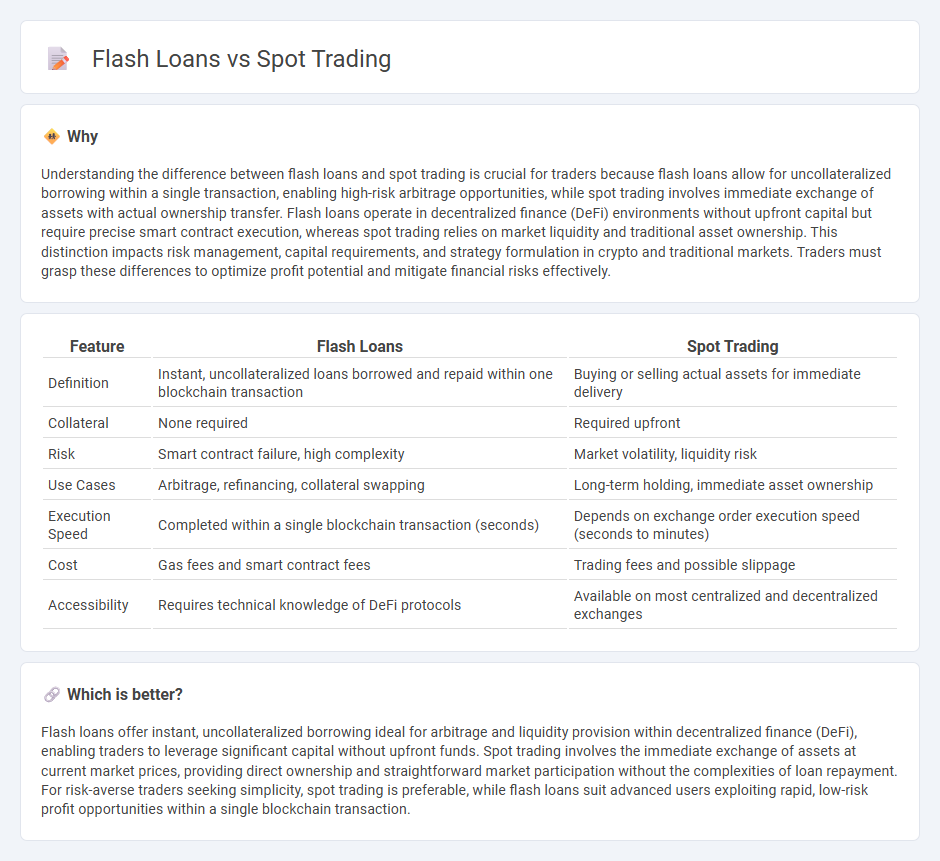
Understanding the difference between flash loans and spot trading is crucial for traders because flash loans allow for uncollateralized borrowing within a single transaction, enabling high-risk arbitrage opportunities, while spot trading involves immediate exchange of assets with actual ownership transfer. Flash loans operate in decentralized finance (DeFi) environments without upfront capital but require precise smart contract execution, whereas spot trading relies on market liquidity and traditional asset ownership. This distinction impacts risk management, capital requirements, and strategy formulation in crypto and traditional markets. Traders must grasp these differences to optimize profit potential and mitigate financial risks effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Flash Loans | Spot Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instant, uncollateralized loans borrowed and repaid within one blockchain transaction | Buying or selling actual assets for immediate delivery |
| Collateral | None required | Required upfront |
| Risk | Smart contract failure, high complexity | Market volatility, liquidity risk |
| Use Cases | Arbitrage, refinancing, collateral swapping | Long-term holding, immediate asset ownership |
| Execution Speed | Completed within a single blockchain transaction (seconds) | Depends on exchange order execution speed (seconds to minutes) |
| Cost | Gas fees and smart contract fees | Trading fees and possible slippage |
| Accessibility | Requires technical knowledge of DeFi protocols | Available on most centralized and decentralized exchanges |
Which is better?
Flash loans offer instant, uncollateralized borrowing ideal for arbitrage and liquidity provision within decentralized finance (DeFi), enabling traders to leverage significant capital without upfront funds. Spot trading involves the immediate exchange of assets at current market prices, providing direct ownership and straightforward market participation without the complexities of loan repayment. For risk-averse traders seeking simplicity, spot trading is preferable, while flash loans suit advanced users exploiting rapid, low-risk profit opportunities within a single blockchain transaction.
Connection
Flash loans enable traders to borrow large amounts of capital instantly without collateral, facilitating arbitrage opportunities across spot trading platforms. Spot trading, where assets are exchanged immediately at current market prices, benefits from flash loans by allowing users to capitalize on price discrepancies between exchanges within a single transaction. This synergy enhances market efficiency and creates opportunities for profit without initial capital investment.
Key Terms
Market Order
Market orders in spot trading execute instantly at the best available price, providing immediate liquidity and straightforward transaction execution. Flash loans, often used in decentralized finance (DeFi), enable borrowing without collateral within a single transaction block, typically for arbitrage or complex strategies rather than direct market orders. Explore the nuances of market order applications in both spot trading and flash loan mechanisms to deepen your understanding.
Collateral
Spot trading involves the direct exchange of assets at current market prices, requiring traders to hold sufficient collateral or funds upfront to complete transactions securely. Flash loans offer uncollateralized borrowing within blockchain ecosystems, relying on the atomicity of transactions to ensure loans are repaid instantly without collateral risk. Explore how collateral mechanisms influence risk management and trading strategies in decentralized finance.
Arbitrage
Spot trading involves buying and selling assets instantly on the market to capitalize on price differences, while flash loans are uncollateralized loans executed within a single blockchain transaction for arbitrage opportunities. Flash loans enable traders to borrow large sums without upfront capital, perform arbitrage across decentralized exchanges, and repay the loan instantly, minimizing risk. Explore how combining spot trading strategies with flash loans can maximize arbitrage profits in decentralized finance.
Source and External Links
What is a Spot Trade? - Spot Trade Definition - FOREX.com US - Spot trading is the immediate purchase or sale of a financial instrument like forex, commodities, or securities at the current market price known as the spot price, with transactions typically settled quickly.
What is spot trading in crypto and how does it work? - Coinbase - Spot trading in cryptocurrency involves buying and selling digital assets instantly at their current prices, allowing traders to directly own the assets they acquire through such transactions.
What is Spot Trading and How Do You Trade Spot Markets? - IG - Spot trading entails buying or selling assets at the current market price with the goal of immediate delivery, popular among day traders for short-term positions and available both in cash markets and via derivatives like CFDs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com