Statistical arbitrage exploits price inefficiencies through complex algorithms analyzing historical data to identify mean-reverting asset pairs, while calendar arbitrage capitalizes on price discrepancies between contracts with different expiration dates in futures markets. Implementing these strategies requires advanced quantitative tools and real-time data for effective execution and risk management. Discover the nuances and applications of both to enhance your trading strategies.
Why it is important
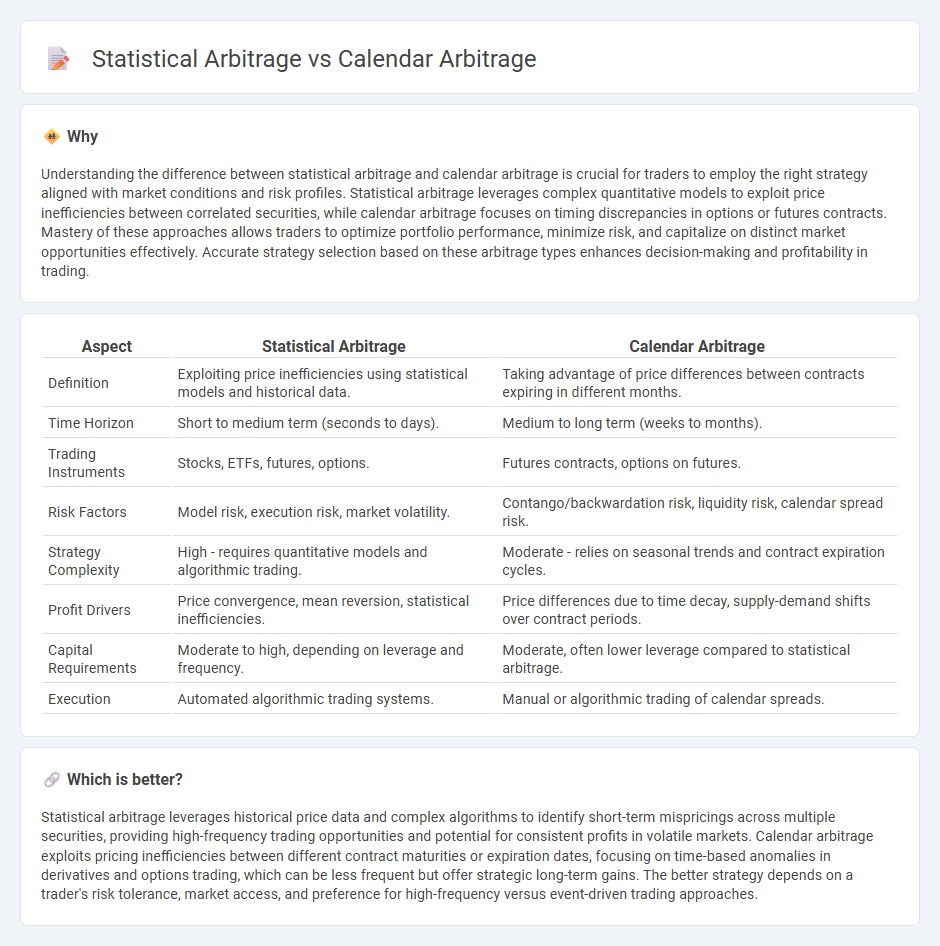
Understanding the difference between statistical arbitrage and calendar arbitrage is crucial for traders to employ the right strategy aligned with market conditions and risk profiles. Statistical arbitrage leverages complex quantitative models to exploit price inefficiencies between correlated securities, while calendar arbitrage focuses on timing discrepancies in options or futures contracts. Mastery of these approaches allows traders to optimize portfolio performance, minimize risk, and capitalize on distinct market opportunities effectively. Accurate strategy selection based on these arbitrage types enhances decision-making and profitability in trading.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Statistical Arbitrage | Calendar Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting price inefficiencies using statistical models and historical data. | Taking advantage of price differences between contracts expiring in different months. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term (seconds to days). | Medium to long term (weeks to months). |
| Trading Instruments | Stocks, ETFs, futures, options. | Futures contracts, options on futures. |
| Risk Factors | Model risk, execution risk, market volatility. | Contango/backwardation risk, liquidity risk, calendar spread risk. |
| Strategy Complexity | High - requires quantitative models and algorithmic trading. | Moderate - relies on seasonal trends and contract expiration cycles. |
| Profit Drivers | Price convergence, mean reversion, statistical inefficiencies. | Price differences due to time decay, supply-demand shifts over contract periods. |
| Capital Requirements | Moderate to high, depending on leverage and frequency. | Moderate, often lower leverage compared to statistical arbitrage. |
| Execution | Automated algorithmic trading systems. | Manual or algorithmic trading of calendar spreads. |
Which is better?
Statistical arbitrage leverages historical price data and complex algorithms to identify short-term mispricings across multiple securities, providing high-frequency trading opportunities and potential for consistent profits in volatile markets. Calendar arbitrage exploits pricing inefficiencies between different contract maturities or expiration dates, focusing on time-based anomalies in derivatives and options trading, which can be less frequent but offer strategic long-term gains. The better strategy depends on a trader's risk tolerance, market access, and preference for high-frequency versus event-driven trading approaches.
Connection
Statistical arbitrage and calendar arbitrage are connected through their reliance on pattern recognition and price inefficiencies in financial markets. Statistical arbitrage uses quantitative models to identify temporary mispricings across assets, while calendar arbitrage exploits price differences in securities related to time, such as options or futures contracts with varying expiration dates. Both strategies aim to capitalize on predictable market deviations by implementing systematic trading approaches.
Key Terms
**Calendar Arbitrage:**
Calendar arbitrage exploits price differences between futures or options contracts with varying expiration dates, capitalizing on the predictable changes in volatility or interest rates over time. This strategy often involves buying undervalued contracts and simultaneously selling overvalued ones within the same underlying asset to profit from time decay or convergence. Explore detailed mechanisms and risk profiles of calendar arbitrage for a comprehensive understanding.
Expiry Dates
Calendar arbitrage capitalizes on price discrepancies between options or futures contracts with different expiry dates, exploiting temporal inefficiencies in the market to generate risk-free profits. Statistical arbitrage uses quantitative models and historical data to identify mispricings and execute trades across multiple securities, often disregarding expiry dates but focusing on correlation patterns and mean reversion. Discover how expiry dates distinctly impact these strategies and optimize your trading approach.
Price Discrepancy
Calendar arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between futures contracts with different expiration dates, capitalizing on shifts in time value and implied volatility. Statistical arbitrage relies on quantitative models to identify and trade price inefficiencies across related securities by analyzing historical correlations and market patterns. Explore deeper insights into these strategies to enhance your trading edge.
Source and External Links
Volatility term structure and calendar spread arbitrage - Binance - Calendar arbitrage, specifically calendar spread arbitrage, involves exploiting the difference in implied volatility between long-term and short-term options, typically by buying long-dated options and selling short-dated options with the same strike price when the volatility term structure is in contango.
Calendar Arbitrage in the FX Volatility Surface - MathFinance - Calendar arbitrage arises when the variance (implied volatility squared times time) of longer maturities is smaller than that of shorter maturities for the same strike, potentially creating theoretical arbitrage opportunities by identifying intersections in total variance curves.
A note on sufficient conditions for no arbitrage - The absence of calendar spread arbitrage in option prices ensures that calendar spreads (long one option at a longer maturity and short another at a shorter maturity with the same strike) are not negatively priced, which is essential for ruling out static arbitrage opportunities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com