Microstructure trading focuses on the detailed mechanisms of how trades are executed within financial markets, analyzing order flow, bid-ask spreads, and market depth to optimize execution strategies. Algorithmic trading employs computer algorithms to automate trading decisions based on predefined criteria, enabling high-frequency trading and managing complex market variables at scale. Explore further to understand how these approaches impact market efficiency and trading performance.
Why it is important
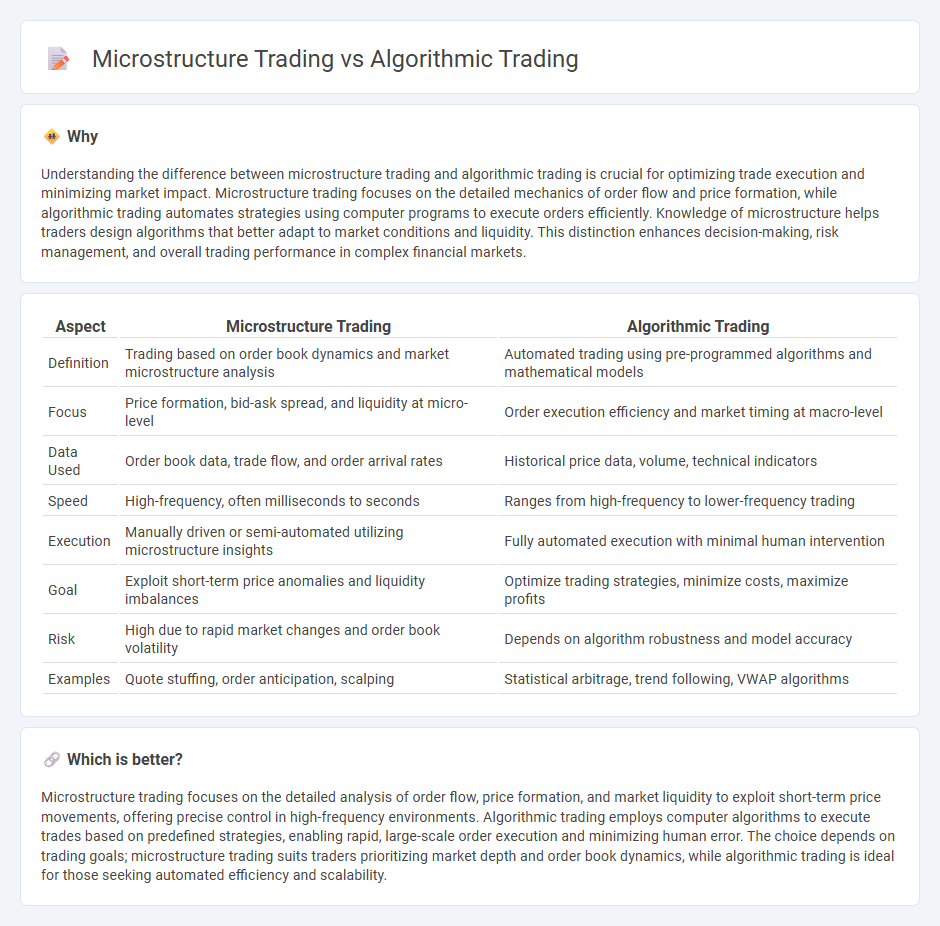
Understanding the difference between microstructure trading and algorithmic trading is crucial for optimizing trade execution and minimizing market impact. Microstructure trading focuses on the detailed mechanics of order flow and price formation, while algorithmic trading automates strategies using computer programs to execute orders efficiently. Knowledge of microstructure helps traders design algorithms that better adapt to market conditions and liquidity. This distinction enhances decision-making, risk management, and overall trading performance in complex financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microstructure Trading | Algorithmic Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading based on order book dynamics and market microstructure analysis | Automated trading using pre-programmed algorithms and mathematical models |
| Focus | Price formation, bid-ask spread, and liquidity at micro-level | Order execution efficiency and market timing at macro-level |
| Data Used | Order book data, trade flow, and order arrival rates | Historical price data, volume, technical indicators |
| Speed | High-frequency, often milliseconds to seconds | Ranges from high-frequency to lower-frequency trading |
| Execution | Manually driven or semi-automated utilizing microstructure insights | Fully automated execution with minimal human intervention |
| Goal | Exploit short-term price anomalies and liquidity imbalances | Optimize trading strategies, minimize costs, maximize profits |
| Risk | High due to rapid market changes and order book volatility | Depends on algorithm robustness and model accuracy |
| Examples | Quote stuffing, order anticipation, scalping | Statistical arbitrage, trend following, VWAP algorithms |
Which is better?
Microstructure trading focuses on the detailed analysis of order flow, price formation, and market liquidity to exploit short-term price movements, offering precise control in high-frequency environments. Algorithmic trading employs computer algorithms to execute trades based on predefined strategies, enabling rapid, large-scale order execution and minimizing human error. The choice depends on trading goals; microstructure trading suits traders prioritizing market depth and order book dynamics, while algorithmic trading is ideal for those seeking automated efficiency and scalability.
Connection
Microstructure trading directly informs algorithmic trading by providing insights into order flow, bid-ask spreads, and market depth, which are critical for developing effective trading algorithms. Algorithmic trading leverages microstructure data to optimize execution strategies, reduce market impact, and enhance price discovery. The integration of microstructure analysis with algorithmic models enables high-frequency traders to capitalize on short-term market inefficiencies.
Key Terms
Execution Algorithms
Execution algorithms in algorithmic trading leverage sophisticated quantitative models to optimize order placement and minimize market impact, enhancing trade efficiency across diverse asset classes. Microstructure trading centers on analyzing the detailed mechanics of order books and trade flows to exploit short-term price inefficiencies and liquidity dynamics at a granular level. Explore in-depth strategies and technological frameworks driving execution algorithms and microstructure trading for advanced market performance insights.
Market Microstructure
Market microstructure examines how trading mechanisms, order types, and price formation impact asset liquidity and transaction costs, emphasizing the role of information asymmetry and investor behavior. Algorithmic trading leverages automated systems to execute trades efficiently but must adapt to microstructure nuances like bid-ask spreads and order book dynamics to optimize performance. Explore detailed insights on how market microstructure principles shape advanced trading strategies and improve execution quality.
Latency
Algorithmic trading leverages high-speed computational algorithms to execute orders based on complex criteria, often prioritizing minimal latency to optimize trade execution and reduce slippage. Microstructure trading focuses on the detailed dynamics of market participants' interactions and order book flows, where latency impacts the ability to exploit short-term price movements and market inefficiencies. Explore the nuances of latency-sensitive strategies in algorithmic and microstructure trading to gain deeper insights into their distinct operational advantages.
Source and External Links
Algorithmic Trading - Definition, Example, Pros, Cons - Algorithmic trading involves using pre-programmed computer rules to make trading decisions and execute trades automatically when conditions are met, such as moving average strategies that buy or sell securities based on price relative to average price over time.
What is Algorithmic Trading and How Do You Get Started? - IG - Algorithmic trading uses computer codes to automatically open and close trades based on defined rules like price action or technical indicators, enabling strategies like high-frequency trading and managing risk through stops and limits.
Algorithmic trading - Wikipedia - Algorithmic trading automates order execution with pre-programmed instructions considering variables such as time and price; modern systems integrate exchanges, servers, and applications for real-time and historical data analysis, using protocols like FIX to connect to markets efficiently.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com