Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets or instruments using automated trading systems to execute rapid, risk-minimized transactions. Basket trading involves simultaneously buying or selling a group of securities to achieve diversification or hedge against market volatility. Explore further to understand the strategic advantages and applications of these advanced trading techniques.
Why it is important
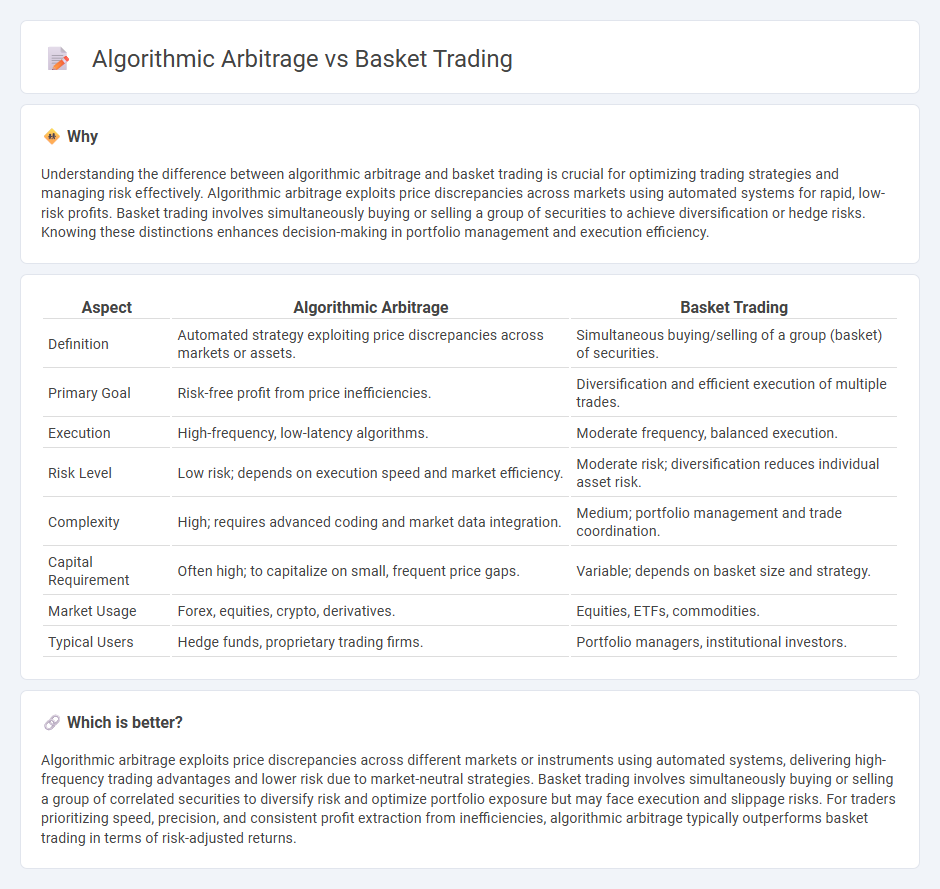
Understanding the difference between algorithmic arbitrage and basket trading is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and managing risk effectively. Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across markets using automated systems for rapid, low-risk profits. Basket trading involves simultaneously buying or selling a group of securities to achieve diversification or hedge risks. Knowing these distinctions enhances decision-making in portfolio management and execution efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Arbitrage | Basket Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated strategy exploiting price discrepancies across markets or assets. | Simultaneous buying/selling of a group (basket) of securities. |
| Primary Goal | Risk-free profit from price inefficiencies. | Diversification and efficient execution of multiple trades. |
| Execution | High-frequency, low-latency algorithms. | Moderate frequency, balanced execution. |
| Risk Level | Low risk; depends on execution speed and market efficiency. | Moderate risk; diversification reduces individual asset risk. |
| Complexity | High; requires advanced coding and market data integration. | Medium; portfolio management and trade coordination. |
| Capital Requirement | Often high; to capitalize on small, frequent price gaps. | Variable; depends on basket size and strategy. |
| Market Usage | Forex, equities, crypto, derivatives. | Equities, ETFs, commodities. |
| Typical Users | Hedge funds, proprietary trading firms. | Portfolio managers, institutional investors. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets or instruments using automated systems, delivering high-frequency trading advantages and lower risk due to market-neutral strategies. Basket trading involves simultaneously buying or selling a group of correlated securities to diversify risk and optimize portfolio exposure but may face execution and slippage risks. For traders prioritizing speed, precision, and consistent profit extraction from inefficiencies, algorithmic arbitrage typically outperforms basket trading in terms of risk-adjusted returns.
Connection
Algorithmic arbitrage and basket trading are interconnected through their reliance on automated strategies to exploit price discrepancies across multiple securities simultaneously. Algorithmic arbitrage uses advanced algorithms to identify and execute trades rapidly, while basket trading involves grouping various assets to optimize portfolio execution and reduce transaction costs. Together, they enhance market efficiency by enabling precise, high-speed trading that capitalizes on transient market inefficiencies.
Key Terms
**Basket Trading:**
Basket trading involves executing a group of securities simultaneously, optimizing portfolio diversification and minimizing transaction costs while exploiting market trends. It leverages correlated asset movements to manage risk and achieve strategic investment goals, often used by institutional investors to implement complex trading strategies efficiently. Explore deeper insights into basket trading techniques and its impact on modern financial markets.
Portfolio Diversification
Basket trading involves purchasing a group of securities simultaneously to diversify and reduce portfolio risk by spreading investments across multiple assets. Algorithmic arbitrage leverages advanced algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across markets, enhancing portfolio diversification through automated, high-frequency trades in varied asset classes. Explore the nuances of these strategies to optimize your portfolio diversification and risk management.
Order Execution
Basket trading involves executing multiple securities as a single transaction to minimize market impact and achieve efficient order execution, while algorithmic arbitrage relies on sophisticated algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across markets with high-speed execution. Algorithmic arbitrage optimizes order execution through real-time data analysis and automated trading strategies, reducing latency and slippage compared to manual basket trades. Explore advanced techniques in order execution to enhance trading performance and gain a competitive edge.
Source and External Links
Basket Trading: What it is, key aspects & examples - Basket trading is a strategy where investors buy or sell a group of securities as one unit, facilitating diversification, risk management, simplified trading, and flexible weighting across stocks, commodities, currencies, or index funds, often used by institutional investors.
What is Basket Trading? Types, Advantages, and Challenges Explained - Basket trading allows simultaneous buying or selling of multiple assets, enabling investors to mimic an index or sector by holding a proportionate portfolio, thus reducing the risk of individual security exposure and aligning with investment goals efficiently.
Basket Trade - Meaning, Types, Working and Benefits - Basket trades involve purchasing or selling multiple securities concurrently, with categories including equity, fixed-income, and commodity baskets, favored by large and institutional investors for portfolio diversification and flexible allocation according to investment objectives.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com