Microstructure modeling analyzes the intricate processes behind order flow, price formation, and market liquidity to capture the dynamics driving asset prices at a granular level. Bid-ask spread estimation focuses on quantifying the cost of trading by measuring the difference between the highest buying and lowest selling prices, reflecting market efficiency and transaction costs. Explore further to understand how these approaches enhance trading strategy optimization and market analysis.
Why it is important
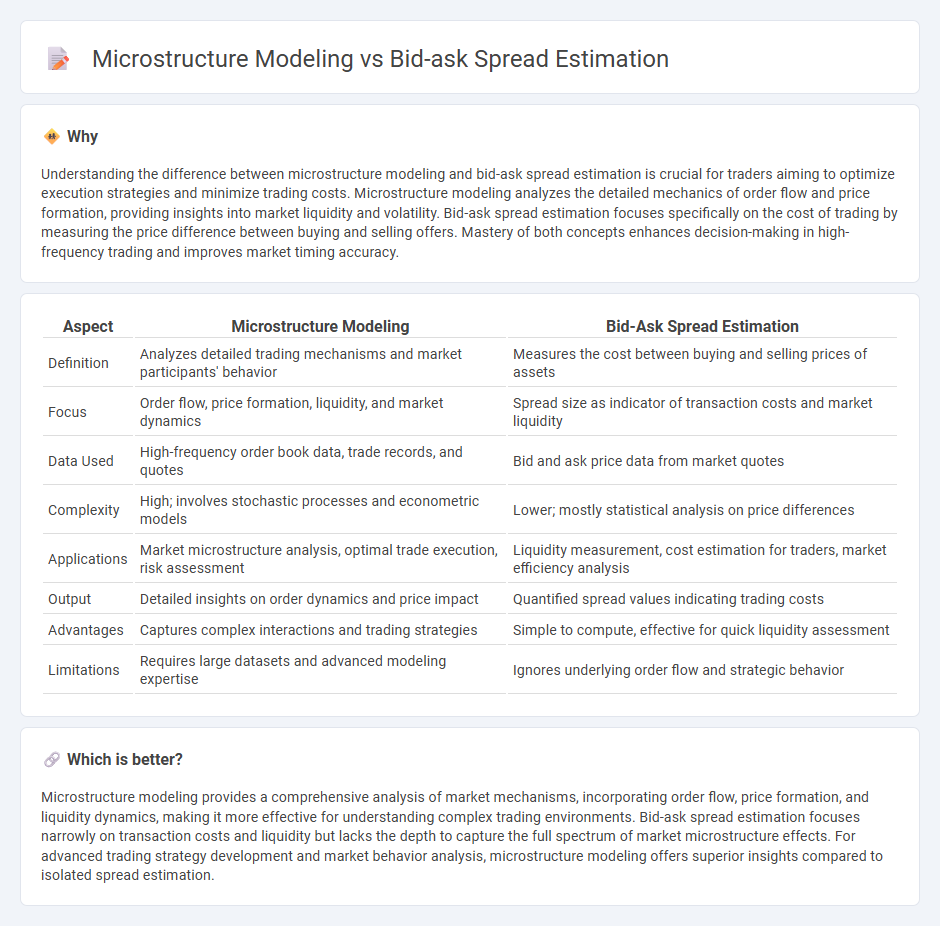
Understanding the difference between microstructure modeling and bid-ask spread estimation is crucial for traders aiming to optimize execution strategies and minimize trading costs. Microstructure modeling analyzes the detailed mechanics of order flow and price formation, providing insights into market liquidity and volatility. Bid-ask spread estimation focuses specifically on the cost of trading by measuring the price difference between buying and selling offers. Mastery of both concepts enhances decision-making in high-frequency trading and improves market timing accuracy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microstructure Modeling | Bid-Ask Spread Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes detailed trading mechanisms and market participants' behavior | Measures the cost between buying and selling prices of assets |
| Focus | Order flow, price formation, liquidity, and market dynamics | Spread size as indicator of transaction costs and market liquidity |
| Data Used | High-frequency order book data, trade records, and quotes | Bid and ask price data from market quotes |
| Complexity | High; involves stochastic processes and econometric models | Lower; mostly statistical analysis on price differences |
| Applications | Market microstructure analysis, optimal trade execution, risk assessment | Liquidity measurement, cost estimation for traders, market efficiency analysis |
| Output | Detailed insights on order dynamics and price impact | Quantified spread values indicating trading costs |
| Advantages | Captures complex interactions and trading strategies | Simple to compute, effective for quick liquidity assessment |
| Limitations | Requires large datasets and advanced modeling expertise | Ignores underlying order flow and strategic behavior |
Which is better?
Microstructure modeling provides a comprehensive analysis of market mechanisms, incorporating order flow, price formation, and liquidity dynamics, making it more effective for understanding complex trading environments. Bid-ask spread estimation focuses narrowly on transaction costs and liquidity but lacks the depth to capture the full spectrum of market microstructure effects. For advanced trading strategy development and market behavior analysis, microstructure modeling offers superior insights compared to isolated spread estimation.
Connection
Microstructure modeling provides a framework to analyze the mechanisms underlying order flow and price formation, which directly influence the bid-ask spread in trading markets. Accurate bid-ask spread estimation relies on understanding factors such as order size, trade frequency, and market liquidity modeled within microstructure theories. This connection enables traders and market makers to optimize pricing strategies and reduce transaction costs by anticipating variations in spread dynamics.
Key Terms
Bid-Ask Spread Estimation:
Bid-Ask Spread Estimation quantifies the difference between the highest bid and lowest ask prices, serving as a crucial indicator of market liquidity and transaction costs. Accurate estimation techniques incorporate historical price data, order book depth, and trade volumes to reflect real-time market dynamics effectively. Explore detailed methodologies and applications to enhance trading strategies and risk management.
Quoted Spread
Quoted Spread represents the difference between the lowest ask price and the highest bid price in the order book, serving as a direct measure of market liquidity and transaction costs. Bid-ask spread estimation techniques often rely on observed quoted spreads, while microstructure modeling delves deeper by capturing the underlying trading mechanisms, order flow dynamics, and inventory risks influencing these spreads. Explore the intricate relationships between Quoted Spread estimation and microstructure models to enhance market efficiency analysis and trading strategies.
Effective Spread
Effective spread provides a precise measure of transaction costs by capturing the true cost investors pay beyond the quoted bid-ask spread, reflecting market microstructure effects like order flow and trade size. Microstructure modeling incorporates factors such as asymmetric information, inventory risk, and dealer behavior to explain fluctuations in the effective spread and its impact on liquidity. Explore deeper insights into effective spread estimation and microstructure approaches to optimize trading strategies and market analysis.
Source and External Links
Bid-Ask Spread | Formula + Calculator - Wall Street Prep - The bid-ask spread is calculated as the difference between the lowest asking price and the highest bid price, with a spread percentage formula being (Ask Price - Bid Price) / Ask Price, useful for standardized comparisons between securities.
A Simple Way to Estimate Bid-Ask Spreads from Daily High and Low Prices - This paper develops an estimator for bid-ask spreads using daily high and low prices by leveraging the idea that daily highs are usually buy trades and daily lows sell trades, allowing spread estimation without intraday data.
A Simple Way to Estimate Bid-Ask Spreads from Daily High and Low Prices (Corwin & Schultz) - The Corwin-Schultz estimator uses price ratios over one-day and two-day intervals to separate volatility from bid-ask spread components, providing a practical and accurate method for transaction cost measurement using only daily prices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com