Option selling strategies like the wheel focus on generating steady income through repeated selling of puts and calls on the same underlying asset, capitalizing on time decay and premium collection. Straddle strategies involve simultaneously buying or selling call and put options at the same strike price, aiming to profit from significant price movement or volatility changes in the underlying security. Explore the unique risk-reward profiles and market scenarios where wheel and straddle strategies excel to enhance your trading approach.
Why it is important
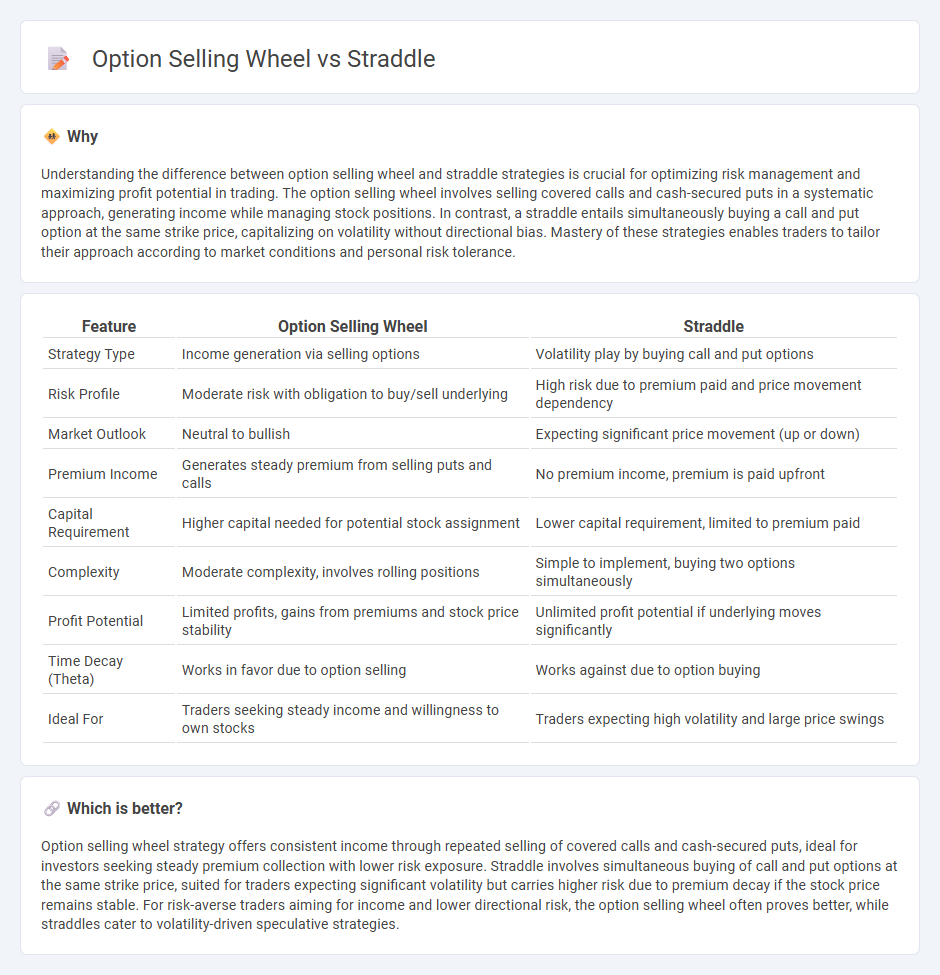
Understanding the difference between option selling wheel and straddle strategies is crucial for optimizing risk management and maximizing profit potential in trading. The option selling wheel involves selling covered calls and cash-secured puts in a systematic approach, generating income while managing stock positions. In contrast, a straddle entails simultaneously buying a call and put option at the same strike price, capitalizing on volatility without directional bias. Mastery of these strategies enables traders to tailor their approach according to market conditions and personal risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Option Selling Wheel | Straddle |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy Type | Income generation via selling options | Volatility play by buying call and put options |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk with obligation to buy/sell underlying | High risk due to premium paid and price movement dependency |
| Market Outlook | Neutral to bullish | Expecting significant price movement (up or down) |
| Premium Income | Generates steady premium from selling puts and calls | No premium income, premium is paid upfront |
| Capital Requirement | Higher capital needed for potential stock assignment | Lower capital requirement, limited to premium paid |
| Complexity | Moderate complexity, involves rolling positions | Simple to implement, buying two options simultaneously |
| Profit Potential | Limited profits, gains from premiums and stock price stability | Unlimited profit potential if underlying moves significantly |
| Time Decay (Theta) | Works in favor due to option selling | Works against due to option buying |
| Ideal For | Traders seeking steady income and willingness to own stocks | Traders expecting high volatility and large price swings |
Which is better?
Option selling wheel strategy offers consistent income through repeated selling of covered calls and cash-secured puts, ideal for investors seeking steady premium collection with lower risk exposure. Straddle involves simultaneous buying of call and put options at the same strike price, suited for traders expecting significant volatility but carries higher risk due to premium decay if the stock price remains stable. For risk-averse traders aiming for income and lower directional risk, the option selling wheel often proves better, while straddles cater to volatility-driven speculative strategies.
Connection
Option selling strategies like the wheel and the straddle are connected through their use of premium collection to generate income while managing risk. The wheel strategy involves selling cash-secured puts followed by covered calls on assigned stock, optimizing returns through iterative option selling cycles. The straddle strategy collects premiums by selling both call and put options at the same strike, benefiting from time decay and low volatility, which complements the wheel's approach of consistent premium extraction.
Key Terms
Volatility
Straddles capitalize on high volatility by buying both call and put options, profiting from significant price swings regardless of direction. The option selling wheel strategy generates income through selling options on established stocks, benefiting from time decay but requiring less volatility for consistent returns. Explore deeper insights on harnessing volatility to optimize your options strategies.
Premium
Straddle and option selling wheel strategies both capitalize on premium collection but differ in risk profile and margin requirements. Straddles involve buying both call and put options at the same strike, benefiting from high implied volatility and premium decay, but carry unlimited risk if the underlying moves sharply. The option selling wheel systematically sells puts and covered calls to generate consistent premium income with defined risk management; explore detailed comparisons to optimize your options trading approach.
Assignment
Straddle strategy involves holding both call and put options at the same strike price, exposing the seller to potential assignment on either side, requiring careful management of assignment risk. Option selling wheel focuses on selling cash-secured puts and covered calls, where assignment leads to buying the underlying stock and then selling calls against it, creating a cycle of ownership and option writing. Explore more to understand how assignment impacts risk, profit potential, and capital allocation in each strategy.
Source and External Links
Straddle - Definition, How to Create It, Examples - A straddle strategy involves simultaneously taking long and short positions on the same security by buying and selling call and put options with the same strike price and expiration date; it is used when a trader expects high price volatility but is uncertain about direction.
Straddle - A straddle in finance is a strategy involving buying or selling call and put options at the same strike price and expiration date to profit from large price movements in either direction, with "long straddle" referring to buying both options and "short straddle" referring to selling them.
Long Straddle Options Strategy - A long straddle consists of purchasing a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration to profit from a significant price change in either direction, with risk limited to the cost of the options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com