Microstructure trading focuses on exploiting short-term price fluctuations and market inefficiencies by analyzing order flow, bid-ask spreads, and trade execution speed. Position trading involves holding assets over longer periods based on fundamental analysis and broader market trends, aiming for substantial gains. Explore the key differences and strategies to determine which trading style suits your investment goals.
Why it is important
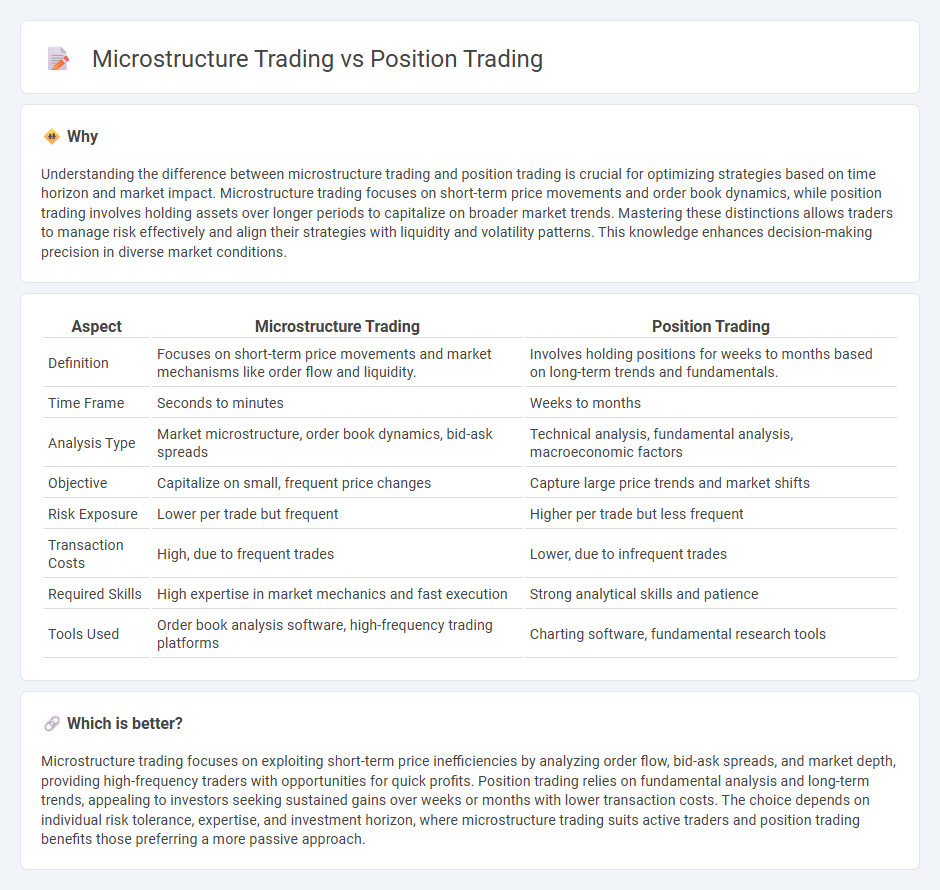
Understanding the difference between microstructure trading and position trading is crucial for optimizing strategies based on time horizon and market impact. Microstructure trading focuses on short-term price movements and order book dynamics, while position trading involves holding assets over longer periods to capitalize on broader market trends. Mastering these distinctions allows traders to manage risk effectively and align their strategies with liquidity and volatility patterns. This knowledge enhances decision-making precision in diverse market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microstructure Trading | Position Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on short-term price movements and market mechanisms like order flow and liquidity. | Involves holding positions for weeks to months based on long-term trends and fundamentals. |
| Time Frame | Seconds to minutes | Weeks to months |
| Analysis Type | Market microstructure, order book dynamics, bid-ask spreads | Technical analysis, fundamental analysis, macroeconomic factors |
| Objective | Capitalize on small, frequent price changes | Capture large price trends and market shifts |
| Risk Exposure | Lower per trade but frequent | Higher per trade but less frequent |
| Transaction Costs | High, due to frequent trades | Lower, due to infrequent trades |
| Required Skills | High expertise in market mechanics and fast execution | Strong analytical skills and patience |
| Tools Used | Order book analysis software, high-frequency trading platforms | Charting software, fundamental research tools |
Which is better?
Microstructure trading focuses on exploiting short-term price inefficiencies by analyzing order flow, bid-ask spreads, and market depth, providing high-frequency traders with opportunities for quick profits. Position trading relies on fundamental analysis and long-term trends, appealing to investors seeking sustained gains over weeks or months with lower transaction costs. The choice depends on individual risk tolerance, expertise, and investment horizon, where microstructure trading suits active traders and position trading benefits those preferring a more passive approach.
Connection
Microstructure trading involves analyzing market mechanics and order flows on a granular level, providing insights into price formation and liquidity that inform Position Trading strategies. Position traders leverage microstructure data to optimize entry and exit points, aligning trades with broader market trends while minimizing slippage and transaction costs. The integration of microstructure analysis enhances risk management and timing accuracy in Position Trading, improving overall trade performance.
Key Terms
**Holding Period**
Position trading involves holding assets for weeks to months, capitalizing on long-term trends and market fundamentals. Microstructure trading operates on seconds to minutes, exploiting short-term price movements driven by order flow and market depth. Explore detailed strategies and techniques to optimize your trading horizon effectively.
**Order Flow**
Position trading relies on long-term market trends and broad price movements, while microstructure trading emphasizes real-time order flow analysis to capture short-term price fluctuations. Order flow provides critical insights into market liquidity, buyer and seller intentions, and supply-demand imbalances, making it essential for microstructure traders to anticipate immediate price changes. Explore the nuances of order flow to enhance your trading strategy and execution precision.
**Market Liquidity**
Position trading relies on market liquidity to enter and exit large trades over extended periods, benefiting from broader trends and stable price movements. Microstructure trading exploits short-term liquidity variations, such as order book dynamics and bid-ask spreads, to execute high-frequency trades with minimal market impact. Explore how different liquidity aspects shape trading strategies and optimize execution efficiency.
Source and External Links
Position Trading 101: A Beginner's Guide With Examples - Position trading is a medium- to long-term trading strategy involving buying and selling financial products over weeks to months, aiming to capitalize on market trends by going long or short, distinct from buy-and-hold investing due to active timing of market entries and exits.
A guide to position trading: definition, examples and ... - Position trading focuses on capturing the majority of an ongoing trend by holding positions for weeks to months, ignoring short-term volatility, and involves opening fewer trades compared to short-term styles like day trading.
Position Trading Strategy: How To Use It - Position trading involves holding a security for months to years, allowing traders to speculate both long and short, with benefits such as lower trading frequency, reduced transaction costs, and potential for larger profits over longer horizons compared to swing or day trading.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com