Volatility harvesting involves exploiting market fluctuations by strategically timing trades to capture gains from price swings, enhancing portfolio returns without relying on trend direction. Arbitrage focuses on profiting from price discrepancies of identical or similar assets across different markets, ensuring near risk-free returns through simultaneous buying and selling. Explore the key differences and strategies behind volatility harvesting and arbitrage to optimize your trading approach.
Why it is important
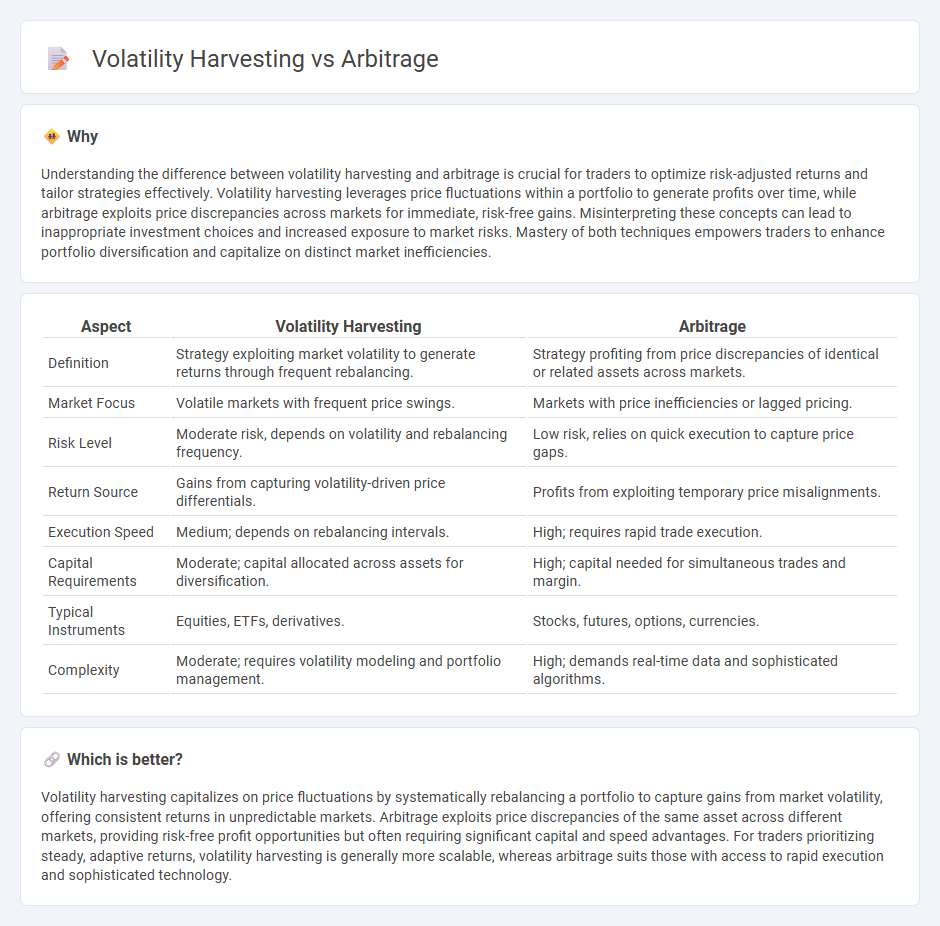
Understanding the difference between volatility harvesting and arbitrage is crucial for traders to optimize risk-adjusted returns and tailor strategies effectively. Volatility harvesting leverages price fluctuations within a portfolio to generate profits over time, while arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across markets for immediate, risk-free gains. Misinterpreting these concepts can lead to inappropriate investment choices and increased exposure to market risks. Mastery of both techniques empowers traders to enhance portfolio diversification and capitalize on distinct market inefficiencies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Volatility Harvesting | Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy exploiting market volatility to generate returns through frequent rebalancing. | Strategy profiting from price discrepancies of identical or related assets across markets. |
| Market Focus | Volatile markets with frequent price swings. | Markets with price inefficiencies or lagged pricing. |
| Risk Level | Moderate risk, depends on volatility and rebalancing frequency. | Low risk, relies on quick execution to capture price gaps. |
| Return Source | Gains from capturing volatility-driven price differentials. | Profits from exploiting temporary price misalignments. |
| Execution Speed | Medium; depends on rebalancing intervals. | High; requires rapid trade execution. |
| Capital Requirements | Moderate; capital allocated across assets for diversification. | High; capital needed for simultaneous trades and margin. |
| Typical Instruments | Equities, ETFs, derivatives. | Stocks, futures, options, currencies. |
| Complexity | Moderate; requires volatility modeling and portfolio management. | High; demands real-time data and sophisticated algorithms. |
Which is better?
Volatility harvesting capitalizes on price fluctuations by systematically rebalancing a portfolio to capture gains from market volatility, offering consistent returns in unpredictable markets. Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies of the same asset across different markets, providing risk-free profit opportunities but often requiring significant capital and speed advantages. For traders prioritizing steady, adaptive returns, volatility harvesting is generally more scalable, whereas arbitrage suits those with access to rapid execution and sophisticated technology.
Connection
Volatility harvesting exploits price fluctuations by systematically rebalancing portfolios to capture gains from market volatility, while arbitrage capitalizes on price discrepancies between related assets for riskless profit. Both strategies rely on market inefficiencies and price movements, with volatility harvesting generating opportunities through market swings and arbitrage identifying temporary mispricings. Combining these approaches enhances trading performance by leveraging volatility patterns and price differentials to achieve consistent returns.
Key Terms
Price Discrepancy
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets by simultaneously buying low and selling high to capture risk-free profits, relying on efficient market mechanisms. Volatility harvesting leverages price fluctuations within a single asset over time to generate returns through systematic rebalancing, independent of outright price differences between markets. Explore deeper insights on how price discrepancy strategies differ in risk profile and execution.
Mean Reversion
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between markets to achieve risk-free profits, while volatility harvesting leverages price fluctuations to enhance returns by systematically buying low and selling high. Mean reversion plays a central role in volatility harvesting by capitalizing on assets' tendency to revert to their historical average prices after deviations. Explore the mechanisms and benefits of mean reversion in trading strategies to deepen your understanding.
Market Efficiency
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across markets to generate risk-free profits, relying on inefficiencies that quickly correct market pricing. Volatility harvesting leverages market fluctuations through systematic rebalancing, aiming to enhance portfolio returns by capturing variance even in efficient markets. Explore further to understand how these strategies interact with market efficiency and portfolio optimization.
Source and External Links
Arbitrage - Arbitrage is the practice of exploiting price differences for the same asset in two or more markets by simultaneously buying low and selling high to realize a risk-free profit, often used by arbitrageurs in financial markets.
What Is Arbitrage? 3 Strategies to Know - Arbitrage is an investment strategy where an investor buys and sells an asset simultaneously in different markets to capitalize on price differences, including types like pure, merger, and convertible arbitrage.
What is arbitrage and how does it work in financial markets - Arbitrage is a trading strategy involving buying and selling the same asset across markets to profit from price differences, with examples such as merger arbitrage, triangular arbitrage, and pure arbitrage explained.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com