Microstructure trading focuses on exploiting short-term market inefficiencies and order book dynamics to gain profits within seconds or minutes. Swing trading targets price patterns and market trends over several days or weeks, aiming to capture more substantial price movements. Explore the key differences and strategies behind these trading approaches to enhance your market understanding.
Why it is important
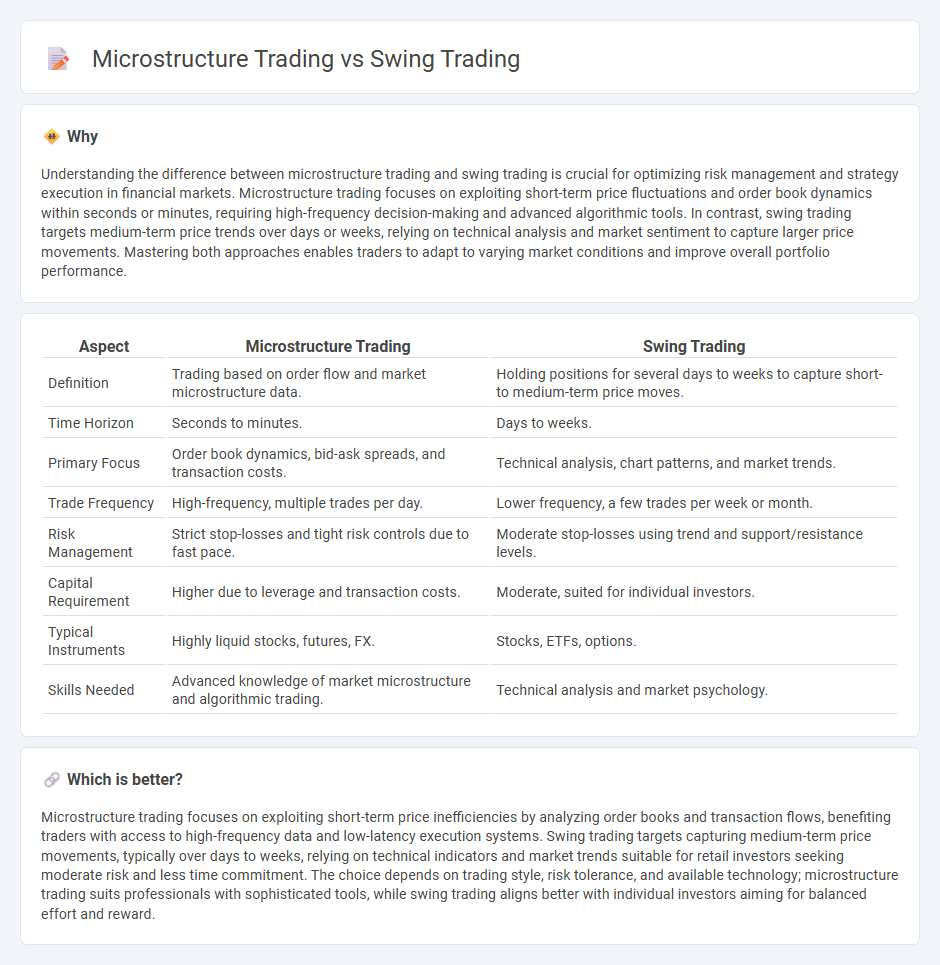
Understanding the difference between microstructure trading and swing trading is crucial for optimizing risk management and strategy execution in financial markets. Microstructure trading focuses on exploiting short-term price fluctuations and order book dynamics within seconds or minutes, requiring high-frequency decision-making and advanced algorithmic tools. In contrast, swing trading targets medium-term price trends over days or weeks, relying on technical analysis and market sentiment to capture larger price movements. Mastering both approaches enables traders to adapt to varying market conditions and improve overall portfolio performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microstructure Trading | Swing Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading based on order flow and market microstructure data. | Holding positions for several days to weeks to capture short- to medium-term price moves. |
| Time Horizon | Seconds to minutes. | Days to weeks. |
| Primary Focus | Order book dynamics, bid-ask spreads, and transaction costs. | Technical analysis, chart patterns, and market trends. |
| Trade Frequency | High-frequency, multiple trades per day. | Lower frequency, a few trades per week or month. |
| Risk Management | Strict stop-losses and tight risk controls due to fast pace. | Moderate stop-losses using trend and support/resistance levels. |
| Capital Requirement | Higher due to leverage and transaction costs. | Moderate, suited for individual investors. |
| Typical Instruments | Highly liquid stocks, futures, FX. | Stocks, ETFs, options. |
| Skills Needed | Advanced knowledge of market microstructure and algorithmic trading. | Technical analysis and market psychology. |
Which is better?
Microstructure trading focuses on exploiting short-term price inefficiencies by analyzing order books and transaction flows, benefiting traders with access to high-frequency data and low-latency execution systems. Swing trading targets capturing medium-term price movements, typically over days to weeks, relying on technical indicators and market trends suitable for retail investors seeking moderate risk and less time commitment. The choice depends on trading style, risk tolerance, and available technology; microstructure trading suits professionals with sophisticated tools, while swing trading aligns better with individual investors aiming for balanced effort and reward.
Connection
Microstructure trading focuses on understanding price formation and order book dynamics at a granular level, enabling traders to exploit short-term inefficiencies. Swing trading leverages these microstructure insights to time entries and exits over several days, capturing intermediate price movements. Integrating microstructure analysis enhances swing traders' ability to anticipate reversals and optimize trade execution.
Key Terms
Holding Period
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks, capitalizing on medium-term price trends and market momentum. Microstructure trading, by contrast, focuses on extremely short holding periods ranging from milliseconds to seconds, leveraging order flow, bid-ask spreads, and market depth for rapid profit. Explore the nuances of these strategies to optimize your trading approach and timing.
Liquidity
Swing trading capitalizes on medium-term price movements, relying on observable liquidity patterns in broader market trends and volume spikes that signal entry and exit points. Microstructure trading, however, delves into the intricacies of order book dynamics, bid-ask spreads, and transaction flow to exploit short-term liquidity imbalances and minimize market impact. Explore these strategies further to understand how liquidity nuances influence trading success.
Execution Speed
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to weeks, relying on technical analysis and market trends to capitalize on price swings. Microstructure trading focuses on executing trades within milliseconds, leveraging order book dynamics, bid-ask spreads, and high-frequency algorithms to profit from market inefficiencies. Explore more to understand how execution speed impacts strategy effectiveness and risk management.
Source and External Links
Swing trading - Wikipedia - Swing trading is a speculative strategy where assets are held for days to weeks to profit from price swings, using technical or fundamental analysis and rule-based systems to time entries and exits.
Swing trading: A complete guide for investors | TD Direct Investing - Swing trading targets short-term price changes by moving in/out of positions over days or weeks, relying mainly on technical analysis and appealing to investors who seek to profit from market volatility between day trading and long-term investing.
Swing Trading Stocks: Strategies and Indicators - Charles Schwab - Swing traders focus on broader trends but trade short-term swings using technical tools like support/resistance and chart patterns to decide when to enter and exit trades, often setting precise rules for trade size and timing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com