Quantitative backtesting uses historical market data to test trading strategies with precise algorithms, enabling traders to evaluate performance metrics such as drawdowns, win rates, and Sharpe ratios. Paper trading, by simulating real-time order execution without risking capital, allows traders to practice strategy application under live market conditions and assess execution quality and slippage. Explore deeper insights to optimize your trading approach and improve strategy reliability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quantitative backtesting and paper trading is crucial in trading as backtesting uses historical data to develop and validate strategies quantitatively, providing statistical confidence in performance. Paper trading simulates real-time market conditions without financial risk, helping traders practice execution and adapt to live dynamics. Backtesting focuses on strategy robustness, while paper trading emphasizes practical implementation and psychological discipline. Mastery of both methods enhances risk management and improves trading strategy effectiveness.
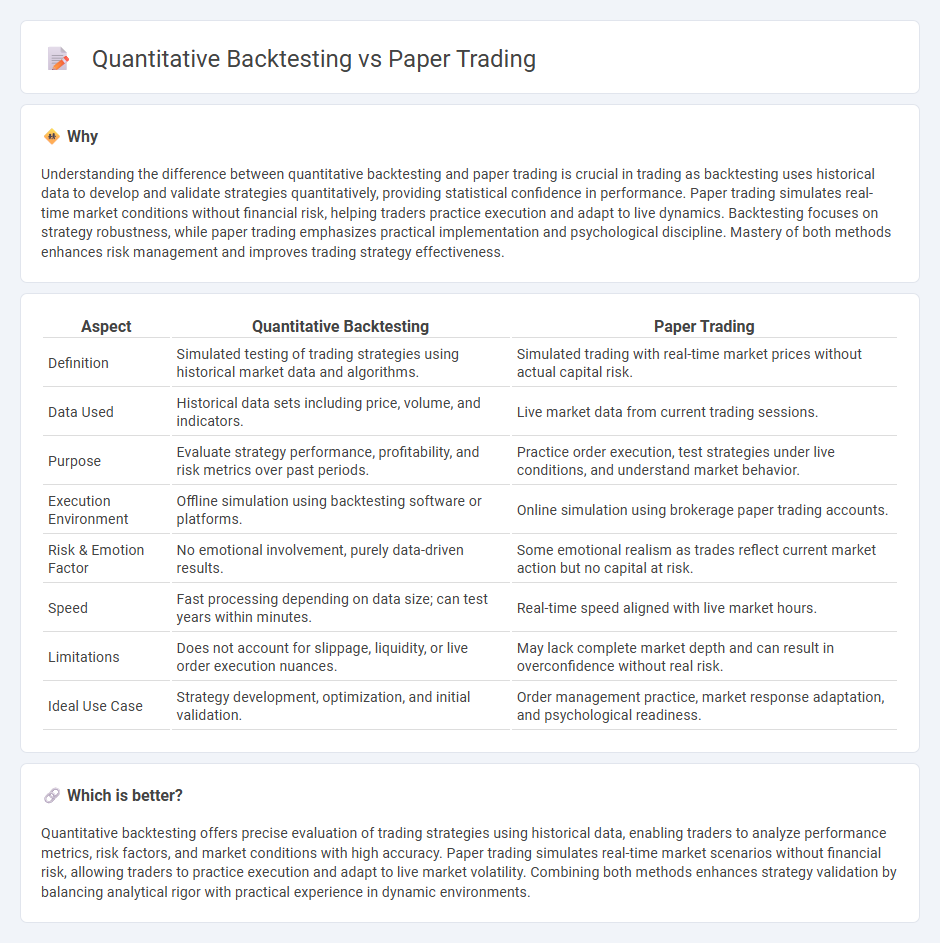
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Backtesting | Paper Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simulated testing of trading strategies using historical market data and algorithms. | Simulated trading with real-time market prices without actual capital risk. |
| Data Used | Historical data sets including price, volume, and indicators. | Live market data from current trading sessions. |
| Purpose | Evaluate strategy performance, profitability, and risk metrics over past periods. | Practice order execution, test strategies under live conditions, and understand market behavior. |
| Execution Environment | Offline simulation using backtesting software or platforms. | Online simulation using brokerage paper trading accounts. |
| Risk & Emotion Factor | No emotional involvement, purely data-driven results. | Some emotional realism as trades reflect current market action but no capital at risk. |
| Speed | Fast processing depending on data size; can test years within minutes. | Real-time speed aligned with live market hours. |
| Limitations | Does not account for slippage, liquidity, or live order execution nuances. | May lack complete market depth and can result in overconfidence without real risk. |
| Ideal Use Case | Strategy development, optimization, and initial validation. | Order management practice, market response adaptation, and psychological readiness. |
Which is better?
Quantitative backtesting offers precise evaluation of trading strategies using historical data, enabling traders to analyze performance metrics, risk factors, and market conditions with high accuracy. Paper trading simulates real-time market scenarios without financial risk, allowing traders to practice execution and adapt to live market volatility. Combining both methods enhances strategy validation by balancing analytical rigor with practical experience in dynamic environments.
Connection
Quantitative backtesting and paper trading are essential components in developing robust trading strategies by simulating market conditions to evaluate performance without financial risk. Backtesting uses historical data to test algorithms' effectiveness, while paper trading applies these strategies in real-time market environments, refining execution and risk management. Together, they bridge theoretical model validation with practical implementation, enhancing strategy reliability before live deployment.
Key Terms
Simulation
Paper trading simulates real market conditions by executing trades without using real capital, allowing traders to test strategies in real-time. Quantitative backtesting uses historical market data to assess trading algorithms' performance by simulating past market scenarios. Explore how these simulation methods impact strategy development and risk management to optimize trading outcomes.
Historical Data
Paper trading simulates real market conditions by executing hypothetical trades in real time, allowing traders to practice strategies without financial risk. Quantitative backtesting analyzes historical data by applying algorithms to past market conditions, providing statistical insights into potential strategy performance over time. Explore how integrating both methods can enhance trading strategy development and risk management.
Strategy Validation
Paper trading simulates real market conditions by executing trades in a risk-free environment, allowing traders to evaluate strategy performance with live price data without financial risk. Quantitative backtesting systematically analyzes historical data using algorithmic models to assess a trading strategy's robustness and profitability over various market scenarios. Explore detailed insights on how each method contributes to effective strategy validation and risk management.
Source and External Links
Paper Trading At TradeZero: 100% Risk Free - TradeZero offers a free, full-featured paper trading platform for 30 days with real-time NASDAQ Basic market data, after which a funded account is required for continued access.
Paper Trading -- main functionality - TradingView - TradingView's paper trading simulator lets you trade a variety of assets with customizable leverage, commission, and starting balance, all without real money, and allows multiple accounts for testing different strategies.
Paper Trading | Charles Schwab - Charles Schwab's paperMoney(r) on thinkorswim(r) provides a virtual trading environment with $100,000 in virtual buying power, real-time market data, and tools to practice equities, options, futures, and forex trading risk-free.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com