Bid-ask spread capture involves profiting from the difference between the buying and selling prices in financial markets, focusing on capturing consistent small gains by executing trades within the quoted spreads. Latency arbitrage exploits speed advantages by identifying and acting on price discrepancies between markets before other participants, relying heavily on low-latency technology and fast execution. Explore the nuances of these trading strategies to understand their impact on market efficiency and trader profitability.
Why it is important
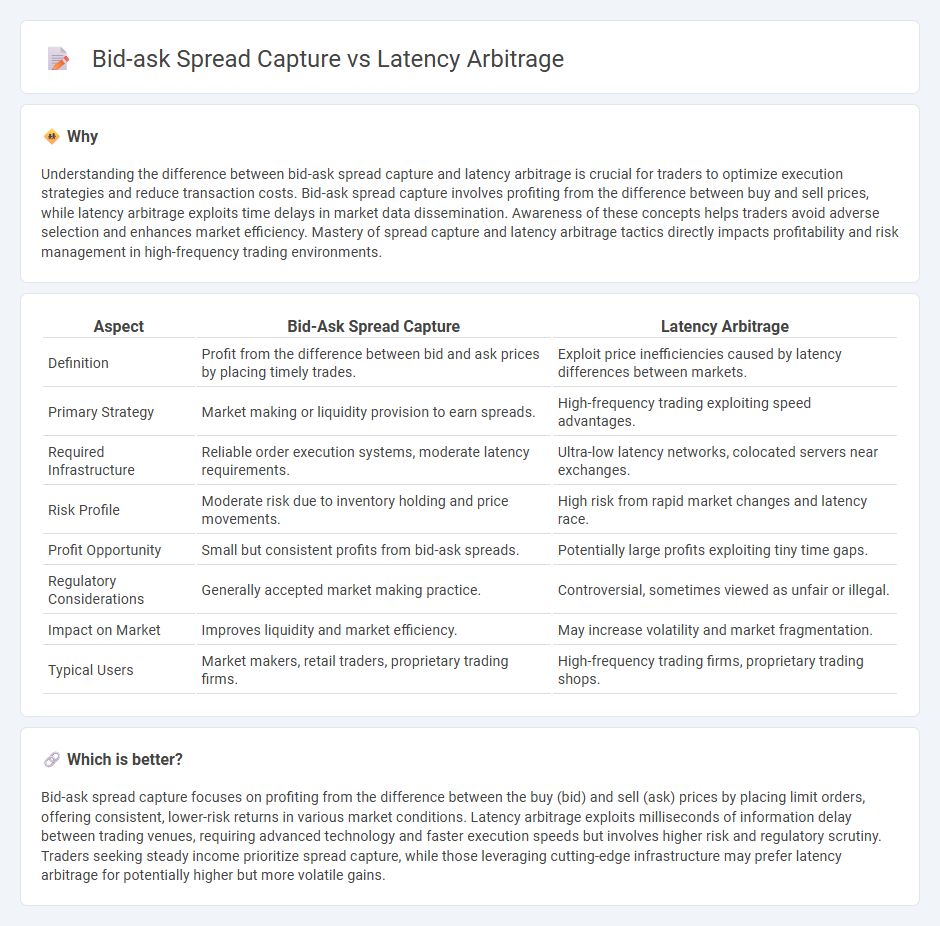
Understanding the difference between bid-ask spread capture and latency arbitrage is crucial for traders to optimize execution strategies and reduce transaction costs. Bid-ask spread capture involves profiting from the difference between buy and sell prices, while latency arbitrage exploits time delays in market data dissemination. Awareness of these concepts helps traders avoid adverse selection and enhances market efficiency. Mastery of spread capture and latency arbitrage tactics directly impacts profitability and risk management in high-frequency trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Bid-Ask Spread Capture | Latency Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profit from the difference between bid and ask prices by placing timely trades. | Exploit price inefficiencies caused by latency differences between markets. |
| Primary Strategy | Market making or liquidity provision to earn spreads. | High-frequency trading exploiting speed advantages. |
| Required Infrastructure | Reliable order execution systems, moderate latency requirements. | Ultra-low latency networks, colocated servers near exchanges. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk due to inventory holding and price movements. | High risk from rapid market changes and latency race. |
| Profit Opportunity | Small but consistent profits from bid-ask spreads. | Potentially large profits exploiting tiny time gaps. |
| Regulatory Considerations | Generally accepted market making practice. | Controversial, sometimes viewed as unfair or illegal. |
| Impact on Market | Improves liquidity and market efficiency. | May increase volatility and market fragmentation. |
| Typical Users | Market makers, retail traders, proprietary trading firms. | High-frequency trading firms, proprietary trading shops. |
Which is better?
Bid-ask spread capture focuses on profiting from the difference between the buy (bid) and sell (ask) prices by placing limit orders, offering consistent, lower-risk returns in various market conditions. Latency arbitrage exploits milliseconds of information delay between trading venues, requiring advanced technology and faster execution speeds but involves higher risk and regulatory scrutiny. Traders seeking steady income prioritize spread capture, while those leveraging cutting-edge infrastructure may prefer latency arbitrage for potentially higher but more volatile gains.
Connection
Bid-ask spread capture involves profiting from the difference between buying and selling prices, which latency arbitrage exploits by using faster trade execution to capitalize on price discrepancies before others can react. High-frequency traders utilize latency arbitrage to swiftly execute orders in microseconds, capturing spreads created by slower market participants. This connection underscores the critical role of low-latency technology in maximizing gains from bid-ask spread differentials in electronic trading environments.
Key Terms
Execution speed
Latency arbitrage exploits differences in execution speed across markets, enabling traders to capitalize on price discrepancies before they vanish, while bid-ask spread capture profits from the natural difference between buying and selling prices regardless of speed. High-frequency trading strategies prioritize ultra-low latency to execute arbitrage opportunities quickly, whereas spread capture relies more on capturing predictable market maker spreads with less emphasis on speed. Discover how execution speed transforms trading strategies by exploring the detailed mechanisms behind latency arbitrage and spread capture.
Price discrepancies
Latency arbitrage exploits time delays in market data to capitalize on price discrepancies before they are corrected, often involving high-frequency trading strategies and ultra-low latency systems. Bid-ask spread capture focuses on profiting from the difference between buy and sell prices by providing liquidity, typically through market making, and is influenced by volatility and order flow. Explore deeper insights into how these strategies impact market efficiency and trader profitability.
Liquidity
Latency arbitrage exploits millisecond differences in market data feeds to capitalize on temporary price discrepancies between venues, often requiring high-frequency trading infrastructure and direct market access. Bid-ask spread capture involves consistently executing trades within the spread, leveraging liquidity provision by placing limit orders that earn the spread as profit. Discover deeper insights into how liquidity dynamics influence these trading strategies and their market impacts.
Source and External Links
Latency Arbitrage, Market Fragmentation, and Efficiency: A Two-Market Model - Latency arbitrage is a high-frequency trading strategy where a trader exploits speed advantages to capture profits from price differences in fragmented markets, but it can reduce overall market efficiency and liquidity.
What Is Latency Arbitrage in Forex Trading? - B2PRIME - Latency arbitrage exploits time delays between brokers' price feeds to gain profits; it is controversial, often regarded as "toxic flow," and may be banned by brokers or regulated due to its potential to compromise market integrity.
Latency Arbitrage - Angel One - Institutional investors use latency arbitrage by leveraging superior low-latency infrastructure to react faster to price changes than slower participants, profiting from the delay in updated market data seen by others.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com