Bid-ask spread capture focuses on profiting from the difference between the buying price (bid) and the selling price (ask) within a single market, exploiting market inefficiencies and liquidity gaps. Arbitrage involves simultaneously buying and selling the same asset across different markets to capitalize on price discrepancies, ensuring a risk-free profit from market imbalances. Explore the nuances between these trading strategies to optimize your market engagement and profitability.
Why it is important
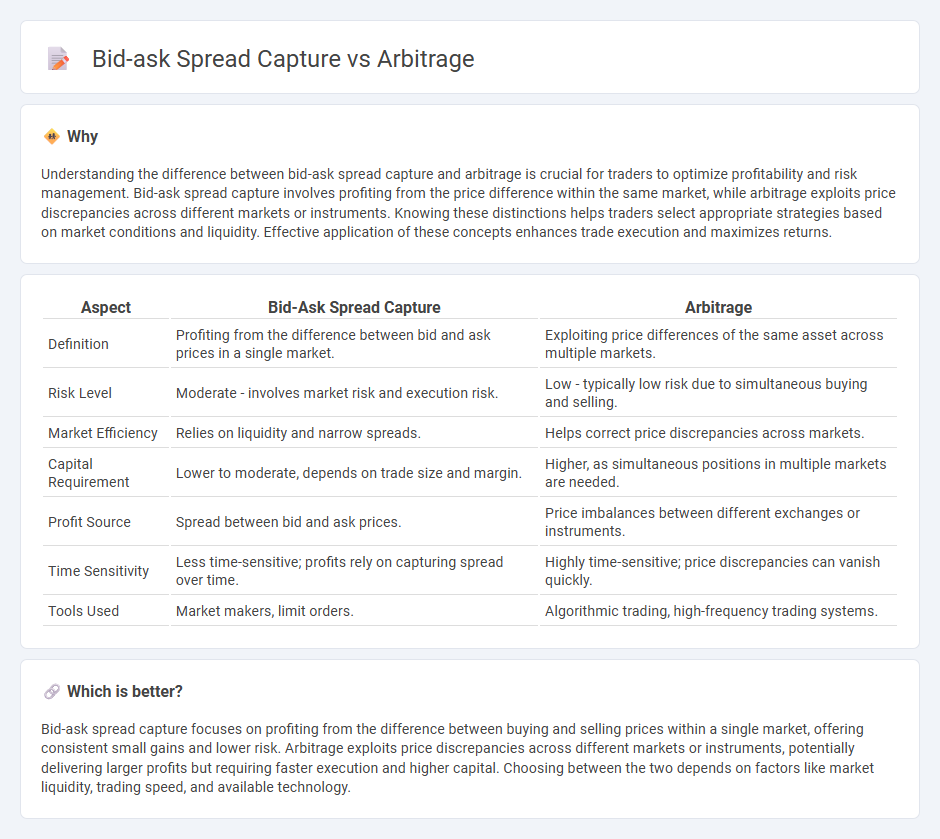
Understanding the difference between bid-ask spread capture and arbitrage is crucial for traders to optimize profitability and risk management. Bid-ask spread capture involves profiting from the price difference within the same market, while arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets or instruments. Knowing these distinctions helps traders select appropriate strategies based on market conditions and liquidity. Effective application of these concepts enhances trade execution and maximizes returns.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Bid-Ask Spread Capture | Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profiting from the difference between bid and ask prices in a single market. | Exploiting price differences of the same asset across multiple markets. |
| Risk Level | Moderate - involves market risk and execution risk. | Low - typically low risk due to simultaneous buying and selling. |
| Market Efficiency | Relies on liquidity and narrow spreads. | Helps correct price discrepancies across markets. |
| Capital Requirement | Lower to moderate, depends on trade size and margin. | Higher, as simultaneous positions in multiple markets are needed. |
| Profit Source | Spread between bid and ask prices. | Price imbalances between different exchanges or instruments. |
| Time Sensitivity | Less time-sensitive; profits rely on capturing spread over time. | Highly time-sensitive; price discrepancies can vanish quickly. |
| Tools Used | Market makers, limit orders. | Algorithmic trading, high-frequency trading systems. |
Which is better?
Bid-ask spread capture focuses on profiting from the difference between buying and selling prices within a single market, offering consistent small gains and lower risk. Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets or instruments, potentially delivering larger profits but requiring faster execution and higher capital. Choosing between the two depends on factors like market liquidity, trading speed, and available technology.
Connection
Bid-ask spread capture involves profiting from the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay (bid) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (ask), while arbitrage exploits price discrepancies of the same asset across different markets. Traders engaged in arbitrage often capitalize on temporary bid-ask spread inefficiencies between exchanges to secure risk-free profits. Efficient markets tend to minimize these spreads, reducing arbitrage opportunities and enhancing price discovery.
Key Terms
Price Discrepancy
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between markets by simultaneously buying low and selling high to lock in risk-free profits, while bid-ask spread capture profits from the difference between a security's bid and ask prices within a single market. Price discrepancies in arbitrage involve cross-market inefficiencies, whereas spread capture relies on capturing the cost embedded in order book liquidity. Explore the nuances of each strategy to understand how traders optimize returns in different market conditions.
Execution Speed
Arbitrage exploits price differences across markets, requiring ultra-fast execution speeds to capitalize on fleeting opportunities before prices converge. Bid-ask spread capture focuses on executing trades within a single market, leveraging speed to swiftly buy at the bid and sell at the ask, thus securing incremental profits. Explore advanced trading strategies to understand how execution speed impacts both arbitrage and bid-ask spread capture.
Liquidity
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets to generate risk-free profits, while bid-ask spread capture targets the difference between buying and selling prices within a single market. Liquidity plays a crucial role in both strategies by influencing transaction costs and the ease of executing trades; higher liquidity typically reduces the bid-ask spread and enhances arbitrage opportunities. Explore how liquidity dynamics shape these profit strategies to optimize trading performance.
Source and External Links
Arbitrage - Wikipedia - Arbitrage is the practice of profiting from price differences of a single asset in two or more markets, often considered risk-free in theory as it involves no negative cash flow and a positive profit in at least one state, with arbitrageurs exploiting such price gaps to cause market prices to converge.
Arbitrage | Definition and Examples - A Common Trading Strategy - Arbitrage is a trading strategy that capitalizes on price differences between equivalent assets in different markets by buying low in one and simultaneously selling high in another, thereby exploiting market inefficiencies until prices converge.
What Is Arbitrage? 3 Strategies to Know - Arbitrage is an investment strategy where an investor buys and sells an asset simultaneously in different markets to profit from price discrepancies, with key types including pure arbitrage, merger arbitrage, and convertible arbitrage, often used by sophisticated investors like hedge funds.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com