Delta-neutral strategies involve balancing positions to maintain a portfolio unaffected by small price movements in the underlying asset, thus reducing directional risk. Arbitrage strategies exploit price discrepancies across different markets or instruments to capture risk-free profits, relying on market inefficiencies. Explore these distinct methods to understand how traders optimize risk and return in dynamic markets.
Why it is important
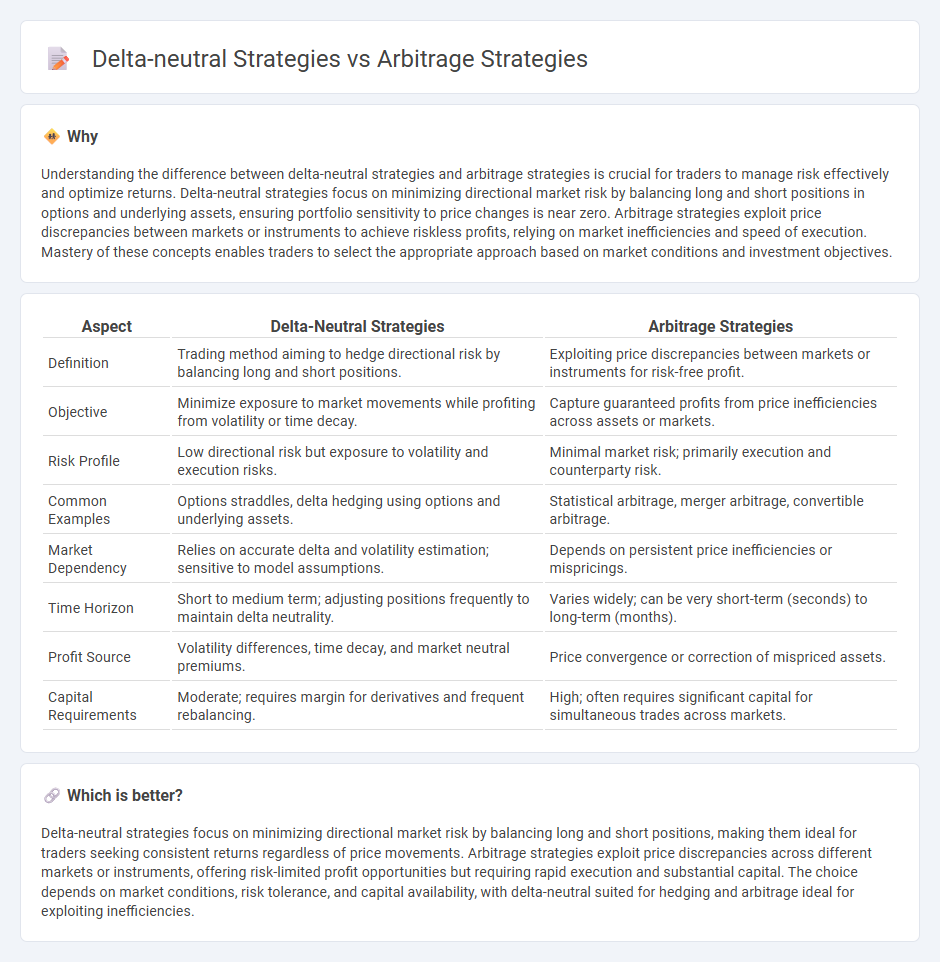
Understanding the difference between delta-neutral strategies and arbitrage strategies is crucial for traders to manage risk effectively and optimize returns. Delta-neutral strategies focus on minimizing directional market risk by balancing long and short positions in options and underlying assets, ensuring portfolio sensitivity to price changes is near zero. Arbitrage strategies exploit price discrepancies between markets or instruments to achieve riskless profits, relying on market inefficiencies and speed of execution. Mastery of these concepts enables traders to select the appropriate approach based on market conditions and investment objectives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Delta-Neutral Strategies | Arbitrage Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading method aiming to hedge directional risk by balancing long and short positions. | Exploiting price discrepancies between markets or instruments for risk-free profit. |
| Objective | Minimize exposure to market movements while profiting from volatility or time decay. | Capture guaranteed profits from price inefficiencies across assets or markets. |
| Risk Profile | Low directional risk but exposure to volatility and execution risks. | Minimal market risk; primarily execution and counterparty risk. |
| Common Examples | Options straddles, delta hedging using options and underlying assets. | Statistical arbitrage, merger arbitrage, convertible arbitrage. |
| Market Dependency | Relies on accurate delta and volatility estimation; sensitive to model assumptions. | Depends on persistent price inefficiencies or mispricings. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term; adjusting positions frequently to maintain delta neutrality. | Varies widely; can be very short-term (seconds) to long-term (months). |
| Profit Source | Volatility differences, time decay, and market neutral premiums. | Price convergence or correction of mispriced assets. |
| Capital Requirements | Moderate; requires margin for derivatives and frequent rebalancing. | High; often requires significant capital for simultaneous trades across markets. |
Which is better?
Delta-neutral strategies focus on minimizing directional market risk by balancing long and short positions, making them ideal for traders seeking consistent returns regardless of price movements. Arbitrage strategies exploit price discrepancies across different markets or instruments, offering risk-limited profit opportunities but requiring rapid execution and substantial capital. The choice depends on market conditions, risk tolerance, and capital availability, with delta-neutral suited for hedging and arbitrage ideal for exploiting inefficiencies.
Connection
Delta-neutral strategies involve maintaining a portfolio with zero net delta to minimize directional risk, which directly supports arbitrage strategies by enabling traders to exploit price discrepancies without exposure to market movements. Arbitrageurs use delta-neutral positions to lock in risk-free profits from price inefficiencies between related securities, such as options and their underlying assets. By combining delta-neutral hedging with arbitrage opportunities, traders achieve consistent returns while controlling volatility and market risk.
Key Terms
**Arbitrage Strategies:**
Arbitrage strategies exploit price discrepancies across different markets or instruments to generate risk-free profits by simultaneously buying and selling assets. These strategies often involve advanced algorithmic trading systems and high-frequency execution to capitalize on fleeting market inefficiencies. Explore detailed insights on how arbitrage strategies can enhance portfolio returns with minimal market risk.
Price Discrepancy
Arbitrage strategies exploit price discrepancies between related assets or markets, enabling traders to buy low and sell high simultaneously for risk-free profits. Delta-neutral strategies focus on maintaining a position insensitive to price movements of the underlying asset, often by balancing long and short options or securities. Discover how mastering these approaches can optimize your trading performance and risk management.
Market Efficiency
Arbitrage strategies exploit price discrepancies across different markets or instruments to generate risk-free profits, enhancing market efficiency by correcting mispricings swiftly. Delta-neutral strategies manage options' price sensitivity to underlying asset movements, aiming to hedge risks and maintain a balanced portfolio, contributing indirectly to price stability. Explore deeper insights on how these strategies impact overall market efficiency and trading dynamics.
Source and External Links
Arbitrage Definition: Types and Uses for Investment Strategy - Strike - Arbitrage strategies include futures arbitrage, which exploits price differences of futures contracts across markets, and pure arbitrage, involving simultaneous buying and selling of the same asset in different markets to earn risk-free profits.
Arbitrage - Wikipedia - Merger arbitrage involves buying shares of a takeover target at a discount and shorting the acquirer's stock, profiting from the convergence of prices if the deal completes successfully.
What Is Arbitrage? 3 Strategies to Know - Merger arbitrage, also called risk arbitrage, is a strategy where investors profit from the spread between the current target company's stock price and the buyout price, balancing deal risk versus reward.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com