Algorithmic arbitrage leverages advanced algorithms to exploit price discrepancies of the same asset across different markets, generating risk-free profits with rapid trade execution. Market making involves continuously providing buy and sell quotes to ensure liquidity, profiting from the bid-ask spread while managing inventory risk. Explore the detailed strategies behind algorithmic arbitrage and market making to optimize your trading approach.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between algorithmic arbitrage and market making is crucial for traders to optimize strategies and manage risks effectively. Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across multiple markets to secure risk-free profits, while market making involves providing liquidity by simultaneously placing buy and sell orders to capture the spread. Recognizing these distinctions enables traders to allocate capital efficiently and tailor algorithms to their specific market conditions. Mastery of both concepts enhances decision-making and maximizes profitability in high-frequency trading environments.
Comparison Table
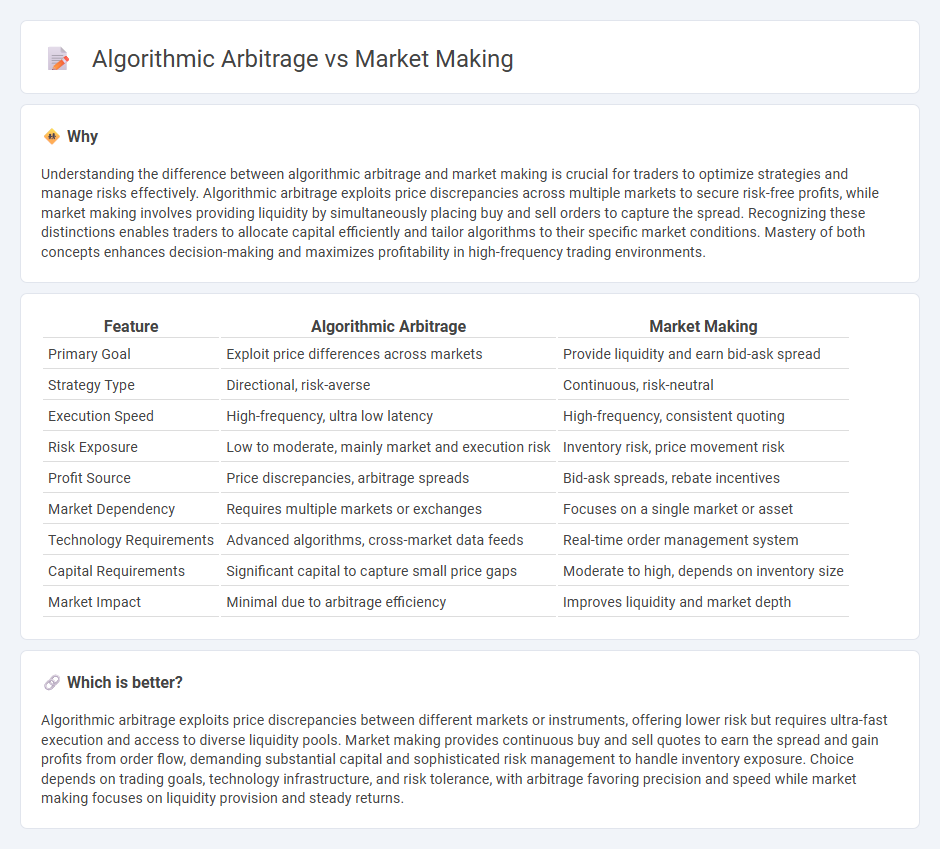
| Feature | Algorithmic Arbitrage | Market Making |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Exploit price differences across markets | Provide liquidity and earn bid-ask spread |
| Strategy Type | Directional, risk-averse | Continuous, risk-neutral |
| Execution Speed | High-frequency, ultra low latency | High-frequency, consistent quoting |
| Risk Exposure | Low to moderate, mainly market and execution risk | Inventory risk, price movement risk |
| Profit Source | Price discrepancies, arbitrage spreads | Bid-ask spreads, rebate incentives |
| Market Dependency | Requires multiple markets or exchanges | Focuses on a single market or asset |
| Technology Requirements | Advanced algorithms, cross-market data feeds | Real-time order management system |
| Capital Requirements | Significant capital to capture small price gaps | Moderate to high, depends on inventory size |
| Market Impact | Minimal due to arbitrage efficiency | Improves liquidity and market depth |
Which is better?
Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between different markets or instruments, offering lower risk but requires ultra-fast execution and access to diverse liquidity pools. Market making provides continuous buy and sell quotes to earn the spread and gain profits from order flow, demanding substantial capital and sophisticated risk management to handle inventory exposure. Choice depends on trading goals, technology infrastructure, and risk tolerance, with arbitrage favoring precision and speed while market making focuses on liquidity provision and steady returns.
Connection
Algorithmic arbitrage and market making both leverage automated trading systems to capitalize on price inefficiencies across financial markets. Algorithmic arbitrage identifies and exploits temporary price discrepancies between different exchanges or assets, while market making continuously provides liquidity by placing buy and sell orders to capture bid-ask spreads. Together, these strategies enhance market efficiency by narrowing spreads and aligning prices, benefiting from speed, precision, and high-frequency data analysis.
Key Terms
Market Making:
Market making involves continuously providing bid and ask quotes to facilitate liquidity and capture the bid-ask spread, playing a crucial role in improving market efficiency. It requires sophisticated algorithms to manage inventory risk and adjust prices dynamically based on market conditions and order flow. Explore the intricacies of market making strategies and their impact on trading ecosystems to deepen your understanding.
Bid-Ask Spread
Market making involves continuously providing liquidity by posting both bid and ask prices, profiting primarily from capturing the bid-ask spread. Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets or instruments, aiming to buy low and sell high nearly simultaneously, with less focus on the spread itself. Explore the nuances of bid-ask spread strategies to deepen your understanding of these trading mechanisms.
Liquidity Provision
Market making centers on continuously providing liquidity by quoting both buy and sell prices, ensuring market stability and tighter spreads. Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across multiple markets or instruments using automated systems to generate risk-free profits while often contributing to liquidity. Explore more to understand how these strategies impact market efficiency and trading dynamics.
Source and External Links
Mastering the Market Maker Trading Strategy - Market makers earn profits primarily through the bid-ask spread by buying securities at a bid price and selling at a slightly higher ask price, while managing inventory and analyzing order flow to anticipate market movements.
Market Making and Mean Reversion - CIS UPenn - Market making involves quoting both buy and sell prices for a financial instrument to provide liquidity and profit from the difference between those prices, while typically avoiding large net positions.
Market Maker - Definition, Role, How They Work - A market maker is a firm or individual providing two-sided markets by continuously posting bid and ask prices, profiting mainly from the bid-ask spread while facilitating liquidity and managing risk from holding securities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com