Flash loan arbitrage leverages instant, uncollateralized loans to exploit price discrepancies across decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, enabling traders to execute rapid, risk-free profits within a single transaction. Scalping involves making numerous small trades throughout the day to capitalize on minimal price movements, focusing on liquidity and tight spreads in highly volatile markets. Explore the differences in strategies, risks, and potential gains to determine which approach suits your trading goals.
Why it is important
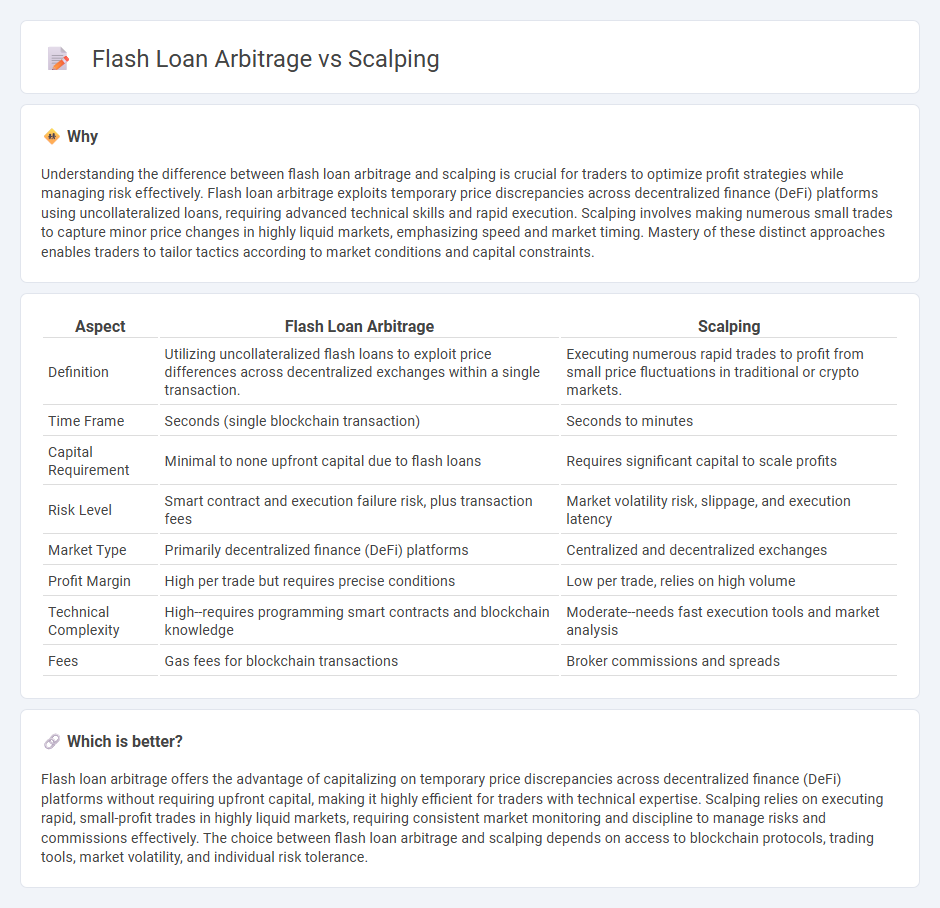
Understanding the difference between flash loan arbitrage and scalping is crucial for traders to optimize profit strategies while managing risk effectively. Flash loan arbitrage exploits temporary price discrepancies across decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms using uncollateralized loans, requiring advanced technical skills and rapid execution. Scalping involves making numerous small trades to capture minor price changes in highly liquid markets, emphasizing speed and market timing. Mastery of these distinct approaches enables traders to tailor tactics according to market conditions and capital constraints.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Flash Loan Arbitrage | Scalping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Utilizing uncollateralized flash loans to exploit price differences across decentralized exchanges within a single transaction. | Executing numerous rapid trades to profit from small price fluctuations in traditional or crypto markets. |
| Time Frame | Seconds (single blockchain transaction) | Seconds to minutes |
| Capital Requirement | Minimal to none upfront capital due to flash loans | Requires significant capital to scale profits |
| Risk Level | Smart contract and execution failure risk, plus transaction fees | Market volatility risk, slippage, and execution latency |
| Market Type | Primarily decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms | Centralized and decentralized exchanges |
| Profit Margin | High per trade but requires precise conditions | Low per trade, relies on high volume |
| Technical Complexity | High--requires programming smart contracts and blockchain knowledge | Moderate--needs fast execution tools and market analysis |
| Fees | Gas fees for blockchain transactions | Broker commissions and spreads |
Which is better?
Flash loan arbitrage offers the advantage of capitalizing on temporary price discrepancies across decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms without requiring upfront capital, making it highly efficient for traders with technical expertise. Scalping relies on executing rapid, small-profit trades in highly liquid markets, requiring consistent market monitoring and discipline to manage risks and commissions effectively. The choice between flash loan arbitrage and scalping depends on access to blockchain protocols, trading tools, market volatility, and individual risk tolerance.
Connection
Flash loan arbitrage and scalping both capitalize on rapid market movements to generate profits, relying heavily on high-speed trade execution and minimal latency. Flash loan arbitrage uses uncollateralized loans to exploit price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges within a single blockchain transaction, while scalping involves making numerous quick trades on price fluctuations in centralized or decentralized markets. The connection lies in their shared focus on leveraging small, short-term price differences to achieve consistent gains.
Key Terms
Execution Speed
Scalping relies on rapid market order execution to exploit small price movements, requiring ultra-fast trade execution and minimal latency. Flash loan arbitrage leverages instant, uncollateralized loans within a single blockchain transaction to capitalize on price discrepancies across DeFi protocols, demanding precise timing and smart contract efficiency. Explore the key differences and how execution speed impacts profitability in these advanced trading strategies.
Liquidity
Scalping leverages small price fluctuations in highly liquid markets to execute rapid trades, requiring immediate access to market liquidity for quick entry and exit. Flash loan arbitrage exploits temporary liquidity imbalances across decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, utilizing instant, unsecured loans to capitalize on price discrepancies without upfront capital. Explore in-depth insights to understand how liquidity dynamics influence these fast-paced trading strategies.
Risk Management
Scalping and flash loan arbitrage both require stringent risk management strategies to navigate market volatility and execution risks effectively. Scalping involves frequent trades to capitalize on small price movements, demanding quick decision-making and tight stop-loss controls to limit exposure. Explore detailed risk management approaches to enhance your trading performance and safeguard capital.
Source and External Links
Scalping (Day Trading Technique) - Corporate Finance Institute - Scalping is a day trading strategy where investors buy and sell the same stock multiple times within the same day to take small profits repeatedly, focusing on highly volatile stocks and making many quick trades.
Scalping (trading) - Wikipedia - Scalping in trading refers either to a legitimate arbitrage method exploiting small price gaps or a fraudulent market manipulation practice, generally involving very short-term trades aiming to profit from bid-ask spreads or minor price movements.
What is a scalping strategy in the stock market and how does it work? - Scalping uses fast buying and selling supported by technical indicators like moving averages, RSI, and MACD, with traders relying on momentum and price trend analysis to execute quick trades either as a primary strategy or a supplement to other portfolio tactics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com