Market making involves continuously quoting buy and sell prices to provide liquidity, profiting from the bid-ask spread, and enhancing market efficiency on exchanges. Algorithmic trading uses automated, predefined strategies to execute large volumes of trades at optimal speeds, minimizing human error and market impact. Discover how these distinct trading techniques shape modern financial markets.
Why it is important
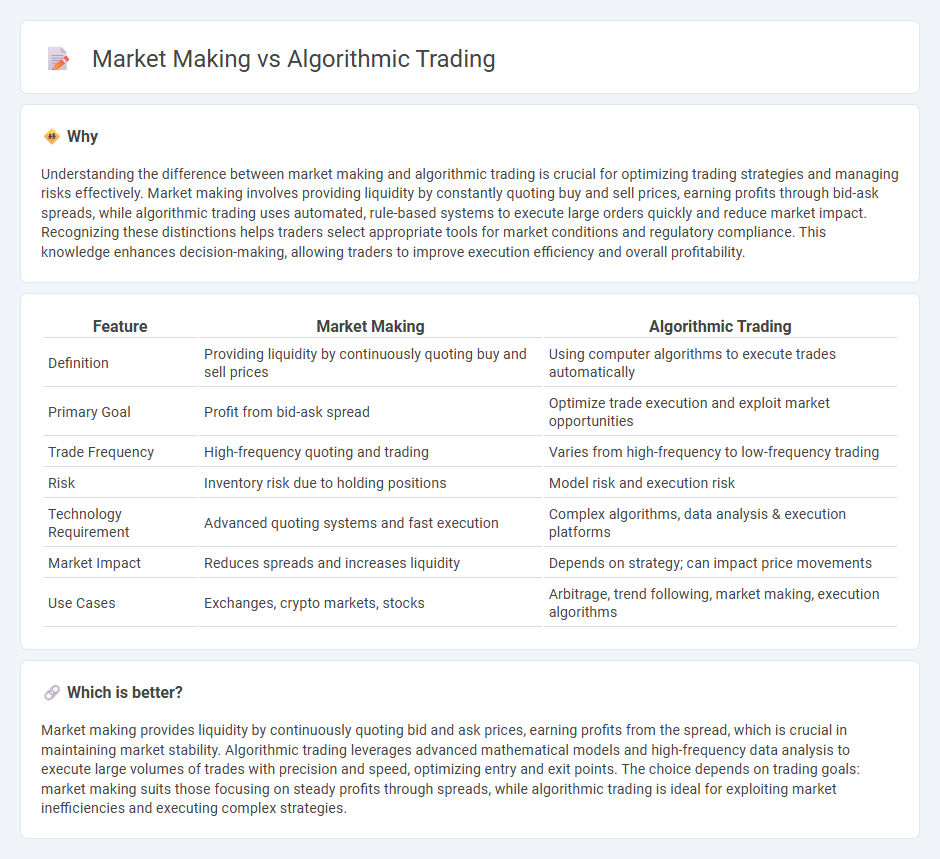
Understanding the difference between market making and algorithmic trading is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and managing risks effectively. Market making involves providing liquidity by constantly quoting buy and sell prices, earning profits through bid-ask spreads, while algorithmic trading uses automated, rule-based systems to execute large orders quickly and reduce market impact. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders select appropriate tools for market conditions and regulatory compliance. This knowledge enhances decision-making, allowing traders to improve execution efficiency and overall profitability.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Market Making | Algorithmic Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices | Using computer algorithms to execute trades automatically |
| Primary Goal | Profit from bid-ask spread | Optimize trade execution and exploit market opportunities |
| Trade Frequency | High-frequency quoting and trading | Varies from high-frequency to low-frequency trading |
| Risk | Inventory risk due to holding positions | Model risk and execution risk |
| Technology Requirement | Advanced quoting systems and fast execution | Complex algorithms, data analysis & execution platforms |
| Market Impact | Reduces spreads and increases liquidity | Depends on strategy; can impact price movements |
| Use Cases | Exchanges, crypto markets, stocks | Arbitrage, trend following, market making, execution algorithms |
Which is better?
Market making provides liquidity by continuously quoting bid and ask prices, earning profits from the spread, which is crucial in maintaining market stability. Algorithmic trading leverages advanced mathematical models and high-frequency data analysis to execute large volumes of trades with precision and speed, optimizing entry and exit points. The choice depends on trading goals: market making suits those focusing on steady profits through spreads, while algorithmic trading is ideal for exploiting market inefficiencies and executing complex strategies.
Connection
Market making relies heavily on algorithmic trading to provide continuous liquidity by automatically placing buy and sell orders based on real-time market data. Algorithmic trading uses complex mathematical models to determine optimal pricing and order execution strategies that market makers implement to manage inventory risk and capture bid-ask spreads efficiently. The integration of both enables faster decision-making and increased market efficiency through reduced transaction costs and tighter spreads.
Key Terms
Algorithmic Trading:
Algorithmic trading leverages advanced mathematical models and automated systems to execute large volumes of trades at high speed, optimizing profit opportunities while minimizing human error. It utilizes historical data, real-time market information, and predictive analytics to make informed decisions across various asset classes. Explore the nuances of algorithmic trading strategies and technologies to gain deeper insights.
Execution Algorithms
Execution algorithms in algorithmic trading are designed to optimize order placement by minimizing market impact and transaction costs, often using strategies like VWAP, TWAP, and iceberg orders. Market making algorithms continuously provide liquidity by placing bid and ask orders, profiting from the bid-ask spread while managing inventory risk. Explore the nuances and performance metrics of these execution strategies to enhance your trading approach.
Backtesting
Backtesting in algorithmic trading involves simulating a strategy using historical market data to evaluate its performance and risk metrics before live deployment. Market making backtesting focuses on order book dynamics, bid-ask spread management, and inventory risk to optimize profitability in providing liquidity. Explore detailed methodologies and tools to enhance your backtesting approach in algorithmic trading and market making.
Source and External Links
What is Algorithmic Trading and How Do You Get Started? - IG - Algorithmic trading uses computer programs to execute trades based on set rules like price movements, with common strategies including price action, technical analysis, or a combination, often employing risk management tools such as stops and limits for effective market operation.
Algorithmic Trading - Definition, Example, Pros, Cons - Algorithmic trading involves automated buy or sell decisions programmed by traders based on preset rules, such as moving average crossovers, often used to break large trades into smaller batches to prevent market price distortion.
Algorithmic trading - Wikipedia - Algorithmic trading utilizes pre-programmed instructions considering variables like time and price, progressively enhanced by machine learning techniques such as deep reinforcement learning to adapt dynamically to volatile markets and improve trading precision.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com