Front running involves a trader executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending large transactions to capitalize on price moves, often seen in brokerage or market maker scenarios. Insider trading occurs when individuals use non-public, material information about a company to trade its securities, violating securities laws and regulatory frameworks such as the SEC in the United States. Explore the legal distinctions and market impacts of these practices to understand their significance in trading regulation.
Why it is important
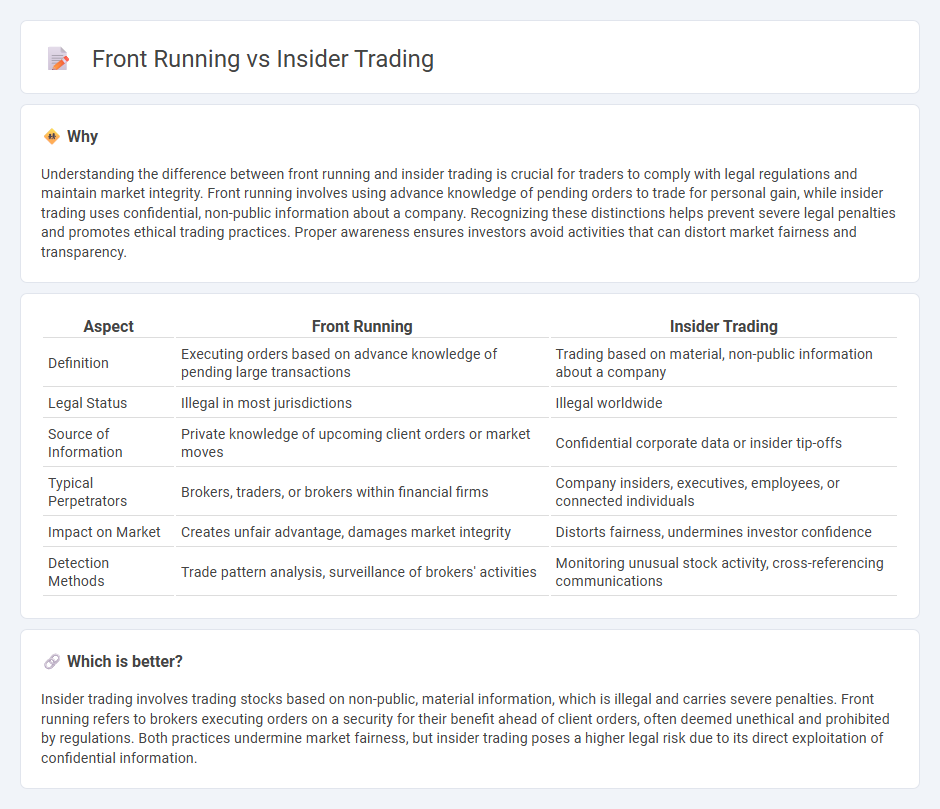
Understanding the difference between front running and insider trading is crucial for traders to comply with legal regulations and maintain market integrity. Front running involves using advance knowledge of pending orders to trade for personal gain, while insider trading uses confidential, non-public information about a company. Recognizing these distinctions helps prevent severe legal penalties and promotes ethical trading practices. Proper awareness ensures investors avoid activities that can distort market fairness and transparency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Front Running | Insider Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending large transactions | Trading based on material, non-public information about a company |
| Legal Status | Illegal in most jurisdictions | Illegal worldwide |
| Source of Information | Private knowledge of upcoming client orders or market moves | Confidential corporate data or insider tip-offs |
| Typical Perpetrators | Brokers, traders, or brokers within financial firms | Company insiders, executives, employees, or connected individuals |
| Impact on Market | Creates unfair advantage, damages market integrity | Distorts fairness, undermines investor confidence |
| Detection Methods | Trade pattern analysis, surveillance of brokers' activities | Monitoring unusual stock activity, cross-referencing communications |
Which is better?
Insider trading involves trading stocks based on non-public, material information, which is illegal and carries severe penalties. Front running refers to brokers executing orders on a security for their benefit ahead of client orders, often deemed unethical and prohibited by regulations. Both practices undermine market fairness, but insider trading poses a higher legal risk due to its direct exploitation of confidential information.
Connection
Front running and insider trading are connected through the exploitation of non-public information to gain an unfair advantage in the financial markets. Both practices involve acting on confidential knowledge before it is reflected in asset prices, undermining market integrity and violating securities laws. Regulatory bodies enforce strict penalties to deter these manipulative behaviors and protect investor confidence.
Key Terms
Non-public Information
Insider trading involves trading securities based on material non-public information obtained from within a company, violating fiduciary duties and securities laws. Front running refers to brokers or traders executing orders on a security for their own account ahead of clients' orders, exploiting privileged non-public knowledge of impending transactions. Explore the legal distinctions and ethical implications to understand how non-public information impacts market fairness.
Client Order
Insider trading involves trading securities based on non-public, material information, whereas front running focuses on executing orders ahead of a client's large trade to benefit from the anticipated price movement. Client orders in front running are exploited by brokers or traders who receive advance knowledge and act before the client's trade is completed, violating fiduciary duties. Explore more about regulatory measures and legal implications surrounding client order protection.
Market Manipulation
Market manipulation involves deceptive practices to gain unfair advantages in trading, where insider trading uses non-public, material information for profit, compromising market integrity. Front running exploits advance knowledge of pending orders to trade ahead, disrupting fair market conditions and disadvantaging other investors. Explore in-depth strategies and regulations governing these practices to better understand their impact on financial markets.
Source and External Links
Insider trading - Insider trading is the buying or selling of a public company's stock or securities based on material, nonpublic information about the company.
Definition, Examples and Penalties for Insider Trading - Insider trading involves trading a company's securities while in possession of confidential, material information not yet public, often leading to legal penalties as in the famous case involving Martha Stewart.
insider trading | Wex | US Law | LII - Insider trading violates fiduciary duty laws by trading on material, nonpublic company information; U.S. law defines insiders broadly, including officers and anyone controlling 10% of company equity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com